Home>Culinary & Beverages>The Optimal Temperatures For Tempering Chocolate


Culinary & Beverages
The Optimal Temperatures For Tempering Chocolate
Modified: February 28, 2024
Discover the ideal temperatures for tempering chocolate with our expert culinary and beverages guide. Achieve perfect results every time!
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- The Science of Tempering Chocolate
- Factors Affecting Chocolate Tempering
- Importance of Temperature Control in Chocolate Tempering
- Recommended Temperatures for Tempering Dark Chocolate
- Recommended Temperatures for Tempering Milk Chocolate
- Recommended Temperatures for Tempering White Chocolate
- Tips for Achieving the Optimal Temperatures for Tempering Chocolate
- Conclusion
Introduction
Tempering chocolate is a crucial process in the world of confectionery and pastry. It involves carefully manipulating the temperature of chocolate to ensure that it sets properly, resulting in a glossy finish, a satisfying snap, and a smooth mouthfeel. Whether you are a professional chocolatier or a passionate home baker, understanding the science behind chocolate tempering and the optimal temperatures for different types of chocolate is essential for achieving delectable results.
Tempering chocolate is a delicate art that requires precision and attention to detail. By controlling the temperature of melted chocolate, the cocoa butter crystals within the chocolate are properly aligned, resulting in a stable crystalline structure. This process is what gives tempered chocolate its desirable characteristics, such as a shiny appearance and a firm texture at room temperature.
In the following sections, we will delve into the intricate science of chocolate tempering, exploring the factors that influence the process and the importance of temperature control. Furthermore, we will provide specific recommended temperatures for tempering dark, milk, and white chocolate, as well as valuable tips for achieving optimal results. Whether you are a seasoned pastry chef or an enthusiastic home cook, mastering the art of chocolate tempering will elevate your confectionery creations to new heights of excellence.
Read more: Mastering The Art Of Tempering Chocolate
The Science of Tempering Chocolate
Tempering chocolate is a precise and scientific process that involves manipulating the cocoa butter crystals within the chocolate to achieve a stable crystalline structure. Cocoa butter, the fat present in chocolate, can form six different types of crystals, but only one of these types, known as the beta crystal, yields the desired characteristics in tempered chocolate. These characteristics include a glossy appearance, a firm texture at room temperature, and a satisfying snap when broken.
When chocolate is melted, the cocoa butter crystals become disorganized and lose their stable structure. This is why melted chocolate that has cooled without tempering often appears dull, has a soft texture, and may exhibit gray streaks or spots known as "bloom." To achieve the optimal crystalline structure, the chocolate must be carefully cooled and agitated to encourage the formation of beta crystals while preventing the formation of undesirable crystal types.
The process of tempering involves precise temperature control to encourage the formation of beta crystals. This is typically achieved through a series of heating, cooling, and reheating steps. By carefully manipulating the temperature, the cocoa butter crystals are encouraged to align in a uniform manner, resulting in the desired characteristics of tempered chocolate.
The science of tempering chocolate is rooted in the principles of crystallography and thermodynamics. Understanding the behavior of cocoa butter crystals at different temperatures is essential for achieving the desired results. By controlling the rate of crystallization and the size of the cocoa butter crystals, chocolatiers and pastry chefs can create chocolate with the perfect texture, appearance, and mouthfeel.
In addition to temperature control, the process of tempering also involves agitation, which helps distribute the cocoa butter crystals evenly throughout the chocolate. This ensures that the chocolate sets uniformly and exhibits a consistent texture and appearance.
Mastering the science of tempering chocolate is a fundamental skill for anyone working with chocolate, whether in a professional kitchen or at home. By understanding the principles behind cocoa butter crystallization and the role of temperature control, individuals can elevate their chocolate creations to a level of excellence that delights the senses and captivates the palate.
Factors Affecting Chocolate Tempering
Several factors influence the process of chocolate tempering, each playing a crucial role in achieving the desired results. Understanding these factors is essential for mastering the art of chocolate tempering and consistently producing high-quality confections.
-
Type of Chocolate: Different types of chocolate, such as dark, milk, and white chocolate, contain varying proportions of cocoa solids, sugar, and milk solids. These differences impact the tempering process, as the fat content and composition of each type of chocolate influence the behavior of cocoa butter crystals during tempering.
-
Temperature Fluctuations: Fluctuations in temperature during the tempering process can disrupt the formation of stable cocoa butter crystals. Sudden changes in temperature can lead to the formation of undesirable crystal types, resulting in chocolate that lacks the desired texture and appearance.
-
Humidity and Moisture: Moisture can adversely affect the tempering process, causing chocolate to seize or become grainy. It is essential to work in a dry environment and ensure that all utensils and equipment are completely dry before tempering chocolate.
-
Quality of Chocolate: The quality of the chocolate used for tempering significantly impacts the final product. High-quality chocolate with a well-balanced composition of cocoa solids and cocoa butter is essential for achieving optimal results in tempering.
-
Agitation and Stirring: Proper agitation and stirring during the tempering process are crucial for distributing the cocoa butter crystals evenly throughout the chocolate. This ensures that the chocolate sets uniformly and exhibits a consistent texture and appearance.
-
Cooling Rate: The rate at which the tempered chocolate is cooled influences the size and distribution of the cocoa butter crystals. A controlled cooling process is essential for achieving the desired characteristics of tempered chocolate.
-
Equipment and Utensils: The type and quality of equipment and utensils used for tempering chocolate can impact the process. Using high-quality thermometers, tempered chocolate molds, and utensils designed for chocolate work can contribute to successful tempering.
By considering these factors and implementing precise temperature control, proper agitation, and attention to detail, chocolatiers and pastry chefs can navigate the complexities of chocolate tempering with confidence, consistently producing exquisite confections that showcase the artistry and precision of the tempering process.
Importance of Temperature Control in Chocolate Tempering
Temperature control is of paramount importance in the process of chocolate tempering. The precise manipulation of temperature is the key to achieving the desired characteristics of tempered chocolate, including a glossy finish, a firm texture, and a satisfying snap. Without proper temperature control, the cocoa butter crystals within the chocolate may not align in the desired manner, resulting in a lackluster appearance and undesirable texture.
During the tempering process, the chocolate must be heated to a specific temperature to ensure that all cocoa butter crystals are melted. This initial heating phase is essential for resetting the crystal structure of the chocolate and preparing it for the subsequent cooling and re-heating steps. Once the chocolate reaches the correct temperature, it is then cooled to encourage the formation of stable beta crystals, which are responsible for the desirable attributes of tempered chocolate.
The importance of temperature control becomes evident during the cooling phase, where the chocolate is gradually brought to a lower temperature. This controlled cooling process allows the beta crystals to form uniformly throughout the chocolate, resulting in a stable crystalline structure. If the temperature drops too quickly or fluctuates unpredictably, the cocoa butter crystals may form undesirable crystal types, leading to a lack of proper tempering and the characteristic flaws associated with improperly tempered chocolate.
Furthermore, maintaining the chocolate at the optimal working temperature during the tempering process is crucial for achieving consistent results. The chocolate must be kept within a specific temperature range to ensure that the beta crystals remain stable and that the chocolate sets properly. This level of precision in temperature control is essential for producing professional-quality confections with the desired texture and appearance.
In essence, temperature control is the linchpin of successful chocolate tempering. It governs the behavior of cocoa butter crystals, determines the texture and appearance of the final product, and ultimately distinguishes properly tempered chocolate from its untempered counterparts. By understanding the critical role of temperature control and implementing precise temperature manipulation, chocolatiers and pastry chefs can elevate their chocolate creations to a level of excellence that delights the senses and captivates the palate.
Recommended Temperatures for Tempering Dark Chocolate
Tempering dark chocolate requires careful attention to temperature control to ensure that the cocoa butter crystals align in the desired manner, resulting in a smooth, glossy finish and a satisfying snap. The recommended temperatures for tempering dark chocolate are as follows:
-
Initial Heating: The dark chocolate should be heated to a temperature between 115°F and 120°F (46°C and 49°C). This initial heating phase ensures that all cocoa butter crystals are melted, resetting the crystal structure of the chocolate and preparing it for the subsequent tempering steps.
-
Cooling: Once the chocolate has been heated to the specified temperature, it is then cooled to approximately 80°F (27°C). This controlled cooling process encourages the formation of stable beta crystals, which are responsible for the desirable attributes of tempered dark chocolate.
-
Reheating: After the chocolate has been sufficiently cooled, it is gently reheated to a working temperature between 88°F and 90°F (31°C and 32°C). This final heating phase ensures that the beta crystals remain stable and that the chocolate is in an optimal state for molding, dipping, or enrobing confections.
By adhering to these recommended temperatures and carefully monitoring the chocolate throughout the tempering process, chocolatiers and pastry chefs can consistently achieve perfectly tempered dark chocolate with a luxurious sheen, a firm texture, and a rich, indulgent flavor. Mastering the art of tempering dark chocolate opens the door to a world of exquisite confections, from decadent truffles and bonbons to intricately molded chocolate decorations, each showcasing the impeccable craftsmanship and artistry of properly tempered chocolate.
Recommended Temperatures for Tempering Milk Chocolate
Tempering milk chocolate requires precision and attention to detail to achieve the desired characteristics of perfectly tempered chocolate. The recommended temperatures for tempering milk chocolate are tailored to ensure that the cocoa butter crystals align in a uniform manner, resulting in a lustrous finish, a pleasing snap, and a creamy, indulgent texture.
-
Initial Heating: The process begins with heating the milk chocolate to a temperature range of 110°F to 115°F (43°C to 46°C). This initial heating phase is crucial for melting all the cocoa butter crystals within the chocolate, effectively resetting its crystal structure and preparing it for the subsequent tempering steps.
-
Cooling: Once the milk chocolate has been heated to the specified temperature, it is then carefully cooled to approximately 79°F (26°C). This controlled cooling process encourages the formation of stable beta crystals, which are essential for imparting the desired attributes of tempered milk chocolate, including a smooth, creamy texture and a rich, full-bodied flavor.
-
Reheating: After the chocolate has been adequately cooled, it is gently reheated to a working temperature between 86°F and 88°F (30°C and 31°C). This final heating phase ensures that the beta crystals remain stable and that the milk chocolate is in an optimal state for molding, enrobing, or creating delectable chocolate-coated treats.
By adhering to these recommended temperatures and meticulously monitoring the milk chocolate throughout the tempering process, chocolatiers and pastry chefs can consistently achieve perfectly tempered milk chocolate with a luxurious sheen, a creamy mouthfeel, and a delightful flavor profile. This meticulously tempered milk chocolate serves as the foundation for an array of delectable creations, from velvety ganache fillings and creamy chocolate truffles to silky-smooth chocolate coatings for an assortment of confections.
Mastering the art of tempering milk chocolate is a testament to the precision and skill of the chocolatier, resulting in a symphony of flavors and textures that elevate chocolate creations to new heights of indulgence and delight.
Recommended Temperatures for Tempering White Chocolate
Tempering white chocolate demands meticulous attention to temperature control to achieve the desired attributes of perfectly tempered chocolate. The recommended temperatures for tempering white chocolate are tailored to ensure that the cocoa butter crystals align in a uniform manner, resulting in a lustrous finish, a pleasing snap, and a creamy, indulgent texture.
-
Initial Heating: The process commences with heating the white chocolate to a temperature range of 105°F to 110°F (40°C to 43°C). This initial heating phase is critical for melting all the cocoa butter crystals within the chocolate, effectively resetting its crystal structure and preparing it for the subsequent tempering steps.
-
Cooling: Once the white chocolate has been heated to the specified temperature, it is then carefully cooled to approximately 78°F (25°C). This controlled cooling process encourages the formation of stable beta crystals, which are essential for imparting the desired attributes of tempered white chocolate, including a creamy, delicate texture and a rich, vanilla-infused flavor.
-
Reheating: After the chocolate has been adequately cooled, it is gently reheated to a working temperature between 84°F and 86°F (29°C and 30°C). This final heating phase ensures that the beta crystals remain stable and that the white chocolate is in an optimal state for molding, enrobing, or creating exquisite chocolate decorations and embellishments.
By adhering to these recommended temperatures and meticulously monitoring the white chocolate throughout the tempering process, chocolatiers and pastry chefs can consistently achieve perfectly tempered white chocolate with a luxurious sheen, a creamy mouthfeel, and a delightful flavor profile. This meticulously tempered white chocolate serves as the foundation for an array of delectable creations, from velvety ganache fillings and delicate truffles to elegant chocolate drizzles and intricate decorations that adorn a myriad of confections.
Mastering the art of tempering white chocolate is a testament to the precision and skill of the chocolatier, resulting in a symphony of flavors and textures that elevate chocolate creations to new heights of indulgence and delight.
Tips for Achieving the Optimal Temperatures for Tempering Chocolate
Achieving the optimal temperatures for tempering chocolate requires precision, patience, and a keen understanding of the tempering process. Here are valuable tips to guide you in mastering the art of chocolate tempering:
-
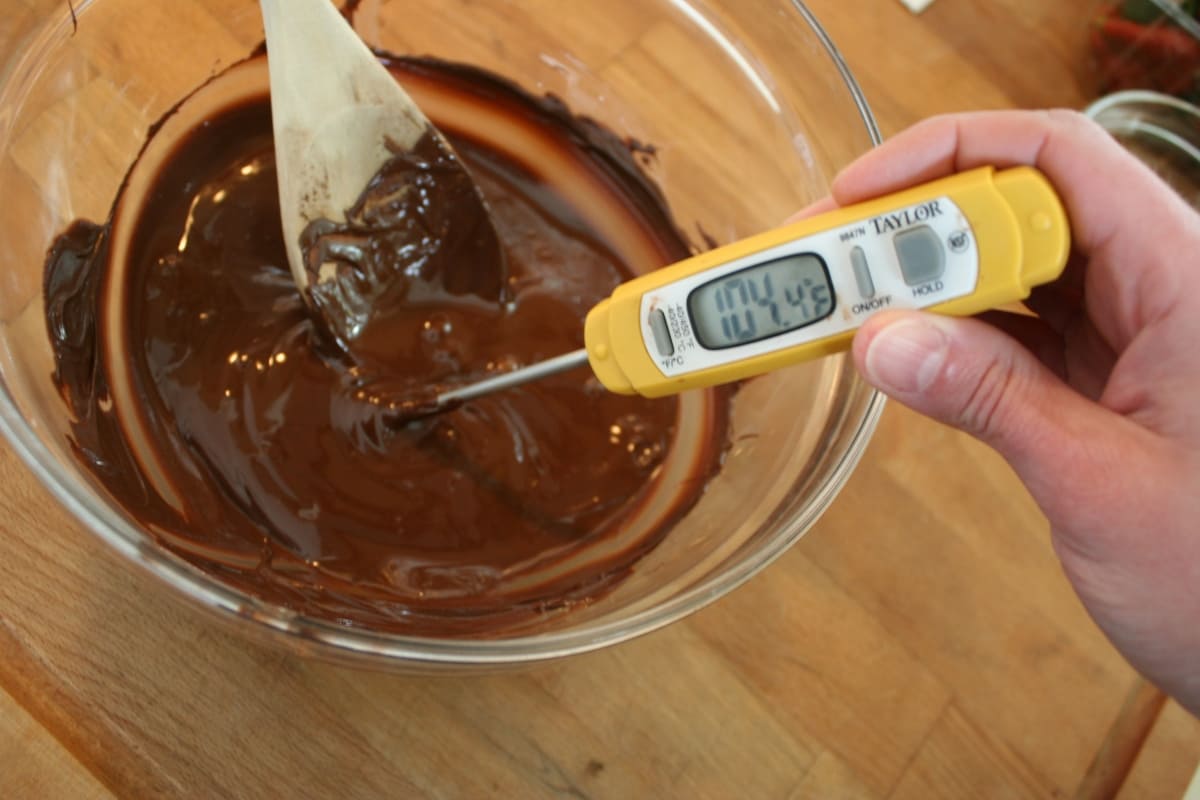
Use a Reliable Thermometer: Invest in a high-quality digital thermometer designed for chocolate work. Accurate temperature readings are essential for achieving the precise temperature ranges required for tempering dark, milk, and white chocolate.
-
Avoid Sudden Temperature Changes: Ensure a gradual transition between heating, cooling, and reheating phases. Sudden temperature fluctuations can disrupt the formation of stable cocoa butter crystals, leading to inconsistent tempering results.
-
Test Small Batches: When tempering chocolate for the first time or working with a new type of chocolate, consider tempering a small test batch. This allows you to observe the behavior of the chocolate and make adjustments before tempering larger quantities.
-
Maintain a Dry Environment: Moisture can cause chocolate to seize or become grainy during the tempering process. Work in a dry environment and ensure that all utensils and equipment are thoroughly dry before tempering chocolate.
-
Use the Seeding Method: Incorporate small pieces of tempered chocolate (seeds) into the melted chocolate during the cooling phase. The addition of seeds helps encourage the formation of stable cocoa butter crystals, aiding in the tempering process.
-
Stir and Agitate Thoroughly: Vigorously stir and agitate the chocolate during the cooling phase to distribute the cocoa butter crystals evenly. This promotes uniform crystallization and ensures a consistent texture and appearance in the tempered chocolate.
-
Monitor Room Temperature: The ambient temperature of the room can impact the tempering process. Ensure that the tempering environment is at a stable, moderate temperature to support the proper crystallization of the chocolate.
-
Adjust Temperatures for Different Chocolate Brands: Different chocolate brands may respond slightly differently to the tempering process. Be prepared to make minor adjustments to the recommended tempering temperatures based on the specific characteristics of the chocolate being used.
By incorporating these tips into your chocolate tempering process, you can enhance your ability to achieve the optimal temperatures for tempering chocolate, resulting in consistently exquisite and professionally tempered chocolate creations.
Conclusion
Mastering the art of chocolate tempering is a journey that combines scientific precision with creative finesse. The meticulous manipulation of temperature, the careful alignment of cocoa butter crystals, and the artful craftsmanship involved in tempering chocolate are essential elements that elevate confectionery creations to new heights of excellence.
In conclusion, the process of tempering chocolate is a testament to the dedication and skill of chocolatiers and pastry chefs, whether in professional kitchens or home settings. By understanding the science of cocoa butter crystallization, the factors influencing the tempering process, and the recommended temperatures for dark, milk, and white chocolate, individuals can embark on a journey of chocolate mastery that yields consistently exquisite results.
The importance of temperature control in chocolate tempering cannot be overstated. Precise temperature manipulation governs the behavior of cocoa butter crystals, ultimately determining the texture, appearance, and mouthfeel of the final product. Whether crafting decadent truffles, delicate chocolate decorations, or silky-smooth ganache fillings, the mastery of temperature control is the cornerstone of achieving professional-quality tempered chocolate.
Furthermore, the art of chocolate tempering is a harmonious blend of science and artistry. It requires a deep understanding of cocoa butter crystallization, the ability to navigate the complexities of temperature control, and the creative vision to transform tempered chocolate into an array of delectable confections that delight the senses and captivate the palate.
As chocolatiers and pastry chefs embark on their chocolate tempering endeavors, the tips for achieving optimal temperatures serve as invaluable guides, offering insights into the nuances of the tempering process and empowering individuals to consistently produce perfectly tempered chocolate creations.
In essence, the journey of mastering chocolate tempering is a testament to the dedication, precision, and artistry of those who seek to create confections that transcend the ordinary and evoke moments of pure indulgence and delight. With a deep understanding of the science of tempering, a mastery of temperature control, and a touch of creative flair, chocolatiers and pastry chefs can embark on a journey that celebrates the exquisite art of chocolate in its most refined and delectable form.