Home>Weather and Climate>Global Temperature Trends


Weather and Climate
Global Temperature Trends
Modified: May 6, 2024
Explore the latest global temperature trends and their impact on weather and climate. Stay informed about the changing environmental conditions.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Earth's climate is a complex and dynamic system that influences every aspect of our lives. One of the key indicators of the state of our climate is global temperature trends. These trends provide crucial insights into the changes occurring in our environment and their potential impacts on ecosystems, weather patterns, and human societies.
Understanding global temperature trends involves analyzing historical data, identifying the factors that influence these trends, and projecting future scenarios. By delving into this topic, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of the Earth's systems and the implications of human activities on the planet's climate.
Global temperature trends are not only a subject of scientific inquiry but also a matter of great public interest and concern. As such, exploring this topic is essential for fostering informed discussions and decision-making regarding climate change mitigation and adaptation strategies.
In the following sections, we will delve into the historical global temperature data, examine the factors that influence global temperature trends, assess the impact of these trends on the environment and society, analyze the current state of global temperatures, and explore future projections. Through this exploration, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of global temperature trends and their significance in the context of climate change and environmental sustainability.
Historical Global Temperature Data
The historical record of global temperature data serves as a vital foundation for understanding the Earth's climate dynamics. Over the past century, scientists have meticulously collected and analyzed temperature measurements from various sources, including weather stations, ocean buoys, and satellite observations. This extensive dataset enables us to trace the trajectory of global temperature trends and discern notable patterns and fluctuations.
The analysis of historical global temperature data reveals compelling evidence of a warming trend over the past century. This is exemplified by the widespread consensus among climate scientists that the Earth's average surface temperature has increased significantly since the late 19th century. The upward trajectory of global temperatures is underscored by the instrumental record, which showcases a consistent rise in average temperatures, particularly in the latter half of the 20th century.
Moreover, the historical data illustrates regional variations in temperature trends, with certain areas experiencing more pronounced warming than others. These disparities are instrumental in understanding the localized impacts of climate change and the differential vulnerabilities of various ecosystems and communities.
The historical global temperature data also unveils noteworthy fluctuations and anomalies, such as periods of rapid warming or temporary cooling trends. These variations provide valuable insights into the natural climatic oscillations and the influence of external factors, including volcanic eruptions, solar activity, and oceanic phenomena, on global temperature dynamics.
Furthermore, the historical temperature record enables scientists to reconstruct past climate conditions and compare them with contemporary observations. This comparative analysis facilitates a deeper understanding of long-term climate patterns and aids in discerning the unprecedented nature of recent temperature trends.
In essence, the historical global temperature data serves as a cornerstone for comprehending the evolving climate dynamics and underpins the scientific consensus regarding anthropogenic influences on global warming. By scrutinizing this rich repository of temperature measurements, researchers can unravel the intricate interplay of natural and human-induced factors shaping the Earth's climate, thereby informing evidence-based climate policies and adaptation strategies.
Factors Influencing Global Temperature Trends
The complex interplay of various natural and anthropogenic factors contributes to the intricate tapestry of global temperature trends. Understanding these influential factors is pivotal in unraveling the mechanisms driving climate change and its far-reaching implications. Here, we delve into the key determinants that shape global temperature trends:
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The emission of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), and nitrous oxide (N2O), is a primary driver of global temperature trends. These gases trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to the greenhouse effect, which results in the retention of thermal energy and subsequent warming of the planet. Human activities, including the burning of fossil fuels, industrial processes, deforestation, and agricultural practices, have significantly amplified the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, intensifying the greenhouse effect and elevating global temperatures.
Solar Variability
Fluctuations in solar radiation, stemming from natural variations in the Sun's activity, exert a discernible influence on global temperature trends. While the Sun is the principal source of energy for the Earth's climate system, subtle changes in solar output can impact the planet's energy balance. Although solar variability contributes to natural climatic oscillations, its direct influence on contemporary global warming is comparatively minor in contrast to the dominant role of greenhouse gas emissions.
Read more: Latest Global Temperature Trends In 2022
Aerosols and Particulate Matter
Aerosols, comprising tiny particles and droplets suspended in the atmosphere, can exert a dual influence on global temperature trends. On one hand, certain aerosols, such as sulfate particles, possess a cooling effect by reflecting sunlight and enhancing cloud formation, thereby offsetting a fraction of the warming induced by greenhouse gases. On the other hand, black carbon aerosols, emitted from incomplete combustion processes, absorb sunlight and contribute to localized warming. The intricate interactions between aerosols and particulate matter play a nuanced role in shaping regional temperature patterns.
Land Use and Land Cover Changes
Human-induced alterations in land use and land cover, including urbanization, deforestation, and agricultural expansion, can engender significant modifications in surface albedo and heat absorption. These changes influence the Earth's energy balance, leading to localized temperature variations and altering regional climate dynamics. The conversion of natural landscapes into urbanized areas and agricultural zones can exacerbate heat retention, exacerbating the urban heat island effect and contributing to elevated local temperatures.
Oceanic Circulation Patterns
The intricate dynamics of oceanic circulation, encompassing phenomena such as El Niño and La Niña, exert a profound influence on global temperature trends. These large-scale oceanic oscillations can engender widespread climatic anomalies, influencing temperature and precipitation patterns across diverse regions. The interplay between oceanic circulation patterns and atmospheric dynamics plays a pivotal role in shaping regional and global climate variability, underscoring the interconnected nature of the Earth's climate systems.
In essence, the multifaceted interplay of greenhouse gas emissions, solar variability, aerosols, land use changes, and oceanic circulation patterns collectively shape global temperature trends, underscoring the intricate web of factors driving contemporary climate change. By comprehensively elucidating these influential determinants, we can foster a deeper understanding of the mechanisms underpinning global temperature dynamics and inform evidence-based strategies for mitigating climate change and fostering environmental resilience.
Impact of Global Temperature Trends
The far-reaching ramifications of global temperature trends permeate every facet of the Earth's ecosystems and human societies, underscoring the profound influence of climate change on our planet. The impact of escalating global temperatures manifests across diverse domains, encompassing ecological, meteorological, and socio-economic dimensions.
Ecological Impacts
Rising global temperatures exert a transformative influence on ecological systems, precipitating shifts in species distributions, phenological events, and ecosystem dynamics. These changes can disrupt delicate ecological balances, leading to biodiversity loss and altering the functioning of ecosystems. Furthermore, the warming climate can exacerbate habitat loss, intensify the frequency and severity of extreme weather events, and elevate the risk of species extinctions. The intricate interplay of temperature trends and ecological dynamics underscores the vulnerability of natural habitats and the imperative of conservation efforts in the face of climate change.
Meteorological Consequences
The escalating global temperatures engender a spectrum of meteorological consequences, including alterations in precipitation patterns, intensification of heatwaves, and amplification of extreme weather events. These manifestations of climate change can precipitate profound disruptions in weather systems, leading to heightened risks of droughts, floods, and tropical cyclones. Moreover, the warming climate can influence atmospheric circulation patterns, contributing to regional climate anomalies and perturbations in seasonal climatic regimes. The meteorological impacts of global temperature trends underscore the imperative of adaptive measures and resilient infrastructure to mitigate the risks posed by extreme weather phenomena.
Socio-Economic Ramifications
The reverberations of global temperature trends extend into the socio-economic sphere, impacting livelihoods, food security, and human well-being. Agricultural systems are particularly susceptible to the vagaries of climate change, with shifting temperature regimes and altered precipitation patterns posing challenges to crop yields and agricultural productivity. Furthermore, the escalating temperatures can exacerbate water scarcity, heighten the incidence of vector-borne diseases, and amplify the socio-economic disparities stemming from climate-induced vulnerabilities. The socio-economic ramifications of global temperature trends underscore the imperative of sustainable development, climate-resilient livelihoods, and equitable adaptation strategies to safeguard the well-being of communities in the face of climate change.
In essence, the impact of global temperature trends permeates the fabric of our planet, exerting profound ecological, meteorological, and socio-economic ramifications. By comprehensively elucidating these impacts, we can foster a deeper appreciation for the urgency of climate action and the imperative of fostering environmental resilience in the face of escalating global temperatures.
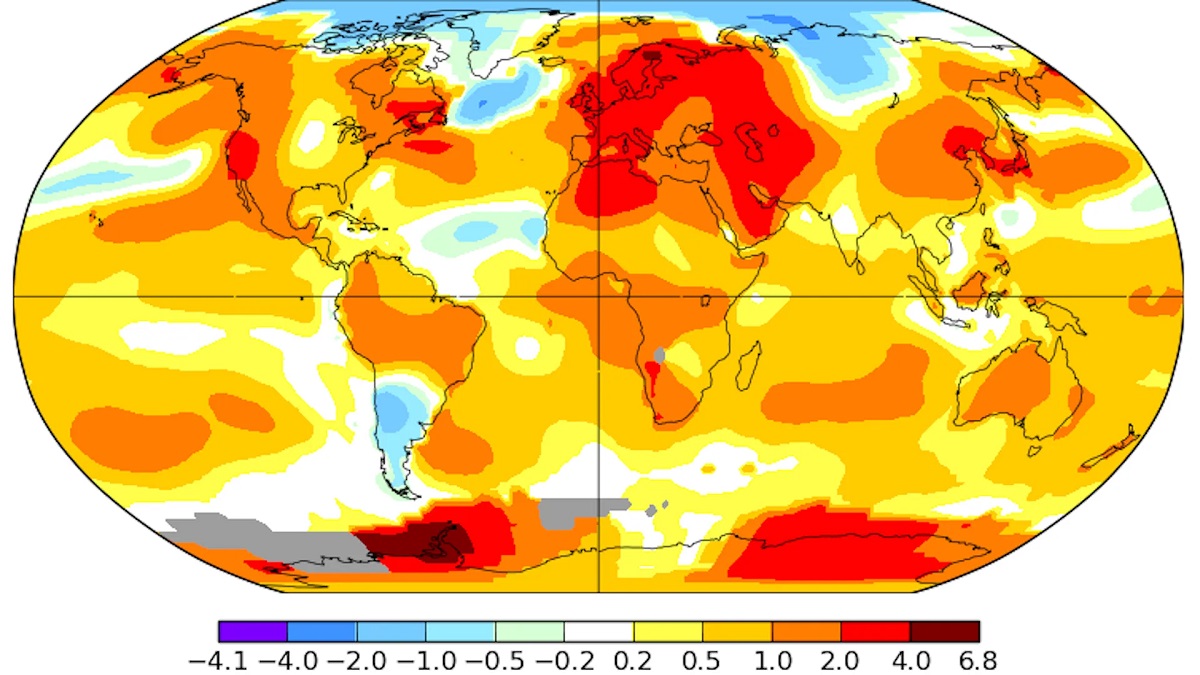
Current Global Temperature Trends
The current global temperature trends underscore the unequivocal reality of ongoing climate change, with compelling evidence pointing to a discernible warming trajectory across diverse regions of the planet. Contemporary temperature records, derived from a network of ground-based weather stations, ocean buoys, and satellite observations, consistently depict a pronounced uptick in average global temperatures over the past few decades. This upward trend is emblematic of the pervasive influence of anthropogenic activities on the Earth's climate system.
Notably, the instrumental record of global temperature trends reveals a series of record-breaking years, characterized by anomalously high average temperatures and recurrent instances of extreme heat events. These manifestations of contemporary climate dynamics underscore the intensifying impact of global warming on the Earth's ecosystems and human societies. Moreover, the discernible amplification of temperature anomalies, including heatwaves, prolonged periods of elevated temperatures, and diminishing occurrences of extreme cold events, underscores the pervasive imprint of climate change on the planet's thermal regime.
Furthermore, regional analyses of current global temperature trends unveil notable disparities in the pace and magnitude of warming across diverse geographical contexts. Certain regions, particularly high-latitude areas and coastal zones, exhibit accelerated rates of temperature increase, accentuating the differential vulnerabilities of ecosystems and communities to the impacts of climate change. These regional variations in temperature trends underscore the localized repercussions of global warming and the imperative of tailored adaptation strategies to address the diverse challenges posed by shifting thermal regimes.
The contemporary global temperature trends also underscore the interconnected nature of climate dynamics, with cascading impacts reverberating across diverse spheres, including ecological systems, weather patterns, and socio-economic dynamics. The escalating temperatures engender multifaceted consequences, ranging from alterations in precipitation patterns and intensification of extreme weather events to perturbations in agricultural productivity and human health outcomes. These manifestations of contemporary temperature trends underscore the imperative of proactive measures to mitigate the risks posed by climate change and foster environmental resilience.
In essence, the current global temperature trends provide compelling insights into the pervasive influence of climate change on the Earth's thermal regime. By scrutinizing these contemporary temperature dynamics, we can foster a deeper understanding of the urgency of climate action and the imperative of fostering adaptive strategies to address the multifaceted challenges posed by escalating global temperatures.
Read more: Monthly Temperature Trends in California
Future Projections of Global Temperature
The future projections of global temperature serve as a crucial lens through which we can anticipate the trajectory of climate change and its implications for the Earth's ecosystems and human societies. Climate models, informed by comprehensive datasets and scientific insights, offer valuable projections regarding the potential scenarios of global temperature trends in the coming decades. These projections are instrumental in informing evidence-based policies, adaptation strategies, and mitigation efforts aimed at addressing the challenges posed by escalating temperatures.
The consensus among climate scientists underscores the robustness of future projections, which consistently indicate a trajectory of continued warming in response to escalating greenhouse gas emissions. Projections derived from state-of-the-art climate models underscore the potential for substantial increases in global average temperatures, with scenarios depicting varying degrees of warming based on different emissions trajectories and mitigation efforts. These projections underscore the imperative of proactive measures to mitigate the risks posed by climate change and foster environmental resilience.
Moreover, future projections of global temperature trends unveil the differential vulnerabilities of diverse regions to the impacts of climate change, with certain areas facing heightened risks of temperature extremes, altered precipitation patterns, and amplified climatic anomalies. These regional disparities in projected temperature trends underscore the imperative of tailored adaptation strategies and localized resilience-building initiatives to address the diverse challenges posed by shifting thermal regimes.
Furthermore, the future projections of global temperature trends underscore the interconnected nature of climate dynamics, with cascading impacts reverberating across diverse spheres, including ecological systems, weather patterns, and socio-economic dynamics. The projected intensification of extreme weather events, alterations in agricultural productivity, and perturbations in human health outcomes underscores the imperative of proactive measures to mitigate the risks posed by climate change and foster environmental resilience.
In essence, the future projections of global temperature trends provide invaluable insights into the trajectory of climate change and the imperative of fostering adaptive strategies to address the multifaceted challenges posed by escalating global temperatures. By scrutinizing these projections, we can foster a deeper understanding of the urgency of climate action and the imperative of informed decision-making to navigate the complexities of a warming world.