Home>Culinary & Beverages>Understanding The Temperature Danger Zone: Importance And Guidelines


Culinary & Beverages
Understanding The Temperature Danger Zone: Importance And Guidelines
Published: February 21, 2024
Learn the importance of the temperature danger zone in culinary and beverages. Follow guidelines to ensure food safety and prevent contamination.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
The Significance of the Temperature Danger Zone
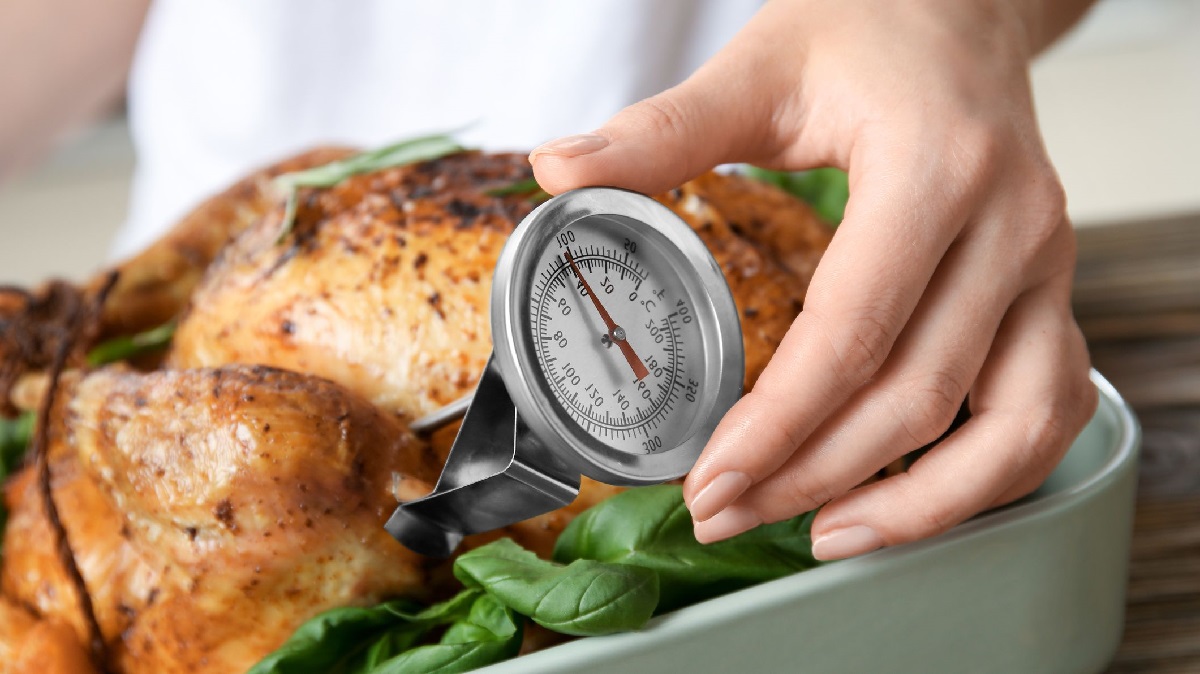
The temperature danger zone is a critical concept in the realm of food safety, playing a pivotal role in preventing foodborne illnesses. This zone, typically ranging from 41°F to 135°F (5°C to 57°C), provides an ideal environment for the rapid growth of harmful bacteria. Understanding the significance of the temperature danger zone is paramount for anyone involved in the handling, preparation, and storage of food.
When food is left within the temperature danger zone, bacteria such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Campylobacter can multiply at an alarming rate. This exponential growth can occur within a short span of time, leading to the potential contamination of food with dangerous pathogens. As a result, consuming such contaminated food can result in severe foodborne illnesses, posing a significant risk to public health.
Moreover, the temperature danger zone is not limited to specific types of food; it encompasses a wide array of perishable items, including meat, poultry, dairy products, cooked vegetables, and more. This universality underscores the importance of vigilance in maintaining safe temperatures across various food categories.
In the context of food establishments, such as restaurants, cafeterias, and catering services, adhering to temperature safety guidelines is not only a matter of compliance but also a fundamental aspect of customer well-being. By recognizing the critical nature of the temperature danger zone, food handlers and managers can prioritize the implementation of stringent protocols to mitigate the risks associated with bacterial proliferation.
Furthermore, the significance of the temperature danger zone extends beyond commercial settings to encompass home kitchens and domestic food preparation. Individuals responsible for cooking and storing food at home must also grasp the implications of this zone to safeguard the health of their families and loved ones.
In essence, comprehending the significance of the temperature danger zone serves as a cornerstone of food safety practices. By acknowledging the potential hazards posed by improper temperature control, individuals and food-related businesses can take proactive measures to uphold the integrity and safety of the food supply chain. This awareness empowers stakeholders to make informed decisions and implement measures that mitigate the risks associated with bacterial contamination, thereby contributing to a safer and healthier food environment for all.
Factors Contributing to the Temperature Danger Zone
The temperature danger zone is influenced by various factors that create an environment conducive to the rapid proliferation of harmful bacteria. Understanding these contributing factors is essential for effectively managing food safety risks associated with temperature control.
-
Ambient Temperature: The surrounding environment plays a pivotal role in determining the temperature at which food is stored and prepared. Factors such as room temperature, kitchen climate, and outdoor conditions can impact the temperature of perishable items. In warmer climates, maintaining safe temperatures becomes particularly challenging, as higher ambient temperatures can expedite bacterial growth within the temperature danger zone.
-
Food Storage Practices: The manner in which food is stored significantly influences its susceptibility to entering the temperature danger zone. Improper storage, such as leaving perishable items on countertops for extended periods or failing to refrigerate cooked food promptly, can elevate the risk of bacterial contamination. Inadequate storage practices compromise the integrity of food, rendering it more susceptible to bacterial proliferation.
-
Food Handling Procedures: The way in which food is handled during preparation and service directly affects its exposure to the temperature danger zone. For instance, prolonged handling of raw meat or seafood at room temperature can elevate the risk of bacterial cross-contamination. Similarly, improper cooling methods for cooked food can lead to prolonged exposure within the danger zone, fostering an environment conducive to bacterial growth.
-
Equipment Functionality: The functionality and calibration of refrigeration units, freezers, and food warming equipment are critical in preventing food from entering the temperature danger zone. Malfunctioning or inadequately maintained equipment can compromise the ability to maintain safe temperatures, thereby increasing the likelihood of bacterial proliferation in perishable items.
-
Temperature Monitoring: The absence of robust temperature monitoring mechanisms can contribute to the inadvertent exposure of food to the temperature danger zone. Inadequate monitoring practices, such as infrequent temperature checks or reliance on inaccurate thermometers, can result in a false sense of security, potentially leading to the oversight of unsafe temperature conditions.
-
Food Transportation: During transit from suppliers to food establishments, as well as during delivery to consumers, perishable items are susceptible to temperature fluctuations. Inadequate temperature control during transportation can expose food to the temperature danger zone, compromising its safety and quality.
By recognizing and addressing these contributing factors, food handlers and establishments can proactively implement measures to mitigate the risks associated with the temperature danger zone. Through diligent attention to ambient conditions, storage practices, handling procedures, equipment functionality, temperature monitoring, and transportation protocols, stakeholders can uphold the integrity of the food supply chain and minimize the potential for bacterial contamination within the critical temperature range.
Potential Risks of Food in the Temperature Danger Zone
The temperature danger zone presents a myriad of potential risks to the safety and quality of food, stemming from the favorable conditions it provides for the rapid proliferation of harmful bacteria. Understanding these risks is paramount for anyone involved in the handling, preparation, and storage of perishable items.
-
Bacterial Proliferation: The primary risk associated with the temperature danger zone is the exponential growth of pathogenic bacteria in food. Within this critical temperature range, bacteria such as Salmonella, Escherichia coli, and Listeria monocytogenes can multiply at an alarming rate, significantly elevating the risk of foodborne illnesses upon consumption. This proliferation poses a direct threat to public health, as it can lead to severe gastrointestinal infections and other adverse health effects.
-
Toxin Production: In addition to bacterial growth, certain pathogens have the ability to produce toxins when exposed to the temperature danger zone. For instance, the bacterium Staphylococcus aureus can generate heat-stable toxins in food, even at temperatures within the danger zone. Consumption of food contaminated with such toxins can result in rapid and severe symptoms, including nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea, underscoring the urgency of preventing toxin formation through proper temperature control.
-
Spoilage and Quality Degradation: Beyond the realm of food safety, the temperature danger zone also poses risks to the overall quality and shelf life of perishable items. Prolonged exposure to temperatures within this range can accelerate the spoilage of food, leading to changes in texture, flavor, and appearance. This degradation not only compromises the sensory attributes of food but also diminishes its nutritional value, resulting in economic losses and diminished consumer satisfaction.
-
Cross-Contamination: The potential for cross-contamination is heightened when food lingers within the temperature danger zone. As bacteria multiply in perishable items, the risk of contaminating other foods, surfaces, and utensils in the vicinity increases. This can perpetuate the spread of harmful pathogens within the food preparation environment, amplifying the risk of foodborne illnesses and compromising overall hygiene standards.
-
Regulatory Non-Compliance: For food establishments and businesses, failure to adhere to temperature safety guidelines can result in regulatory non-compliance and legal repercussions. Health and safety regulations mandate strict adherence to temperature control measures to safeguard public health. Inadequate temperature management not only jeopardizes consumer well-being but also exposes food-related businesses to potential fines, penalties, and reputational damage.
In essence, the potential risks of food in the temperature danger zone encompass a spectrum of threats to both public health and the integrity of the food supply chain. By recognizing these risks and implementing robust temperature control measures, stakeholders can mitigate the adverse effects associated with bacterial proliferation, toxin formation, spoilage, cross-contamination, and regulatory non-compliance. This proactive approach is essential in upholding the safety, quality, and trustworthiness of the food industry.
Guidelines for Avoiding the Temperature Danger Zone
Adhering to stringent guidelines for avoiding the temperature danger zone is paramount in safeguarding the safety and integrity of perishable food items. By implementing proactive measures and best practices, individuals and food-related establishments can mitigate the risks associated with bacterial proliferation and uphold the highest standards of food safety. The following guidelines serve as a comprehensive framework for effectively avoiding the temperature danger zone:
-
Temperature Monitoring: Regular and systematic monitoring of temperatures in storage units, refrigerators, and food preparation areas is essential. Utilizing calibrated thermometers and digital temperature monitoring systems enables real-time tracking of temperature fluctuations, allowing for prompt corrective action when deviations occur.
-
Proper Storage Protocols: Categorizing and storing perishable items according to their specific temperature requirements is crucial. This includes promptly refrigerating or freezing items that require cold storage and ensuring that refrigeration units are maintained at the appropriate temperatures to prevent food from entering the danger zone.
-
Timely Refrigeration: Cooked food, raw meat, poultry, seafood, and dairy products should be promptly refrigerated to inhibit bacterial growth. Implementing a "first in, first out" approach ensures that older perishable items are utilized before newer ones, reducing the likelihood of items languishing in the temperature danger zone.
-
Effective Cooling Methods: When cooling cooked food for storage, employing rapid cooling methods such as ice baths, shallow pans, or blast chillers accelerates the process, minimizing the duration during which food remains within the danger zone.
-
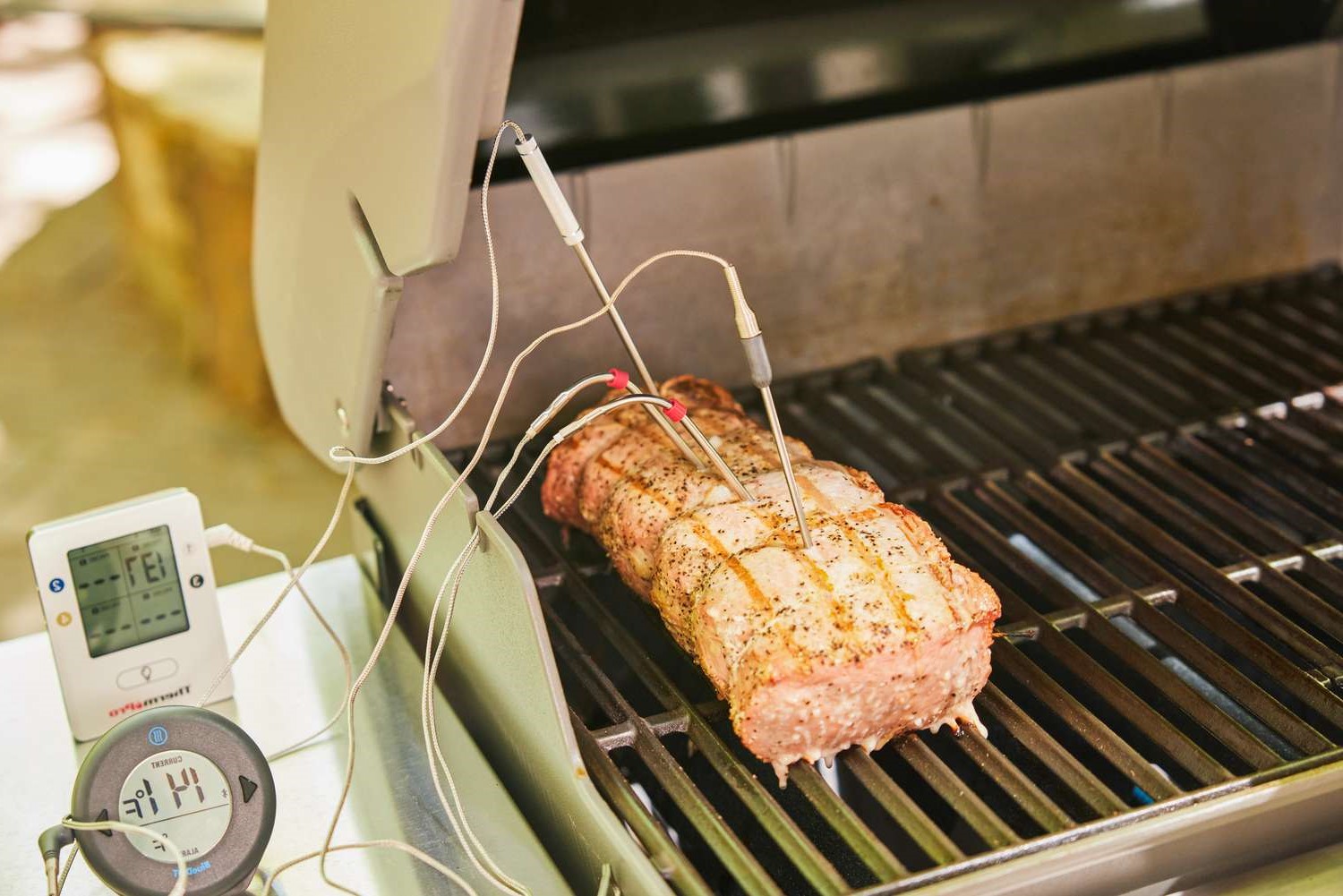
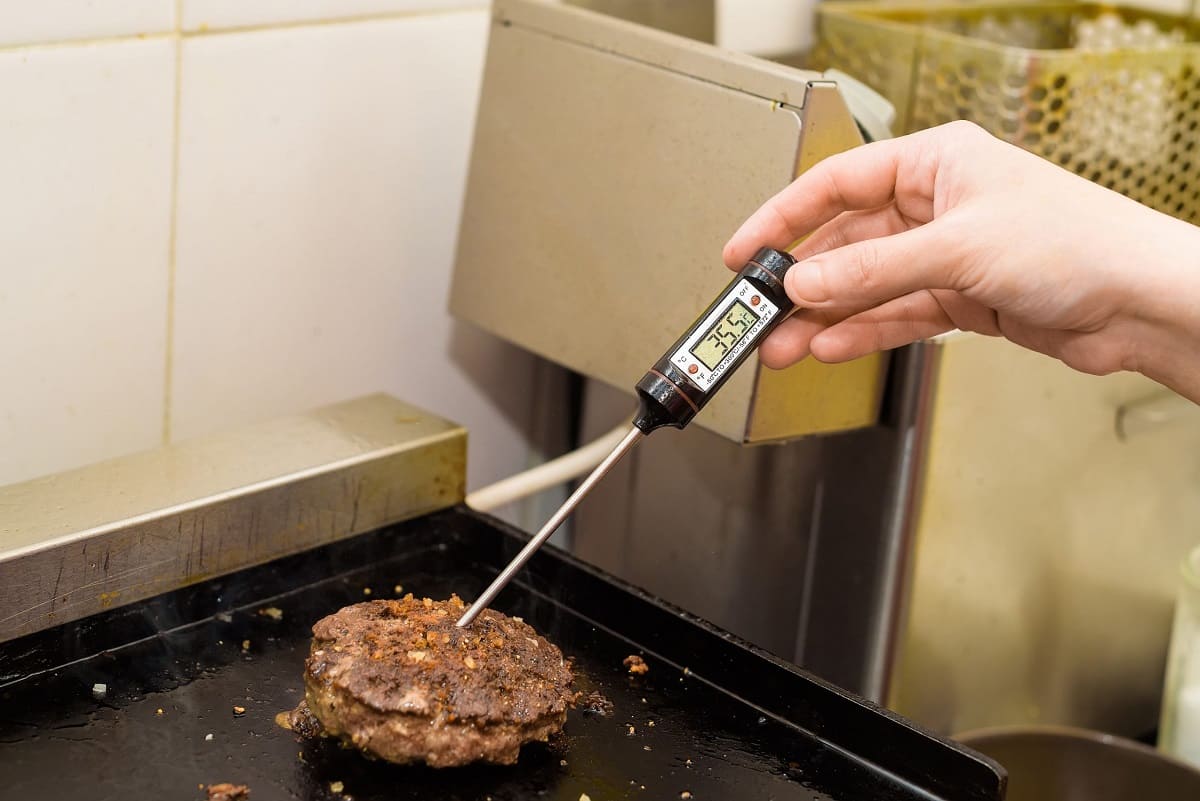
Thorough Cooking Practices: Ensuring that food is thoroughly cooked to the recommended internal temperatures effectively eliminates harmful bacteria, reducing the risk of contamination post-cooking.
-
Hygienic Food Handling: Adhering to stringent hygiene practices during food handling, including frequent handwashing, use of separate utensils for raw and cooked items, and regular sanitation of food contact surfaces, mitigates the risk of cross-contamination and bacterial proliferation.
-
Transportation Protocols: During transit, maintaining proper temperature control for perishable items is essential. Utilizing insulated containers, refrigerated vehicles, and temperature-monitoring devices safeguards food from exposure to the temperature danger zone during transportation.
-
Staff Training and Awareness: Providing comprehensive training to food handlers and staff members on the significance of temperature control, as well as the implementation of temperature safety protocols, fosters a culture of vigilance and accountability in preventing food from entering the danger zone.
By diligently adhering to these guidelines, individuals and food establishments can significantly reduce the likelihood of food entering the temperature danger zone, thereby enhancing food safety, minimizing health risks, and upholding the highest standards of quality and integrity in the handling and preparation of perishable items.
Importance of Monitoring and Controlling Temperature in Food Safety
The importance of monitoring and controlling temperature in food safety cannot be overstated, as it serves as a linchpin in preventing foodborne illnesses and upholding the integrity of the food supply chain. By meticulously overseeing and regulating temperatures throughout the handling, storage, and preparation of perishable items, stakeholders can mitigate the risks associated with bacterial proliferation and ensure the delivery of safe, high-quality food to consumers.
Effective temperature monitoring is the cornerstone of proactive food safety management. By employing calibrated thermometers and digital temperature monitoring systems, food handlers can diligently track temperature fluctuations in storage units, refrigerators, and food preparation areas. This real-time oversight enables swift corrective action in response to deviations, preventing food from entering the temperature danger zone and inhibiting the rapid growth of harmful bacteria.
Controlling temperature is equally pivotal in safeguarding food safety. Proper storage protocols, such as promptly refrigerating perishable items and maintaining refrigeration units at optimal temperatures, prevent food from lingering within the danger zone. Timely refrigeration of cooked food, raw meat, poultry, seafood, and dairy products inhibits bacterial growth, reducing the likelihood of contamination and foodborne illnesses.
Furthermore, effective cooling methods play a crucial role in temperature control. Rapidly cooling cooked food for storage through techniques such as ice baths, shallow pans, or blast chillers minimizes the duration during which food remains within the danger zone, mitigating the risk of bacterial proliferation. Thorough cooking practices also contribute to temperature control, as ensuring that food reaches recommended internal temperatures effectively eliminates harmful bacteria, bolstering food safety.
Hygienic food handling practices, including frequent handwashing, segregation of raw and cooked items, and regular sanitation of food contact surfaces, further reinforce the importance of temperature control in preventing cross-contamination and bacterial proliferation. Additionally, maintaining proper temperature control during food transportation, coupled with comprehensive staff training on temperature safety protocols, underscores the holistic approach required to uphold food safety standards.
In essence, monitoring and controlling temperature in food safety is indispensable in mitigating the risks associated with the temperature danger zone. By prioritizing temperature oversight and regulation, stakeholders uphold the highest standards of food safety, minimize health risks, and fortify consumer confidence in the safety and quality of the food they consume. This unwavering commitment to temperature control underscores the dedication of food-related establishments and individuals to delivering uncompromisingly safe and wholesome food to the public.