Home>Fashion & Beauty>Breast Milk Freezer Storage: Duration And Guidelines


Fashion & Beauty
Breast Milk Freezer Storage: Duration And Guidelines
Published: February 19, 2024
Learn the best practices for storing breast milk in the freezer. Find out the recommended duration and guidelines for maintaining its quality. Discover expert tips for preserving breast milk.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Breast milk is a precious gift that provides infants with essential nutrients, antibodies, and comfort. For nursing mothers, the ability to express and store breast milk can be a game-changer, offering flexibility and peace of mind. Freezing breast milk is a common practice that allows mothers to build a stash for future use, whether for returning to work, traveling, or simply having a backup supply on hand.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of breast milk freezer storage, exploring the benefits, duration, guidelines, and best practices for freezing and thawing breast milk. Whether you are a new mother navigating the intricacies of breastfeeding or a seasoned pro looking to optimize your milk storage routine, this article will provide valuable insights and practical tips to support your breastfeeding journey.
As we embark on this exploration, it's important to recognize the significance of breast milk in nourishing and nurturing infants. The unique composition of breast milk, tailored to meet a baby's evolving needs, underscores its irreplaceable role in early childhood development. By understanding the best practices for freezing and storing breast milk, mothers can ensure that this invaluable resource remains readily available when needed, contributing to the well-being and health of their little ones.
Throughout this article, we will uncover the science behind freezing breast milk, dispel common myths, and offer actionable guidance to empower mothers in making informed decisions about their milk storage practices. Whether you are seeking to extend the shelf life of expressed breast milk or gain confidence in managing a freezer stash, this guide will equip you with the knowledge and strategies to navigate the world of breast milk freezer storage with confidence and ease.
Benefits of Freezing Breast Milk
Freezing breast milk offers a multitude of advantages for nursing mothers and their infants. Understanding these benefits can empower mothers to make informed decisions about their breastfeeding journey and milk storage practices. Here are the key advantages of freezing breast milk:
-
Extended Shelf Life: By freezing breast milk, mothers can effectively extend its shelf life, preserving its nutritional value and ensuring that it remains safe for consumption for an extended period. This is particularly beneficial for mothers who need to build a stash for future use or have an oversupply of milk.
-
Flexibility and Convenience: Freezing breast milk provides mothers with the flexibility to store a surplus supply for times when direct breastfeeding may not be feasible. Whether returning to work, traveling, or facing unexpected circumstances, having frozen breast milk on hand offers a convenient solution to ensure that infants continue to receive the nourishment they need.
-
Emergency Preparedness: Freezing breast milk serves as a valuable resource for emergency situations. In the event of illness, separation, or other unforeseen events, having a stockpile of frozen breast milk can provide peace of mind, ensuring that infants have access to a safe and familiar source of nutrition.
-
Nutritional Preservation: The process of freezing breast milk effectively preserves its nutritional content, including essential vitamins, minerals, and antibodies. This means that infants can continue to benefit from the unique composition of breast milk even when direct breastfeeding is not possible.
-
Reduction of Milk Waste: For mothers who may produce more milk than their infants consume, freezing breast milk offers a practical solution to prevent wastage. Rather than discarding excess milk, freezing allows mothers to store it for future use, minimizing waste and maximizing the utilization of this valuable resource.
By recognizing and leveraging these benefits, mothers can optimize their breastfeeding experience and ensure that their infants receive the nourishment they need, even in challenging or unpredictable circumstances. The advantages of freezing breast milk extend beyond mere convenience, encompassing the preservation of essential nutrients and the provision of a reliable safety net for both mothers and their little ones.
Duration of Breast Milk Freezer Storage
The duration for which breast milk can be safely stored in a freezer is a critical consideration for nursing mothers seeking to maintain the quality and nutritional integrity of their expressed milk. Understanding the recommended time frames for freezing breast milk is essential for ensuring that infants receive the best possible nourishment when consuming thawed milk. While breast milk can be safely stored in a freezer, the duration of storage varies based on the type of freezer and the specific guidelines provided by health authorities and lactation experts.
In general, the duration of breast milk freezer storage depends on the type of freezer being used. For standard refrigerator freezers, the recommended storage time for frozen breast milk is approximately 3 to 6 months. These freezers, while suitable for short-term storage, may not maintain consistently low temperatures, which can impact the longevity of frozen breast milk.
On the other hand, standalone deep freezers, also known as chest freezers, offer more stable and consistently low temperatures, making them ideal for long-term breast milk storage. In a deep freezer, breast milk can be safely stored for up to 6 to 12 months or even longer, provided that the freezer maintains a constant temperature of 0°F (-18°C) or lower.
It's important to note that the recommended storage times are based on preserving the optimal nutritional quality of breast milk. While frozen breast milk may remain safe for consumption beyond these time frames, there may be a gradual decline in certain nutrients and antibodies, highlighting the importance of adhering to the suggested storage guidelines.
Factors such as temperature fluctuations, exposure to light, and variations in freezer performance can impact the longevity of frozen breast milk. Therefore, proper storage practices, including using airtight containers or breast milk storage bags, labeling containers with the date of expression, and organizing milk based on the first-in, first-out principle, are essential for maintaining the quality and safety of frozen breast milk.
By understanding the duration of breast milk freezer storage and following recommended guidelines, nursing mothers can confidently manage their milk storage practices, ensuring that their infants receive the full benefits of breast milk, even when direct breastfeeding is not possible. This knowledge empowers mothers to make informed decisions about building a freezer stash, optimizing milk storage, and providing their little ones with the nourishment they need for healthy development.
Guidelines for Freezing Breast Milk
Properly freezing breast milk is essential for preserving its nutritional quality and ensuring its safety for future use. Following specific guidelines for freezing breast milk can help nursing mothers maintain the integrity of this valuable resource. Here are the key guidelines to consider when freezing breast milk:
-
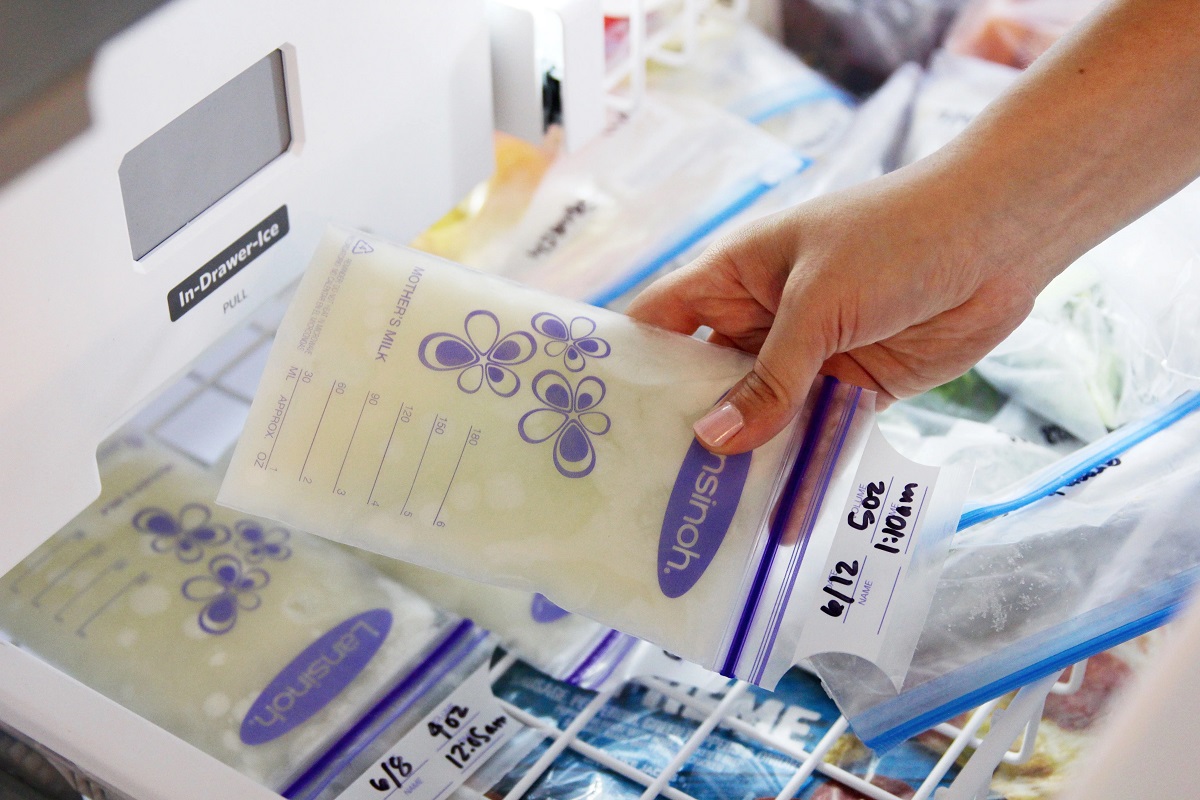
Use Clean and Sterilized Containers: Before expressing and storing breast milk, it is crucial to use clean and sterilized containers to prevent contamination. This helps maintain the purity of the milk and reduces the risk of bacterial growth during storage.
-
Choose Appropriate Storage Containers: Opt for containers specifically designed for breast milk storage, such as BPA-free plastic bottles or breast milk storage bags. These containers are designed to withstand freezing temperatures and minimize the risk of leaks or spills.
-
Label Containers with Date and Time of Expression: Clearly label each storage container with the date and time when the breast milk was expressed. This practice ensures that older milk is used first, following the "first in, first out" principle to maintain freshness.
-
Avoid Filling Containers to the Brim: When filling storage containers, leave some space at the top to account for the expansion of the milk as it freezes. This prevents the containers from bursting or leaking during the freezing process.
-
Cool Expressed Milk Before Freezing: Place freshly expressed breast milk in the refrigerator for a few hours to allow it to cool before transferring it to the freezer. This helps maintain the milk's quality and minimizes temperature fluctuations in the freezer.
-
Freeze Milk in Small Portions: Consider freezing breast milk in small portions to facilitate thawing and minimize waste. Smaller portions are also beneficial for infants with varying feeding needs.
-
Maintain Consistent Freezer Temperatures: Ensure that the freezer maintains a constant temperature of 0°F (-18°C) or lower to preserve the quality of the frozen breast milk. Avoid frequent temperature fluctuations, as they can compromise the milk's integrity.
-
Store Milk at the Back of the Freezer: Place the containers of breast milk at the back of the freezer, away from the door, to minimize exposure to temperature fluctuations when the freezer is opened.
By adhering to these guidelines, nursing mothers can optimize the process of freezing breast milk, safeguarding its nutritional value and ensuring its safety for future use. These practices empower mothers to build a reliable freezer stash, providing a consistent supply of high-quality breast milk for their infants' nourishment.
Thawing and Using Frozen Breast Milk
Thawing and using frozen breast milk requires careful consideration to maintain its nutritional integrity and ensure its safety for infants. When the time comes to use frozen breast milk, proper thawing techniques and handling practices are essential to preserve the milk's quality. Here's a detailed guide on thawing and using frozen breast milk:
Thawing Process
-
Refrigerator Thawing: The recommended method for thawing frozen breast milk is to transfer it from the freezer to the refrigerator. This gradual thawing process allows the milk to retain its nutritional properties while ensuring that it remains safe for consumption. It's advisable to place the frozen breast milk in the refrigerator the night before it is needed, allowing ample time for the milk to thaw thoroughly.
-
Warm Water Bath: If immediate use of frozen breast milk is required, a warm water bath can expedite the thawing process. Place the sealed container of frozen breast milk in a bowl of warm water, ensuring that the water level remains below the lid of the container. Swirl the container gently to facilitate even thawing, taking care to avoid exposing the milk to high temperatures that could compromise its quality.
Handling Thawed Breast Milk
-
Gentle Mixing: Once the frozen breast milk is fully thawed, gently swirl the container to mix any separated layers. Avoid vigorous shaking, as this can lead to the breakdown of beneficial components in the milk.
-
Avoid Microwaving: It's crucial to refrain from microwaving frozen breast milk for thawing, as microwaves can create hot spots that may scald the infant's mouth and degrade the milk's nutritional content.
Using Thawed Breast Milk
-
Expiration Time: Thawed breast milk should be used within 24 hours of complete thawing when stored in the refrigerator. Discard any remaining milk after this period to maintain safety and quality.
-
Room Temperature Use: Thawed breast milk can be kept at room temperature for up to 2 hours, allowing flexibility for feeding schedules and on-the-go convenience.
-
Avoid Refreezing: Once breast milk has been thawed, it should not be refrozen. It's essential to plan the quantity of milk to thaw based on the infant's feeding needs to minimize waste.
By following these guidelines for thawing and using frozen breast milk, nursing mothers can ensure that their infants receive the full benefits of breast milk, even when direct breastfeeding is not possible. These practices empower mothers to manage their freezer stash effectively, providing a reliable supply of high-quality breast milk for their infants' nourishment.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the practice of freezing breast milk offers a multitude of benefits for nursing mothers and their infants. By extending the shelf life of breast milk, freezing provides flexibility, convenience, and a valuable safety net for emergency situations. The nutritional preservation and reduction of milk waste further underscore the significance of freezing breast milk as a practical and sustainable approach to managing breast milk supply.
Understanding the duration of breast milk freezer storage is essential for maintaining the quality and safety of frozen breast milk. Whether stored in a standard refrigerator freezer or a standalone deep freezer, adhering to recommended storage times and proper storage practices ensures that infants receive the best possible nourishment when consuming thawed milk. By recognizing the impact of temperature stability and storage conditions, nursing mothers can confidently manage their milk storage practices, optimizing the nutritional benefits of frozen breast milk.
Guidelines for freezing breast milk provide essential insights into maintaining the integrity of expressed milk. From using clean and sterilized containers to labeling containers with the date and time of expression, these guidelines empower mothers to safeguard the purity and quality of their frozen breast milk. By following these best practices, nursing mothers can build a reliable freezer stash, providing a consistent supply of high-quality breast milk for their infants' nourishment.
Thawing and using frozen breast milk require careful consideration to preserve its nutritional integrity and ensure its safety for infants. By following proper thawing techniques and handling practices, nursing mothers can ensure that their infants receive the full benefits of breast milk, even when direct breastfeeding is not possible. These practices empower mothers to manage their freezer stash effectively, providing a reliable supply of high-quality breast milk for their infants' nourishment.
In essence, the comprehensive understanding of freezing breast milk, including its benefits, duration of storage, guidelines for freezing, and proper thawing and usage, equips nursing mothers with the knowledge and strategies to navigate the world of breast milk freezer storage with confidence and ease. By leveraging these insights, nursing mothers can optimize their breastfeeding experience, ensure the well-being of their infants, and embrace the flexibility and convenience that freezing breast milk affords.