Home>Health & Nutrition>Using An Infrared Thermometer: A Step-by-Step Guide


Health & Nutrition
Using An Infrared Thermometer: A Step-by-Step Guide
Published: February 19, 2024
Learn how to use an infrared thermometer for health and nutrition purposes with this comprehensive step-by-step guide. Ensure accurate temperature readings for optimal well-being.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
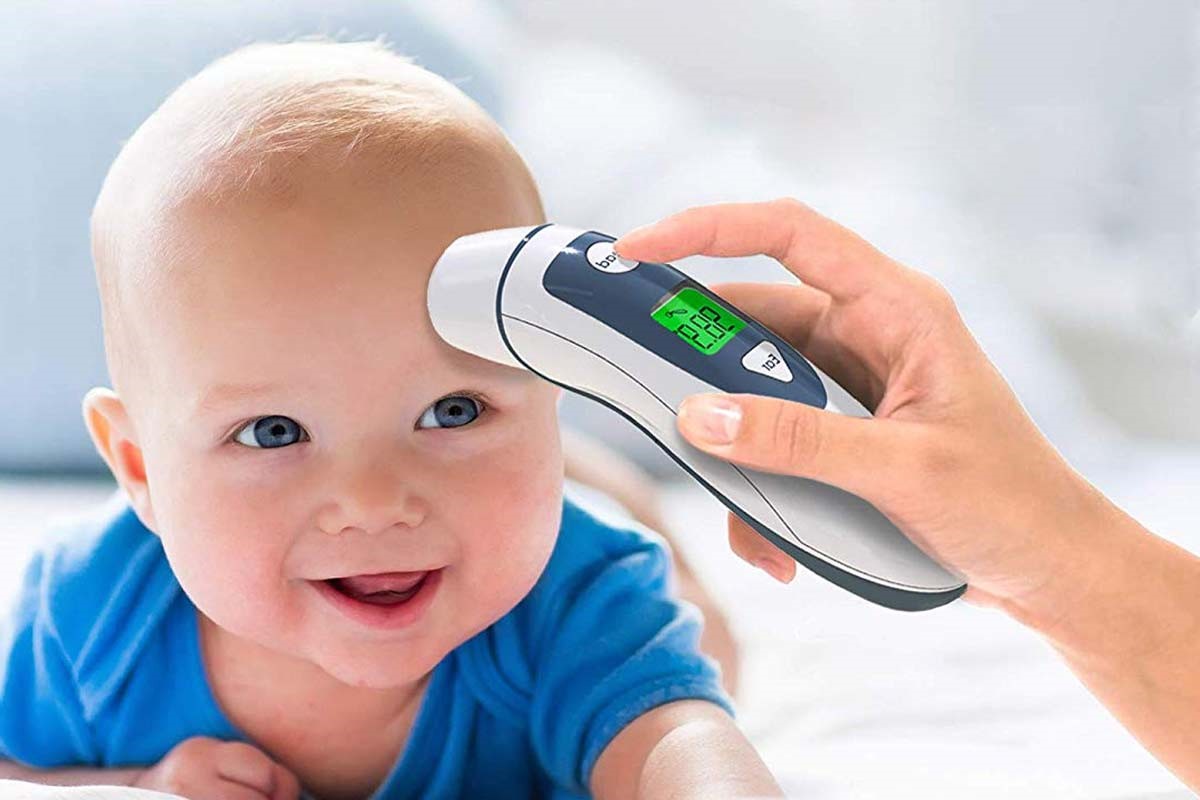
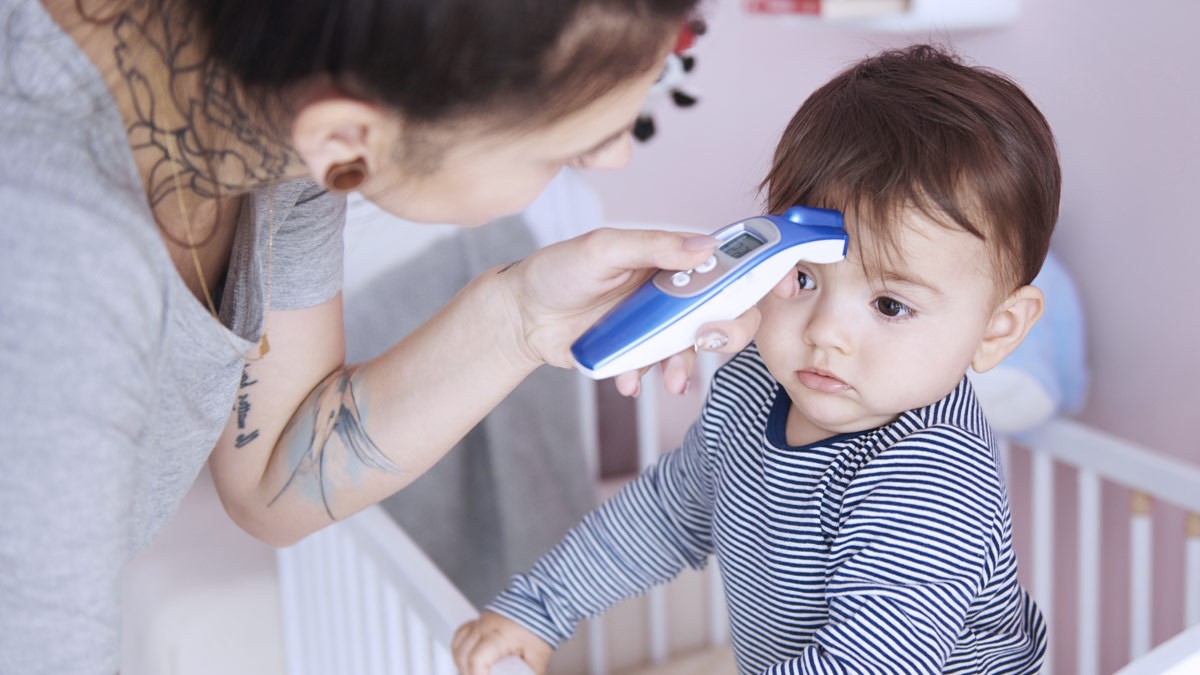
Infrared thermometers have become an indispensable tool in various settings, from medical facilities and industrial environments to everyday household use. These innovative devices offer a non-invasive and quick method for measuring temperature, making them incredibly convenient and versatile. Whether you're monitoring the temperature of a child, checking the surface temperature of an object, or ensuring the efficiency of mechanical equipment, an infrared thermometer provides accurate and reliable readings without direct contact.
The technology behind infrared thermometers is based on the principle of detecting infrared energy emitted by an object. This energy, also known as thermal radiation, is invisible to the human eye but can be captured and measured by the sensor within the thermometer. By simply pointing the device at the target object and pressing a button, you can obtain an instant temperature reading, eliminating the need for traditional thermometers that require physical contact and often take longer to provide results.
In addition to their speed and convenience, infrared thermometers offer exceptional precision, allowing for consistent and dependable temperature measurements. This makes them particularly valuable in situations where accuracy is paramount, such as in medical diagnoses, food safety inspections, and HVAC system maintenance.
Moreover, the non-contact nature of infrared thermometers minimizes the risk of cross-contamination, making them an ideal choice for use in healthcare settings. By eliminating the need for direct contact with the skin or surfaces, these thermometers contribute to maintaining hygienic conditions and reducing the spread of germs and infections.
As we delve into the intricacies of using an infrared thermometer, it's important to recognize the diverse applications and benefits of this technology. Whether you're a healthcare professional, a maintenance technician, or a concerned parent, understanding how to effectively utilize an infrared thermometer can empower you to make informed decisions and take proactive measures based on accurate temperature data. With this comprehensive guide, you'll gain the knowledge and confidence to harness the full potential of an infrared thermometer in various aspects of your daily life.
Understanding Infrared Thermometers
Infrared thermometers, also known as non-contact thermometers or IR thermometers, are innovative devices designed to measure temperature without physically touching the object or surface being assessed. They operate based on the principle of detecting thermal radiation, or infrared energy, emitted by an object. This energy is captured by the sensor within the thermometer, allowing for the precise measurement of temperature.
These thermometers are equipped with a lens that focuses the infrared energy onto a detector, which then converts the energy into an electrical signal. This signal is processed and displayed as a temperature reading on the thermometer's screen. The accuracy of the reading is attributed to the ability of the device to detect and capture the infrared energy emitted by the object, regardless of its surface texture or composition.
Infrared thermometers are available in various models, including handheld devices for personal or professional use, as well as more advanced models used in industrial and scientific applications. Some models feature a laser pointer that helps to pinpoint the exact spot being measured, enhancing precision and ease of use.
One of the key advantages of infrared thermometers is their speed. Unlike traditional contact thermometers, which require time to equilibrate with the object's temperature, infrared thermometers provide instant readings, making them ideal for situations where efficiency is crucial. This rapid response time is particularly valuable in healthcare settings, where quick and accurate temperature measurements are essential for diagnosing and monitoring patients.
Furthermore, the non-contact nature of infrared thermometers minimizes the risk of contamination, making them suitable for use in sterile environments such as hospitals and laboratories. This feature also contributes to their versatility in measuring the temperature of moving objects, hazardous substances, or hard-to-reach areas, where traditional thermometers would be impractical or unsafe to use.
In summary, understanding the fundamental principles and capabilities of infrared thermometers is essential for harnessing their full potential. These devices offer a convenient, hygienic, and precise method for measuring temperature, making them indispensable tools in a wide range of applications, from healthcare and food safety to industrial and household use.
Preparing the Infrared Thermometer
Before using an infrared thermometer, it is essential to ensure that the device is properly prepared to deliver accurate and reliable temperature readings. The following steps outline the necessary preparations to optimize the performance of an infrared thermometer:
-
Powering On the Thermometer: Begin by turning on the infrared thermometer using the designated power button or switch. In most cases, the device will display a startup screen or indicator light to signal that it is ready for use. It is important to allow the thermometer to complete its initialization process before proceeding to take measurements.
-
Checking the Battery: Verify that the battery level of the infrared thermometer is adequate for operation. Low battery power can compromise the accuracy and functionality of the device. If the thermometer is powered by disposable batteries, ensure that they are fresh and properly installed. For rechargeable models, confirm that the battery is sufficiently charged to support continuous use.
-
Calibration: Some infrared thermometers may require calibration to maintain precision. Refer to the manufacturer's instructions for specific guidelines on calibrating the device. Calibration ensures that the thermometer provides accurate readings within the specified tolerance range, making it an essential step in preparing the device for use.
-
Selecting the Measurement Mode: Depending on the model, the infrared thermometer may offer different measurement modes, such as surface temperature, body temperature, or ambient temperature. Select the appropriate mode based on the intended application to ensure that the thermometer interprets the infrared energy correctly and provides the relevant temperature readings.
-
Allowing for Thermal Equilibration: If the infrared thermometer has been stored in a significantly different environment than the intended measurement area, allow it to acclimate to the new surroundings. This thermal equilibration minimizes the impact of temperature differentials on the accuracy of the readings.
-
Cleaning and Maintenance: Inspect the lens and sensor of the infrared thermometer for any debris or contaminants that may affect its performance. Clean the device according to the manufacturer's recommendations to ensure clear and unobstructed infrared energy detection.
By meticulously preparing the infrared thermometer in accordance with these steps, users can optimize its functionality and accuracy, setting the stage for obtaining precise temperature measurements in various settings. These preparations contribute to the reliability and effectiveness of the infrared thermometer, making it a valuable tool for diverse applications.
Using the Infrared Thermometer
Using an infrared thermometer is a straightforward process that involves a few simple steps to ensure accurate and reliable temperature measurements. Whether you are measuring the temperature of a person, an object, or a specific environment, the following guidelines will help you effectively utilize an infrared thermometer:
-
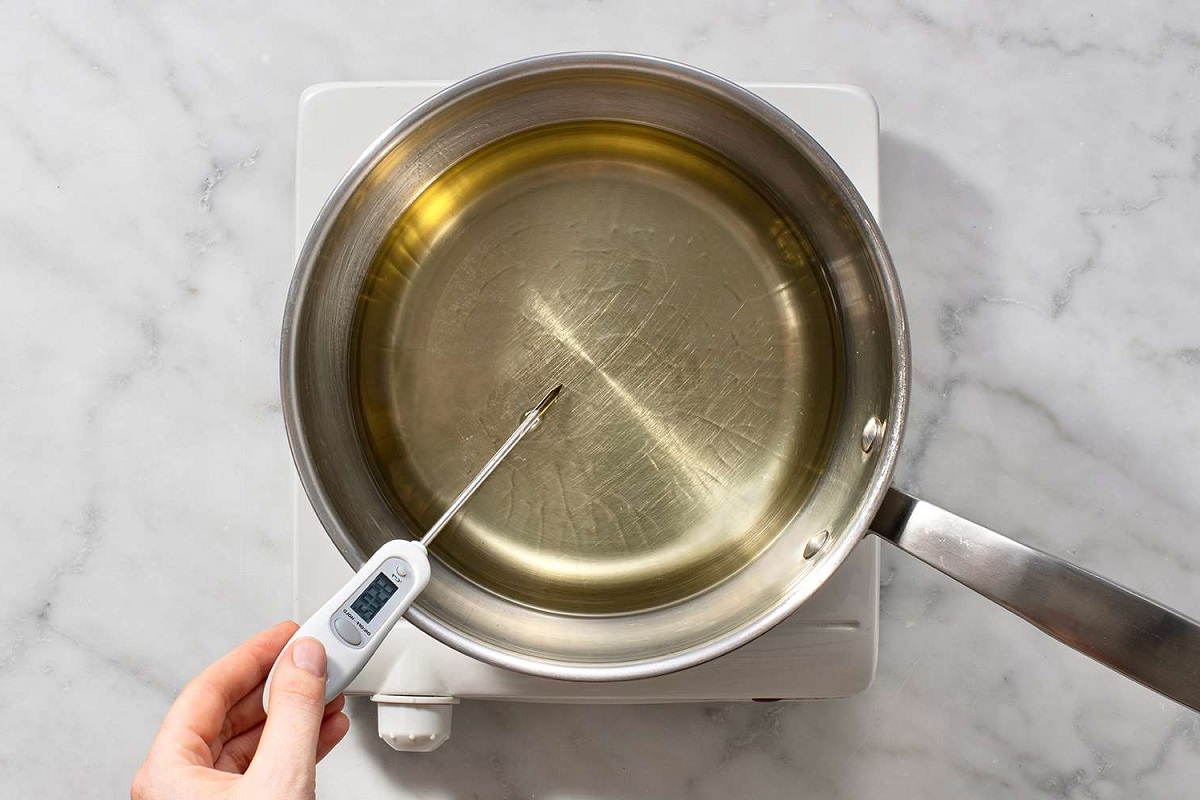
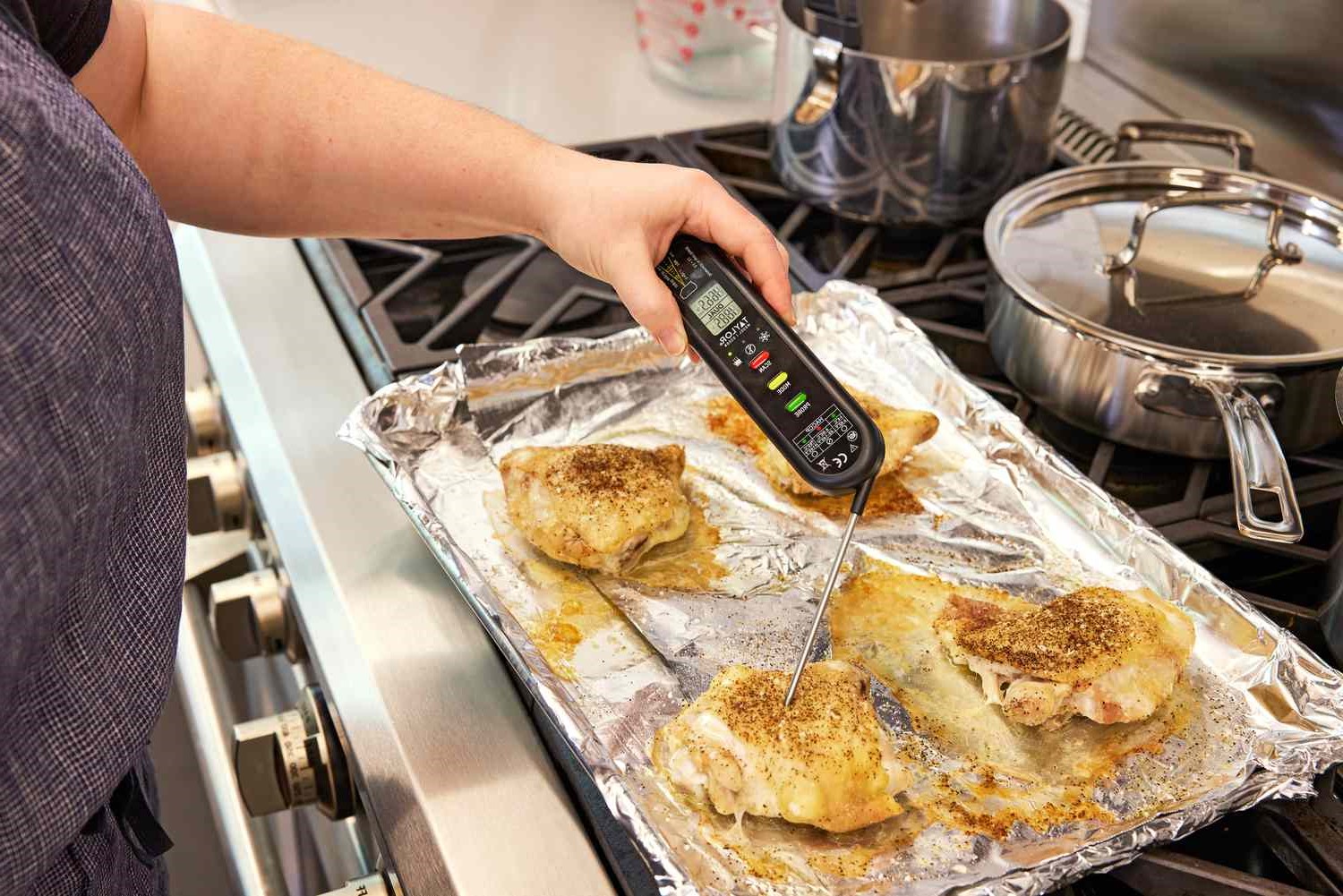
Pointing the Thermometer: Begin by aiming the infrared thermometer at the target object or surface from the appropriate distance. It is crucial to align the device's sensor with the area of interest to capture the infrared energy emitted by the object accurately.
-
Activating the Measurement: Most infrared thermometers feature a trigger or button that initiates the temperature measurement. Press the designated control to activate the device and capture the infrared energy from the target area. Some models may emit a laser pointer to indicate the precise spot being measured, enhancing the accuracy of the reading.
-
Maintaining Proper Distance: Ensure that you maintain the recommended distance between the infrared thermometer and the object being measured. This distance is specified by the manufacturer and is essential for obtaining precise readings. Deviating from the specified distance may result in inaccurate measurements due to the dispersion of infrared energy.
-
Steady and Still Target: To achieve the most accurate results, it is important to measure the temperature of a stationary target. Movement during the measurement process can affect the consistency and reliability of the reading. If measuring the temperature of a person, ensure that they remain still during the measurement to obtain an accurate reflection of their body temperature.
-
Recording the Reading: Once the infrared thermometer captures the infrared energy and processes the data, the temperature reading is displayed on the device's screen. Take note of the reading for future reference or record-keeping, especially in scenarios where temperature monitoring is critical for health, safety, or quality control purposes.
By following these steps, users can effectively utilize an infrared thermometer to obtain accurate temperature measurements in a wide range of applications. Whether used in healthcare, food safety, HVAC maintenance, or industrial settings, the proper use of an infrared thermometer ensures reliable and consistent temperature data, empowering individuals to make informed decisions and take appropriate actions based on precise temperature readings.
Tips for Accurate Readings
Obtaining precise and reliable temperature readings with an infrared thermometer requires attention to detail and adherence to best practices. By implementing the following tips, users can enhance the accuracy of their measurements and optimize the performance of the infrared thermometer:
-
Understanding Emissivity: Emissivity refers to the efficiency of an object's surface in emitting infrared energy. Different materials have varying emissivity values, which can impact the accuracy of temperature measurements. It is essential to adjust the infrared thermometer's emissivity setting to match the surface being measured. Consult the device's manual or emissivity table to select the appropriate emissivity value for different materials, such as metals, plastics, or organic substances.
-
Accounting for Reflective Surfaces: When measuring the temperature of reflective surfaces, such as mirrors or polished metals, it is crucial to consider the potential impact of reflected infrared energy on the readings. To mitigate this effect, minimize the angle of incidence between the infrared thermometer and the reflective surface, or use a non-reflective tape to cover a small area for measurement.
-
Avoiding Environmental Interference: External factors, such as drafts, air conditioning vents, or direct sunlight, can influence temperature readings obtained with an infrared thermometer. To minimize environmental interference, conduct measurements in stable and controlled conditions. Shield the target area from direct sunlight or drafts, and ensure that the surrounding environment does not introduce significant temperature variations during the measurement process.
-
Maintaining Clean Optics: The lens and sensor of an infrared thermometer should be kept clean and free from debris to ensure accurate readings. Regularly inspect the device for any obstructions or contaminants that may hinder the detection of infrared energy. Clean the optics according to the manufacturer's guidelines using a soft, lint-free cloth to maintain clear and unobstructed detection of thermal radiation.
-
Verifying Measurement Distance: Adhering to the recommended measurement distance specified by the manufacturer is crucial for obtaining accurate readings. Deviating from the specified distance can lead to inaccurate measurements due to the dispersion of infrared energy. Always maintain the appropriate distance between the infrared thermometer and the target object or surface to ensure precise temperature readings.
By incorporating these tips into the usage of an infrared thermometer, users can elevate the accuracy and reliability of their temperature measurements across various applications, from industrial processes and scientific research to healthcare and everyday household use. Understanding the nuances of emissivity, mitigating the impact of reflective surfaces, minimizing environmental interference, maintaining clean optics, and verifying measurement distance are essential elements in achieving consistently accurate readings with an infrared thermometer.
Safety Precautions
When using an infrared thermometer, it is essential to observe safety precautions to ensure the well-being of individuals and the accuracy of temperature measurements. Adhering to these precautions mitigates potential risks and contributes to the effective and responsible use of the device.
-
Eye Protection: Avoid directing the infrared thermometer's laser, if equipped, into the eyes. While the laser is harmless and designed for aiming purposes, prolonged exposure to the laser beam should be prevented to safeguard the eyes from any potential discomfort.
-
Avoiding Hazardous Environments: Exercise caution when using an infrared thermometer in environments with potential hazards, such as areas with flammable gases or volatile chemicals. Ensure that the device is suitable for use in such environments and follow any specific safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer.
-
Maintaining Distance: When measuring the temperature of objects or surfaces with elevated temperatures, maintain a safe distance to prevent exposure to excessive heat. Adhere to the recommended measurement distance specified by the manufacturer to minimize the risk of thermal exposure.
-
Handling with Care: Handle the infrared thermometer with care to prevent accidental damage or breakage. Avoid dropping the device or subjecting it to excessive force, as this can compromise its functionality and accuracy.
-
Storage and Transportation: Store the infrared thermometer in a secure and appropriate location when not in use. Protect the device from extreme temperatures, moisture, and physical damage during transportation and storage to maintain its performance and longevity.
-
Battery Safety: If the infrared thermometer is battery-powered, handle the batteries according to the manufacturer's instructions. Ensure that the batteries are inserted correctly and replaced with the appropriate type to prevent malfunctions or potential leakage.
-
Cleaning and Disinfection: If the infrared thermometer comes into contact with potentially infectious substances, follow the recommended cleaning and disinfection procedures to maintain hygienic conditions. Adhere to relevant guidelines for healthcare settings to prevent cross-contamination.
-
Compliance with Regulations: In certain professional or industrial settings, ensure that the use of the infrared thermometer complies with relevant regulations and standards. Adhere to any specific guidelines or protocols established for the safe and appropriate use of the device in specific applications.
By prioritizing safety precautions, users can harness the benefits of an infrared thermometer while minimizing potential risks and ensuring the well-being of individuals and the integrity of temperature measurements. These precautions underscore the responsible and conscientious utilization of the device across diverse environments and applications, contributing to safe and effective temperature monitoring practices.
Maintenance and Care of the Infrared Thermometer
Proper maintenance and care are essential for preserving the functionality, accuracy, and longevity of an infrared thermometer. By adhering to recommended maintenance practices and exercising diligent care, users can optimize the performance of the device and ensure reliable temperature measurements across various applications.
Cleaning and Inspection
Regular cleaning of the lens and sensor is paramount to prevent any obstruction that may impede the detection of infrared energy. Use a soft, lint-free cloth to gently clean the optics, ensuring that they remain free from dust, dirt, or other contaminants. Additionally, periodic inspection of the device's exterior and components is advisable to identify any signs of wear, damage, or deterioration that may affect its performance.
Battery Maintenance
For battery-powered infrared thermometers, proper battery maintenance is crucial to sustain uninterrupted operation. Ensure that the batteries are replaced according to the manufacturer's recommendations and that the battery compartment remains free from corrosion or debris. Regularly check the battery status to prevent unexpected power depletion during critical usage.
Calibration and Accuracy Verification
Periodic calibration of the infrared thermometer is essential to maintain its accuracy within the specified tolerance range. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for calibration procedures, and if necessary, utilize certified calibration equipment or professional services to verify the device's accuracy. Calibration ensures that the thermometer continues to deliver precise temperature readings, making it an indispensable aspect of maintenance.
Storage and Protection
When not in use, store the infrared thermometer in a secure and suitable environment to safeguard it from physical damage, extreme temperatures, and moisture. Utilize the provided storage case or designated storage area to protect the device from potential impacts or environmental factors that may compromise its integrity. Proper storage contributes to the preservation of the device's functionality and ensures its readiness for future use.
Firmware Updates and Maintenance
For digital infrared thermometers equipped with firmware or software components, staying informed about available updates and maintenance requirements is essential. Regularly check for firmware updates provided by the manufacturer and follow the recommended procedures for updating the device's software. Keeping the firmware up to date enhances the device's performance and may introduce new features or improvements.
By incorporating these maintenance and care practices into the routine management of an infrared thermometer, users can uphold its reliability, accuracy, and operational efficiency. These proactive measures contribute to the sustained performance of the device, ensuring that it remains a dependable tool for temperature measurement in diverse settings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the utilization of an infrared thermometer represents a significant advancement in temperature measurement technology, offering unparalleled convenience, precision, and versatility across a wide spectrum of applications. From healthcare and industrial settings to everyday household use, the non-contact nature of infrared thermometers has revolutionized temperature monitoring, providing rapid and accurate readings without physical interaction.
The comprehensive understanding of infrared thermometers, including their operational principles, preparation, usage, and maintenance, empowers users to harness the full potential of these innovative devices. By adhering to best practices and safety precautions, individuals can ensure the responsible and effective utilization of infrared thermometers, contributing to reliable temperature measurements and the well-being of those being monitored.
The seamless integration of infrared thermometers into various fields, such as medical diagnostics, food safety inspections, HVAC maintenance, and scientific research, underscores their indispensable role in modern temperature monitoring practices. The speed and precision offered by these devices not only streamline temperature assessment processes but also enhance the accuracy of critical measurements, enabling informed decision-making and proactive interventions.
Furthermore, the non-invasive nature of infrared thermometers minimizes the risk of cross-contamination, particularly in healthcare environments, where maintaining hygienic conditions is paramount. This feature, coupled with their rapid response time, positions infrared thermometers as essential tools for frontline healthcare professionals, ensuring efficient and safe temperature monitoring of patients.
As technology continues to evolve, the ongoing advancements in infrared thermometer design and functionality will further expand their applicability and impact. With continuous innovation, these devices will continue to play a pivotal role in temperature monitoring across diverse industries, contributing to enhanced efficiency, safety, and accuracy in various operational contexts.
In essence, the comprehensive guide to using an infrared thermometer underscores its significance as a transformative tool for temperature measurement. By embracing the principles and best practices outlined in this guide, users can leverage the capabilities of infrared thermometers to facilitate informed decision-making, ensure safety, and maintain optimal conditions in a myriad of settings, ultimately enhancing the quality and reliability of temperature monitoring practices.