Home>Weather and Climate>2021 Global Average Temperature: Insights And Trends


Weather and Climate
2021 Global Average Temperature: Insights And Trends
Published: March 4, 2024
Gain insights into the 2021 global average temperature trends and their impact on weather and climate. Stay informed with the latest data and analysis.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Understanding Global Average Temperature
- Factors Influencing Global Average Temperature
- Historical Trends in Global Average Temperature
- Current Insights on Global Average Temperature
- Projections for Future Global Average Temperature
- Implications of Changing Global Average Temperature
- Conclusion
Introduction
The global average temperature is a critical metric that provides invaluable insights into the Earth's climate system. It serves as a key indicator of the planet's overall temperature trends, reflecting the complex interplay of various climatic factors. Understanding the nuances of global average temperature is essential for comprehending the broader implications of climate change and its far-reaching impacts on the environment, ecosystems, and human societies.
The significance of monitoring global average temperature cannot be overstated, as it serves as a barometer for assessing the health of the planet's climate. By analyzing temperature data from diverse geographical regions and time periods, scientists can discern patterns, anomalies, and long-term shifts in global temperature trends. This comprehensive approach enables a deeper understanding of the intricate dynamics driving climate variability and change.
Moreover, the global average temperature encapsulates the collective thermal behavior of the Earth's atmosphere, oceans, and land surfaces. It reflects the cumulative influence of natural climatic processes, such as solar radiation, ocean currents, and atmospheric circulation, as well as the impact of human activities, including industrialization, deforestation, and greenhouse gas emissions.
In essence, the global average temperature serves as a vital yardstick for gauging the evolving state of the planet's climate. By delving into the multifaceted dimensions of this fundamental metric, we can unravel the intricate tapestry of climate dynamics and gain profound insights into the past, present, and future trajectory of global temperatures. This, in turn, equips us with the knowledge needed to address the challenges posed by climate change and work towards sustainable solutions for the benefit of current and future generations.
Understanding Global Average Temperature
The global average temperature serves as a pivotal metric for comprehending the overarching thermal behavior of the Earth's climate system. It represents the mean temperature of the entire planet, encompassing diverse geographical regions, from polar ice caps to equatorial rainforests. This comprehensive metric is derived from a complex network of weather stations, ocean buoys, and satellite observations, which collectively capture the thermal profile of the Earth's atmosphere, oceans, and land surfaces.
The calculation of the global average temperature involves synthesizing temperature data from myriad sources across the globe. This process entails meticulous analysis and statistical techniques to harmonize diverse datasets and account for variations in measurement methodologies. By amalgamating temperature readings from different locations and time periods, scientists can derive a representative value that encapsulates the collective thermal state of the planet.
Furthermore, the global average temperature is instrumental in discerning long-term climate trends and variations. By scrutinizing historical temperature records, researchers can identify patterns of temperature change, including fluctuations, anomalies, and sustained shifts. This historical perspective enables a deeper understanding of the evolving dynamics of global temperatures and provides crucial context for interpreting contemporary climate trends.
Moreover, the global average temperature serves as a linchpin for assessing the impacts of climate change on the planet's ecosystems and human societies. It offers a comprehensive vantage point for evaluating the ramifications of shifting temperature patterns on agricultural productivity, water resources, biodiversity, and extreme weather events. By monitoring changes in the global average temperature, scientists can glean insights into the multifaceted repercussions of climate change and formulate strategies to mitigate its adverse effects.
In essence, understanding the global average temperature is pivotal for unraveling the complex interplay of climatic factors shaping the planet's thermal equilibrium. By delving into the intricacies of this fundamental metric, we can gain profound insights into the dynamic nature of the Earth's climate and foster a deeper appreciation for the interconnectedness of global temperature patterns with the broader fabric of the natural world.
Factors Influencing Global Average Temperature
The global average temperature is influenced by a myriad of interconnected factors, encompassing natural climatic processes and human-induced activities. Understanding these influential elements is crucial for deciphering the complex dynamics driving temperature variations on a planetary scale.
Natural Factors
-
Solar Radiation: The amount of solar energy reaching the Earth's surface plays a pivotal role in shaping global temperatures. Variations in solar radiation, influenced by solar cycles and orbital dynamics, can instigate fluctuations in the planet's thermal balance.
-
Atmospheric Composition: The composition of the Earth's atmosphere, particularly the concentration of greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide, methane, and water vapor, profoundly impacts the retention of heat within the atmosphere. This greenhouse effect is instrumental in regulating the planet's overall temperature.
-
Oceanic Circulation: The intricate network of ocean currents and circulation patterns exerts a significant influence on global temperature distribution. The transport of heat across the oceans, facilitated by currents like the Gulf Stream, can modulate regional and global climate patterns.
-
Volcanic Activity: Major volcanic eruptions can release copious amounts of ash and aerosols into the atmosphere, which can temporarily shield the Earth from solar radiation, leading to a cooling effect on global temperatures.
Human-Induced Factors
-
Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Anthropogenic activities, including the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes, have substantially increased the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This heightened greenhouse effect has contributed to the amplification of global temperatures, leading to the phenomenon commonly referred to as global warming.
-
Land Use Changes: Human alterations to land surfaces, such as urbanization, agriculture, and deforestation, can influence local and regional temperature patterns. The replacement of natural vegetation with built environments or agricultural landscapes can modify the surface albedo and heat absorption characteristics, thereby impacting temperature dynamics.
-
Aerosol Emissions: The release of aerosols and particulate matter into the atmosphere from industrial activities and biomass burning can exert a complex influence on global temperatures. While certain aerosols can contribute to cooling by reflecting solar radiation, others may have a warming effect through interactions with clouds and radiation.
By comprehensively examining these diverse factors, we can gain a nuanced understanding of the intricate web of influences shaping the global average temperature. This holistic perspective is indispensable for devising effective strategies to address climate change and mitigate its far-reaching impacts on the planet's ecosystems and human societies.
Read more: Global Temperature Trends
Historical Trends in Global Average Temperature
The historical trends in global average temperature provide compelling insights into the evolving thermal dynamics of the Earth's climate over extended time periods. By scrutinizing temperature records dating back centuries, scientists have discerned notable patterns and shifts in global temperatures, shedding light on the profound impact of natural climatic processes and human activities on the planet's thermal equilibrium.
One of the pivotal revelations gleaned from historical temperature data is the discernible upward trajectory of global temperatures over the past century. The onset of the Industrial Revolution marked a pivotal juncture, coinciding with a discernible uptick in global average temperatures. This phenomenon, commonly referred to as global warming, has been attributed to the intensification of human-induced activities, particularly the combustion of fossil fuels and the resultant surge in greenhouse gas emissions.
Moreover, historical temperature records unveil periods of climatic variability, including notable fluctuations and anomalies. For instance, the mid-20th century witnessed a phase of cooling, often termed the "global cooling" scare, which engendered widespread concern about the potential onset of a new ice age. However, subsequent analyses revealed that this cooling phase was largely offset by the overarching warming trend, underscoring the complexity of global temperature dynamics.
Furthermore, historical temperature reconstructions derived from proxy data, such as ice cores and tree rings, have elucidated temperature variations predating the instrumental record. These paleoclimate insights have unveiled past episodes of climatic shifts, including periods of pronounced warmth, such as the Medieval Warm Period, and intervals of relative cooling, such as the Little Ice Age. These historical benchmarks offer crucial context for interpreting contemporary temperature trends and accentuate the significance of long-term perspectives in climate analysis.
In essence, delving into historical trends in global average temperature unveils a tapestry of climatic nuances, encompassing sustained warming trends, episodic fluctuations, and profound climatic shifts. This historical vantage point is indispensable for contextualizing the contemporary trajectory of global temperatures and underscores the imperative of proactive measures to address the challenges posed by climate change. By harnessing the insights gleaned from historical temperature records, we can chart a course towards sustainable solutions and informed climate action, thereby fostering a resilient and harmonious coexistence with the dynamic forces shaping our planet's climate.
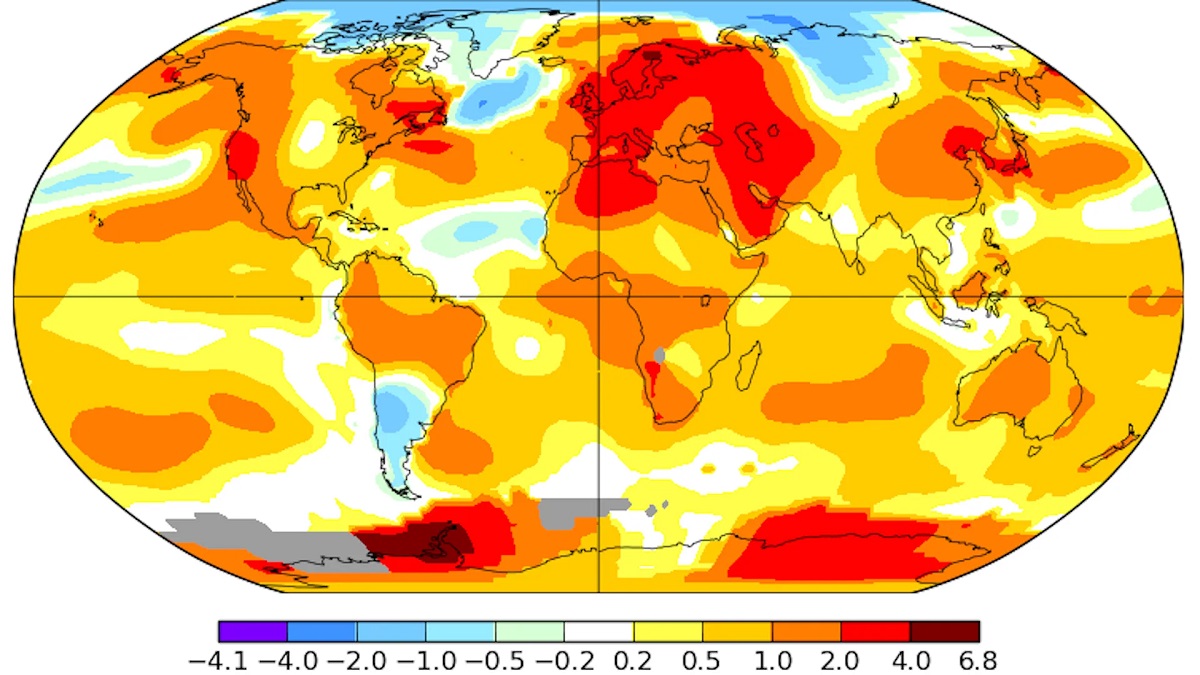
Current Insights on Global Average Temperature
In the contemporary context, the monitoring and analysis of global average temperature have unveiled compelling insights into the ongoing dynamics of the Earth's climate system. Current observations and research endeavors have illuminated several noteworthy facets of global temperature patterns, offering valuable perspectives on the state of the planet's thermal equilibrium.
One salient insight pertains to the sustained upward trend in global average temperatures. Contemporary temperature records underscore the persistence of this warming trajectory, with successive years frequently registering as some of the warmest on record. This consistent elevation in global temperatures underscores the enduring influence of human-induced factors, particularly the escalation of greenhouse gas emissions stemming from industrial activities, transportation, and land use changes.
Moreover, current insights into global average temperature patterns have accentuated the amplification of temperature anomalies and extreme weather events. The intensification of heatwaves, prolonged droughts, and erratic precipitation patterns has underscored the far-reaching repercussions of shifting global temperatures on ecosystems, agriculture, and human well-being. These manifestations of a changing climate serve as poignant reminders of the imperative to address the underlying drivers of global temperature rise and bolster resilience against its impacts.
Furthermore, contemporary research endeavors have shed light on the regional heterogeneity of temperature trends, elucidating variations in warming rates across different geographical locales. This nuanced understanding of regional temperature dynamics is instrumental for devising targeted adaptation and mitigation strategies tailored to the specific challenges posed by localized climate changes.
Additionally, advancements in climate modeling and data analytics have facilitated a more comprehensive assessment of the intricate interplay between global average temperature trends and other climatic variables. This holistic approach enables a deeper comprehension of the cascading effects of temperature changes on phenomena such as sea level rise, ocean acidification, and shifts in precipitation patterns, thereby enriching our grasp of the multifaceted dimensions of climate change.
In essence, the current insights on global average temperature underscore the urgency of concerted action to address climate change and its manifold impacts. By leveraging these insights to inform evidence-based policies, innovative technologies, and collective efforts towards sustainability, we can endeavor to mitigate the adverse effects of global temperature rise and chart a course towards a resilient and harmonious coexistence with the dynamic forces shaping our planet's climate.
Projections for Future Global Average Temperature
The projections for future global average temperature paint a sobering picture of the trajectory that lies ahead, underscoring the imperative of proactive measures to address the challenges posed by climate change. Climate models and scenario-based analyses offer compelling insights into the potential evolution of global temperatures, taking into account various factors such as greenhouse gas emissions, land use changes, and socio-economic dynamics.
Forecasts indicate a continuation of the upward trend in global average temperatures, with scenarios projecting varying degrees of temperature rise based on different emission trajectories. Under high-emission scenarios, characterized by unabated greenhouse gas emissions, the prospects point towards a substantial escalation in global temperatures, leading to far-reaching impacts on ecosystems, weather patterns, and human societies. Conversely, under scenarios aligned with stringent emission reductions and sustainable practices, the pace of temperature rise could be moderated, offering a more favorable outlook for climate resilience and adaptation.
Furthermore, projections for future global average temperature underscore the regional disparities in temperature trends, highlighting the differential impacts of climate change across diverse geographical areas. Certain regions may experience amplified warming rates, exacerbating the frequency and intensity of heatwaves, droughts, and extreme weather events. Conversely, other regions may confront distinct challenges, such as shifts in precipitation patterns and the destabilization of ecological systems. This regional heterogeneity necessitates tailored strategies for climate adaptation and mitigation, acknowledging the localized nuances of temperature dynamics.
Moreover, the projections for future global average temperature emphasize the critical importance of international cooperation and concerted efforts to curb greenhouse gas emissions and foster sustainable practices. By aligning with the goals outlined in international climate agreements, such as the Paris Agreement, and embracing innovative technologies and policies aimed at decarbonization and climate resilience, the global community can strive towards a future characterized by stabilized temperatures and a harmonious coexistence with the natural environment.
In essence, the projections for future global average temperature underscore the pivotal juncture at which humanity stands, presenting a compelling call to action to address climate change and forge a sustainable path forward. By heeding these projections and embracing a collective commitment to environmental stewardship, we can endeavor to mitigate the impacts of global temperature rise and cultivate a resilient and balanced relationship with the intricate forces shaping our planet's climate.
Implications of Changing Global Average Temperature
The changing global average temperature carries profound implications for the planet's ecosystems, human societies, and the broader fabric of the natural world. As temperatures continue to rise, a cascade of far-reaching impacts unfolds, underscoring the urgency of addressing climate change and fostering resilience against its repercussions.
One of the foremost implications of shifting global temperatures is the exacerbation of extreme weather events. Heatwaves, intense storms, and erratic precipitation patterns are amplified in a warming climate, posing heightened risks to human health, agriculture, and infrastructure. Moreover, rising temperatures can engender shifts in the frequency and intensity of natural disasters, including hurricanes, floods, and wildfires, amplifying the imperative for robust disaster preparedness and adaptive strategies.
Furthermore, changing global average temperature patterns exert profound effects on ecosystems and biodiversity. Shifts in temperature regimes can disrupt ecological balance, leading to alterations in species distributions, phenological shifts, and the destabilization of habitats. These impacts reverberate across interconnected ecosystems, influencing food webs, species interactions, and the provision of ecosystem services, thereby necessitating concerted efforts to conserve biodiversity and enhance ecological resilience.
The implications of changing global average temperature extend to critical sectors such as agriculture, water resources, and public health. Agricultural productivity is susceptible to temperature variations, with heat stress, altered growing seasons, and water scarcity posing challenges to food security. Similarly, water resources face heightened pressures, as changing temperatures influence precipitation patterns, snowmelt dynamics, and the availability of freshwater, necessitating adaptive water management strategies. Additionally, rising temperatures can exacerbate health risks, amplifying the prevalence of heat-related illnesses, vector-borne diseases, and air quality concerns, accentuating the imperative for public health interventions and climate-resilient infrastructure.
Moreover, the implications of shifting global temperatures underscore the imperative of addressing climate change as a multifaceted challenge with profound ethical, social, and economic dimensions. Vulnerable communities, particularly in low-lying coastal areas and regions prone to climate extremes, face heightened risks and disparities, necessitating equitable and inclusive approaches to climate adaptation and mitigation.
In essence, the implications of changing global average temperature permeate every facet of the natural world and human civilization, accentuating the imperative of proactive measures to address climate change and foster resilience. By acknowledging these implications and embracing a collective commitment to environmental stewardship, we can endeavor to mitigate the impacts of global temperature rise and cultivate a resilient and balanced relationship with the intricate forces shaping our planet's climate.
Read more: Latest Global Temperature Trends In 2022
Conclusion
In conclusion, the global average temperature stands as a barometer of the Earth's climate health, encapsulating the collective thermal behavior of the planet's atmosphere, oceans, and land surfaces. It serves as a pivotal metric for comprehending the overarching thermal dynamics of the Earth's climate system, offering profound insights into the complex interplay of natural climatic processes and human-induced activities. By delving into the multifaceted dimensions of this fundamental metric, we gain a deeper understanding of the past, present, and future trajectory of global temperatures.
The historical trends in global average temperature unveil a tapestry of climatic nuances, encompassing sustained warming trends, episodic fluctuations, and profound climatic shifts. These historical benchmarks offer crucial context for interpreting contemporary temperature trends and accentuate the significance of long-term perspectives in climate analysis. Furthermore, the current insights on global average temperature underscore the urgency of concerted action to address climate change and its manifold impacts. By leveraging these insights to inform evidence-based policies, innovative technologies, and collective efforts towards sustainability, we can endeavor to mitigate the adverse effects of global temperature rise and chart a course towards a resilient and harmonious coexistence with the dynamic forces shaping our planet's climate.
Looking ahead, the projections for future global average temperature underscore the pivotal juncture at which humanity stands, presenting a compelling call to action to address climate change and forge a sustainable path forward. By heeding these projections and embracing a collective commitment to environmental stewardship, we can endeavor to mitigate the impacts of global temperature rise and cultivate a resilient and balanced relationship with the intricate forces shaping our planet's climate.
In essence, the implications of changing global average temperature permeate every facet of the natural world and human civilization, accentuating the imperative of proactive measures to address climate change and foster resilience. By acknowledging these implications and embracing a collective commitment to environmental stewardship, we can endeavor to mitigate the impacts of global temperature rise and cultivate a resilient and balanced relationship with the intricate forces shaping our planet's climate.