Home>Health & Nutrition>The Accuracy Of Tympanic Thermometers: A Comprehensive Analysis

Health & Nutrition
The Accuracy Of Tympanic Thermometers: A Comprehensive Analysis
Published: March 6, 2024
Discover the accuracy of tympanic thermometers in this comprehensive analysis. Learn about the latest advancements in health and nutrition.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Background of Tympanic Thermometers
- Factors Affecting the Accuracy of Tympanic Thermometers
- Comparison of Tympanic Thermometers with Other Types of Thermometers
- Studies and Research on the Accuracy of Tympanic Thermometers
- Limitations and Challenges in Using Tympanic Thermometers
- Recommendations for Improving the Accuracy of Tympanic Thermometers
- Conclusion
Introduction
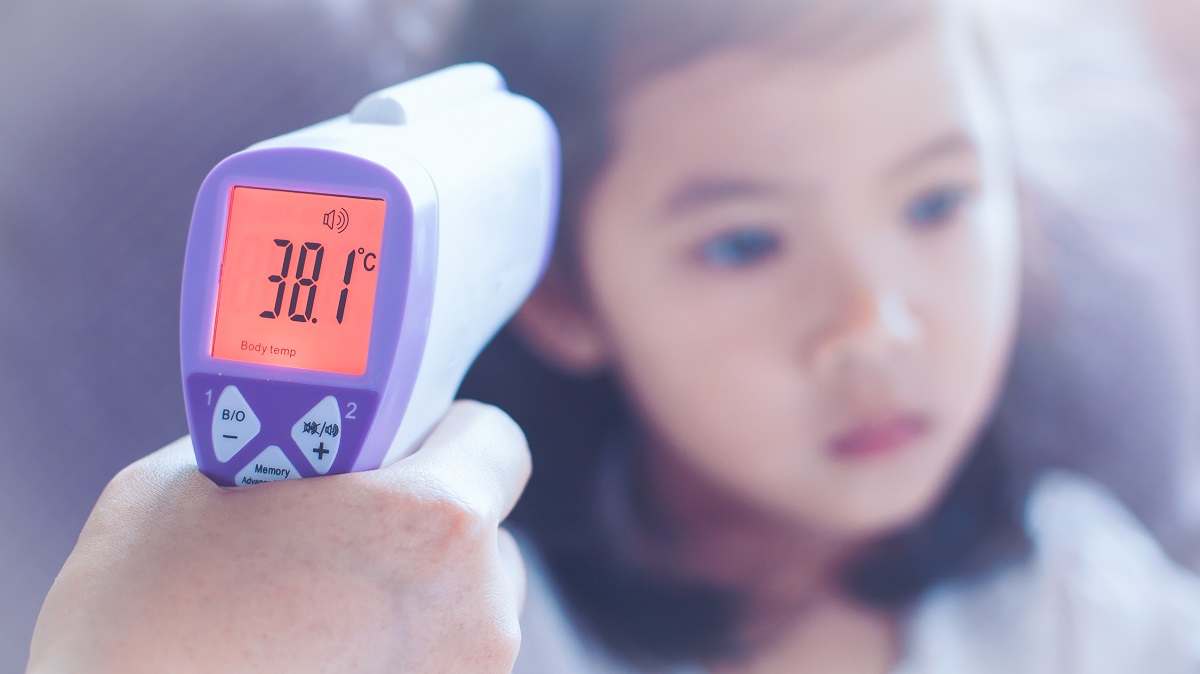
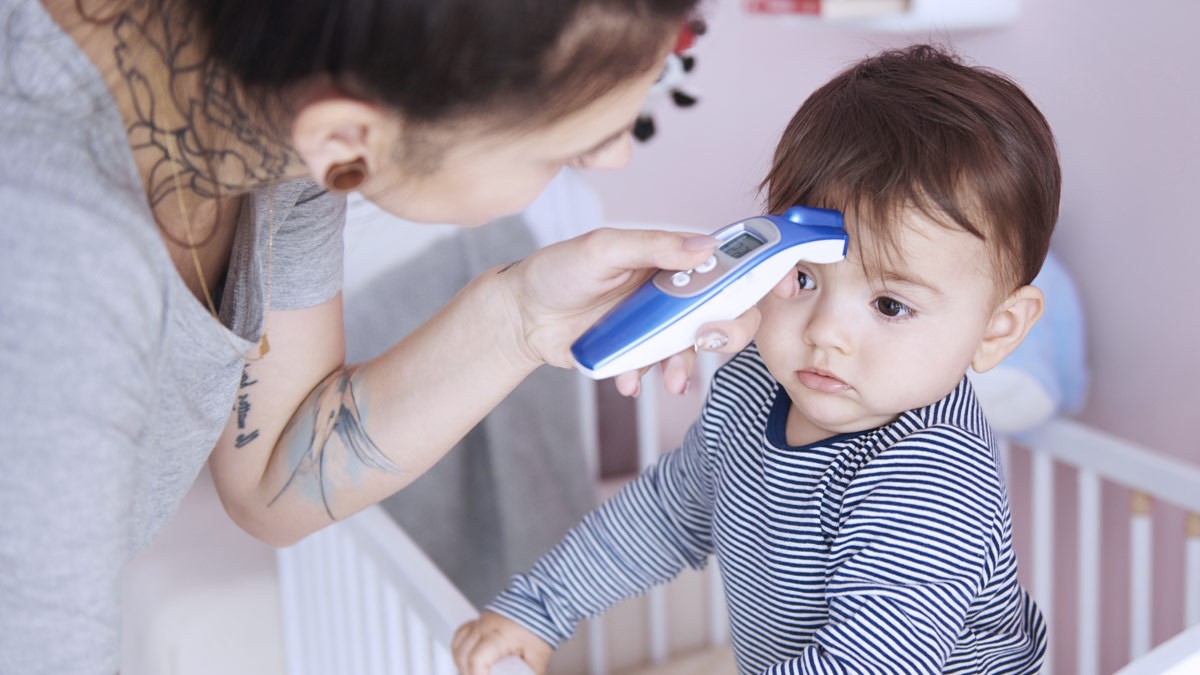
Tympanic thermometers have become increasingly popular in healthcare settings due to their convenience and speed in measuring body temperature. These devices are designed to capture the infrared radiation emitted from the eardrum and convert it into a temperature reading. The appeal of tympanic thermometers lies in their non-invasive nature and ability to provide quick results, making them particularly suitable for young children and individuals with limited mobility.
As the demand for accurate and efficient temperature measurement tools continues to rise, it is crucial to critically evaluate the reliability of tympanic thermometers. This comprehensive analysis aims to delve into the factors influencing the accuracy of these devices, compare them with other types of thermometers, and examine the existing research on their precision. By shedding light on the strengths and limitations of tympanic thermometers, this analysis seeks to provide valuable insights for healthcare professionals and individuals relying on these devices for temperature monitoring.
In the following sections, we will explore the background of tympanic thermometers, elucidate the factors affecting their accuracy, compare them with alternative thermometer types, examine relevant studies and research, and address the limitations and challenges associated with their use. Furthermore, recommendations for enhancing the accuracy of tympanic thermometers will be presented, offering a comprehensive perspective on the practicality and effectiveness of these devices in clinical and home settings.
The accuracy of temperature measurements is paramount in healthcare, as it directly impacts diagnostic decisions and treatment plans. By critically examining the accuracy of tympanic thermometers, we aim to provide a nuanced understanding of their reliability and potential areas for improvement. This analysis seeks to empower healthcare professionals and individuals with the knowledge needed to make informed decisions regarding the selection and utilization of temperature measurement tools, ultimately contributing to enhanced patient care and well-being.
Background of Tympanic Thermometers
Tympanic thermometers, also known as ear thermometers, have revolutionized the process of measuring body temperature. The concept of utilizing the ear canal as a site for temperature assessment stems from the understanding that the eardrum shares blood supply with the hypothalamus, the body's temperature-regulating center. This close physiological relationship allows tympanic thermometers to capture infrared radiation emitted from the eardrum and translate it into a temperature reading, providing a rapid and non-invasive method for determining body temperature.
The development of tympanic thermometers was driven by the need for efficient and comfortable temperature measurement, particularly in pediatric and clinical settings. Traditional methods such as oral, axillary, and rectal thermometers posed challenges in terms of accuracy, discomfort, and time consumption. Tympanic thermometers addressed these limitations by offering a quick and convenient alternative, making them particularly valuable for assessing the temperature of young children, individuals with cognitive impairments, and patients in critical care settings.
The evolution of tympanic thermometers has seen advancements in technology, leading to the introduction of digital infrared models that offer enhanced precision and user-friendly features. These modern devices are equipped with infrared sensors and microprocessors that enable accurate temperature readings within seconds, further solidifying their position as a preferred choice for temperature monitoring in various healthcare environments.
Moreover, the widespread adoption of tympanic thermometers can be attributed to their versatility and ease of use. The ergonomic design of these devices, coupled with their ability to deliver results without causing discomfort or distress, has contributed to their acceptance among healthcare professionals and individuals alike. Additionally, the portability and hygienic nature of tympanic thermometers have made them indispensable tools in home healthcare settings, where regular temperature monitoring is essential for managing acute and chronic conditions.
In summary, the background of tympanic thermometers underscores their evolution from a novel approach to temperature measurement to a mainstream and indispensable tool in healthcare. The amalgamation of physiological understanding, technological innovation, and user-centric design has propelled tympanic thermometers to the forefront of temperature assessment, catering to the diverse needs of healthcare providers and individuals seeking reliable and efficient temperature monitoring solutions.
Factors Affecting the Accuracy of Tympanic Thermometers
The accuracy of tympanic thermometers, crucial for reliable temperature assessment, is influenced by various factors that warrant careful consideration. Understanding these determinants is essential for optimizing the performance and precision of these devices in clinical and home settings.
-
Proper Positioning: Ensuring the correct positioning of the tympanic thermometer within the ear canal is fundamental for accurate readings. Deviations from the recommended positioning can lead to variations in temperature measurements, emphasizing the significance of proper technique in utilizing these thermometers.
-
Earwax Buildup: Accumulation of earwax can impede the infrared radiation detection by tympanic thermometers, potentially resulting in inaccurate temperature readings. Regular cleaning and maintenance of the ear canal are essential to mitigate the impact of earwax buildup on the accuracy of temperature measurements.
-
External Factors: Environmental conditions, such as ambient temperature and humidity, can influence the performance of tympanic thermometers. Exposure to extreme temperatures or moisture may affect the infrared detection process, necessitating controlled environmental conditions for optimal accuracy.
-
Patient Cooperation: Patient cooperation and compliance play a pivotal role in obtaining accurate temperature readings with tympanic thermometers, particularly in pediatric and geriatric populations. Ensuring patient comfort and cooperation during the measurement process is essential for minimizing errors associated with movement or resistance.
-
Device Calibration and Maintenance: Regular calibration and maintenance of tympanic thermometers are imperative for preserving their accuracy. Over time, factors such as sensor degradation and electronic drift can compromise the precision of these devices, highlighting the importance of routine maintenance and calibration protocols.
-
Age and Ear Anatomy: Variations in ear anatomy and the presence of ear infections can impact the accuracy of tympanic thermometers, particularly in pediatric and elderly populations. Understanding the anatomical nuances and potential implications of ear-related conditions is essential for interpreting temperature measurements accurately.
-
User Proficiency: Adequate training and proficiency among healthcare professionals and caregivers in utilizing tympanic thermometers are essential for minimizing errors and optimizing accuracy. Competency in proper technique and interpretation of temperature readings is pivotal for reliable temperature assessment.
By acknowledging and addressing these factors, healthcare providers and individuals can enhance the accuracy and reliability of tympanic thermometers, thereby optimizing temperature monitoring and contributing to informed clinical decisions and interventions.
Comparison of Tympanic Thermometers with Other Types of Thermometers
Tympanic thermometers offer distinct advantages and limitations compared to other types of thermometers commonly used for temperature measurement. Understanding the comparative aspects of these devices is essential for healthcare professionals and individuals seeking the most suitable temperature monitoring tools for diverse clinical and home settings.
Advantages of Tympanic Thermometers
Speed and Convenience
Tympanic thermometers excel in providing rapid temperature readings, typically within seconds, making them ideal for situations where swift assessment is crucial. This attribute is particularly valuable in pediatric care, emergency medicine, and critical care settings, where prompt decision-making is imperative.
Non-Invasive Nature
Unlike rectal thermometers, which can cause discomfort and distress, tympanic thermometers offer a non-invasive method for temperature measurement. This feature is especially beneficial for pediatric and geriatric populations, as well as individuals with sensory sensitivities or cognitive impairments.
User-Friendly Design
Modern tympanic thermometers are designed with user convenience in mind, featuring ergonomic shapes and intuitive operation. This user-friendly design enhances the overall experience for both healthcare professionals and individuals utilizing these devices for temperature monitoring.
Read more: Monthly Temperature Trends Analysis
Limitations of Tympanic Thermometers
Accuracy Variability
Tympanic thermometers may exhibit variability in accuracy due to factors such as ear canal anatomy, earwax buildup, and environmental conditions. This variability necessitates careful attention to proper technique and environmental considerations to ensure consistent and reliable temperature measurements.
Age-Dependent Reliability
The accuracy of tympanic thermometers can be influenced by age-related factors, particularly in pediatric and elderly populations. Understanding the nuances of temperature assessment in different age groups is essential for interpreting tympanic thermometer readings accurately.
Comparison with Oral and Axillary Thermometers
Compared to oral and axillary thermometers, tympanic thermometers offer the advantage of rapid results and reduced discomfort, particularly in pediatric and uncooperative patients. However, they may be more susceptible to accuracy variations influenced by factors such as earwax buildup and ear anatomy.
Comparison with Forehead and Infrared Thermometers
Forehead and infrared thermometers share the non-invasive nature of tympanic thermometers but may exhibit differences in accuracy and ease of use. While forehead thermometers offer convenience, they may pose challenges in obtaining consistent readings, especially in dynamic clinical environments.
Considerations for Selection and Application
When considering the use of tympanic thermometers in comparison to other types of thermometers, factors such as patient population, clinical context, and environmental conditions should be carefully evaluated. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each thermometer type is essential for making informed decisions regarding temperature monitoring in diverse healthcare scenarios.
In summary, the comparison of tympanic thermometers with other types of thermometers underscores the need for a nuanced approach to selecting the most suitable temperature measurement tools based on specific clinical requirements and patient considerations. By recognizing the distinct attributes of each thermometer type, healthcare professionals and individuals can optimize temperature monitoring practices and contribute to enhanced patient care outcomes.
Read more: Central England Weather Trends Analysis
Studies and Research on the Accuracy of Tympanic Thermometers
Numerous studies and research endeavors have been dedicated to evaluating the accuracy and reliability of tympanic thermometers in diverse clinical and home settings. These investigations have sought to elucidate the performance of tympanic thermometers across different patient populations, environmental conditions, and comparative analyses with alternative thermometer types.
One notable area of research focuses on the validation of tympanic thermometers against reference standards, such as rectal thermometry, considered the gold standard for core body temperature measurement. These validation studies have aimed to assess the agreement and consistency between tympanic temperature readings and those obtained from rectal measurements, particularly in pediatric and adult populations. By comparing the accuracy of tympanic thermometers with rectal thermometry, researchers have sought to establish the reliability of tympanic temperature assessment in various clinical scenarios.
Furthermore, research endeavors have delved into the impact of factors such as ear canal anatomy, earwax buildup, and environmental influences on the accuracy of tympanic thermometers. These investigations have aimed to identify the nuances of temperature measurement using tympanic thermometers and the potential sources of variability in their performance. By elucidating the influence of these factors on temperature readings, researchers have contributed to a deeper understanding of the practical considerations and limitations associated with tympanic thermometry.
Moreover, comparative studies have been conducted to evaluate the performance of tympanic thermometers in comparison to other thermometer types, including oral, axillary, forehead, and infrared thermometers. These comparative analyses have provided valuable insights into the strengths and limitations of tympanic thermometers relative to alternative temperature measurement tools. By examining the concordance, variability, and user experience associated with different thermometer types, researchers have contributed to the evidence base guiding the selection and application of temperature monitoring devices in diverse healthcare settings.
In summary, the body of studies and research on the accuracy of tympanic thermometers underscores the multifaceted nature of temperature assessment using these devices. Through validation studies, investigations into influencing factors, and comparative analyses, researchers have contributed to a comprehensive understanding of the reliability and practical considerations associated with tympanic thermometry. These research endeavors have informed clinical practice and decision-making, empowering healthcare professionals and individuals with valuable insights into the accuracy and applicability of tympanic thermometers for temperature monitoring.
Limitations and Challenges in Using Tympanic Thermometers
While tympanic thermometers offer notable advantages in terms of speed, convenience, and non-invasiveness, they are also accompanied by specific limitations and challenges that warrant careful consideration in clinical and home healthcare settings.
One significant limitation of tympanic thermometers pertains to the potential variability in accuracy due to factors such as ear canal anatomy, earwax buildup, and environmental conditions. Variations in the positioning of the thermometer within the ear canal can lead to inconsistent temperature readings, necessitating meticulous attention to proper technique and patient cooperation. Moreover, the presence of earwax can impede the detection of infrared radiation, potentially compromising the precision of temperature measurements. Addressing these limitations requires regular monitoring and maintenance of the ear canal, as well as adherence to standardized protocols for utilizing tympanic thermometers.
Age-related considerations pose another challenge in the use of tympanic thermometers, particularly in pediatric and elderly populations. The anatomical differences in the ear canal among different age groups can impact the accuracy of temperature readings, necessitating tailored approaches to temperature assessment. Additionally, the potential discomfort experienced by elderly individuals or those with ear-related conditions may affect their cooperation during temperature measurement, further emphasizing the need for sensitivity and adaptability when utilizing tympanic thermometers in these populations.
Environmental factors, such as ambient temperature and humidity, present additional challenges in ensuring the accuracy of tympanic thermometers. Exposure to extreme temperatures or moisture can influence the performance of these devices, highlighting the importance of controlled environmental conditions for reliable temperature assessment. Furthermore, the portability of tympanic thermometers may lead to variations in usage across different clinical settings, necessitating standardized protocols and training to mitigate the impact of environmental influences on temperature measurements.
In summary, the limitations and challenges associated with tympanic thermometers underscore the need for comprehensive understanding and proactive measures to optimize their accuracy and reliability. By addressing factors such as ear canal variability, age-related considerations, and environmental influences, healthcare professionals and individuals can navigate these challenges effectively, ensuring consistent and precise temperature monitoring in diverse healthcare scenarios.
Recommendations for Improving the Accuracy of Tympanic Thermometers
-
Standardized Positioning Protocols: Implementing standardized protocols for the positioning of tympanic thermometers within the ear canal is essential for ensuring consistent and accurate temperature measurements. Healthcare providers should receive comprehensive training on proper positioning techniques, emphasizing the alignment of the thermometer with the ear canal to minimize variability in readings.
-
Routine Maintenance and Calibration: Establishing regular maintenance schedules and calibration protocols for tympanic thermometers is crucial for preserving their accuracy. Routine inspection of the devices, including sensor integrity checks and electronic calibration, can mitigate the impact of sensor degradation and electronic drift on temperature measurements.
-
Patient Education and Cooperation: Educating patients and caregivers on the importance of cooperation during temperature measurement can enhance the reliability of tympanic thermometers. Clear communication regarding the significance of remaining still and cooperative during the assessment process is pivotal for minimizing errors associated with patient movement.
-
Ear Canal Hygiene Management: Emphasizing the importance of ear canal hygiene and regular cleaning can mitigate the impact of earwax buildup on the accuracy of tympanic thermometers. Providing guidance on safe and effective ear cleaning practices can contribute to consistent and reliable temperature readings.
-
Environmental Control Measures: Implementing environmental control measures, such as monitoring ambient temperature and humidity levels, can optimize the performance of tympanic thermometers. Creating standardized environmental conditions within clinical settings can minimize the influence of external factors on temperature measurements.
-
Age-Specific Considerations: Tailoring temperature assessment approaches based on age-specific considerations is essential for optimizing the accuracy of tympanic thermometers. Understanding the anatomical nuances and potential challenges associated with temperature measurement in pediatric and elderly populations is pivotal for interpreting temperature readings accurately.
-
Quality Assurance Protocols: Establishing quality assurance protocols, including regular audits and proficiency assessments, can uphold the accuracy of tympanic thermometers. Continuous monitoring of device usage and proficiency among healthcare providers can contribute to consistent and reliable temperature monitoring practices.
By implementing these recommendations, healthcare providers and individuals can enhance the accuracy and reliability of tympanic thermometers, ultimately contributing to informed clinical decisions and improved patient care outcomes.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the accuracy of tympanic thermometers is influenced by a myriad of factors, including proper positioning, earwax buildup, environmental conditions, patient cooperation, device maintenance, age-related considerations, and user proficiency. While these devices offer advantages such as speed, convenience, and non-invasiveness, they also present limitations and challenges that necessitate careful consideration in clinical and home healthcare settings.
The comparison of tympanic thermometers with other types of thermometers highlights the need for a nuanced approach to selecting the most suitable temperature measurement tools based on specific clinical requirements and patient considerations. Understanding the distinct attributes of each thermometer type is essential for optimizing temperature monitoring practices and contributing to enhanced patient care outcomes.
Numerous studies and research endeavors have contributed to a comprehensive understanding of the reliability and practical considerations associated with tympanic thermometry. These investigations have informed clinical practice and decision-making, empowering healthcare professionals and individuals with valuable insights into the accuracy and applicability of tympanic thermometers for temperature monitoring.
Moreover, the limitations and challenges associated with tympanic thermometers underscore the need for comprehensive understanding and proactive measures to optimize their accuracy and reliability. By addressing factors such as ear canal variability, age-related considerations, and environmental influences, healthcare professionals and individuals can navigate these challenges effectively, ensuring consistent and precise temperature monitoring in diverse healthcare scenarios.
The recommendations for improving the accuracy of tympanic thermometers encompass standardized positioning protocols, routine maintenance and calibration, patient education and cooperation, ear canal hygiene management, environmental control measures, age-specific considerations, and quality assurance protocols. Implementing these recommendations can enhance the accuracy and reliability of tympanic thermometers, ultimately contributing to informed clinical decisions and improved patient care outcomes.
In essence, the comprehensive analysis of the accuracy of tympanic thermometers underscores the significance of understanding their strengths, limitations, and practical considerations in temperature monitoring. By integrating knowledge, best practices, and proactive measures, healthcare professionals and individuals can harness the potential of tympanic thermometers as valuable tools for reliable and efficient temperature assessment, ultimately contributing to enhanced patient care and well-being.













