Home>Health & Nutrition>Rectal Temperatures Indicating Hyperthermia


Health & Nutrition
Rectal Temperatures Indicating Hyperthermia
Published: February 19, 2024
Learn about the impact of hyperthermia on health and nutrition through rectal temperature readings. Understand the correlation between body temperature and overall well-being.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia refers to a condition characterized by an elevated body temperature, often exceeding the normal range of 98.6°F (37°C). This increase in body temperature can be attributed to various factors, including environmental conditions, underlying health issues, or medication side effects. It's important to note that hyperthermia is distinct from fever, as fever is a regulated response to an infection or illness, while hyperthermia results from the body's inability to dissipate heat effectively.
The human body maintains a delicate balance of temperature regulation through a process known as thermoregulation. When external factors, such as high temperatures or strenuous physical activity, disrupt this balance, the body may struggle to cool down, leading to hyperthermia. Additionally, certain medical conditions, such as heat stroke, malignant hyperthermia, and drug-induced hyperthermia, can also contribute to this condition.
Understanding the mechanisms behind hyperthermia is crucial for recognizing its symptoms and implementing appropriate interventions. The body's natural cooling mechanisms, including sweating and vasodilation, may become overwhelmed in cases of hyperthermia, leading to a rapid increase in core body temperature. This can result in severe health complications if not promptly addressed.
By comprehending the complexities of hyperthermia, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent its onset, especially during hot weather or when engaging in vigorous physical activities. Moreover, healthcare professionals can utilize this knowledge to accurately diagnose and treat hyperthermia, thereby safeguarding the well-being of affected individuals.
In summary, hyperthermia poses a significant risk to human health, necessitating a comprehensive understanding of its causes, symptoms, and potential complications. Through increased awareness and education, the impact of hyperthermia can be mitigated, ultimately promoting better health outcomes for individuals at risk of this condition.
Importance of Rectal Temperatures in Hyperthermia Diagnosis
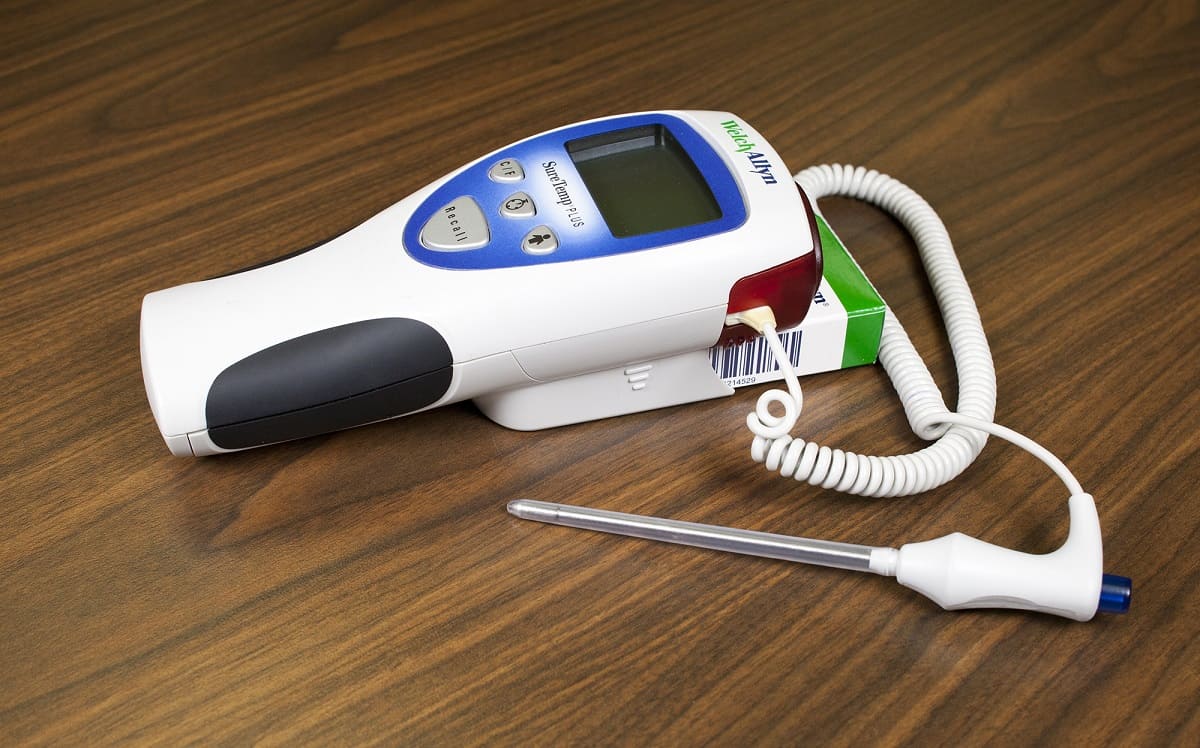
Rectal temperatures play a crucial role in accurately diagnosing hyperthermia, providing healthcare professionals with vital insights into the severity of the condition and guiding appropriate treatment strategies. Unlike oral or axillary temperature measurements, rectal temperatures offer a more reliable indication of core body temperature, making them indispensable in the assessment of hyperthermia.
When an individual experiences hyperthermia, it is essential to obtain an accurate representation of their core body temperature, as this directly influences the urgency and type of intervention required. Rectal temperature measurements are preferred in hyperthermia diagnosis due to their close approximation to the body's internal temperature, offering a more precise assessment of the severity of hyperthermia. This is particularly important in cases where rapid and accurate diagnosis is critical for initiating prompt treatment and preventing potential complications.
Furthermore, rectal temperatures are less susceptible to external factors that can affect the accuracy of oral or axillary measurements. Factors such as oral intake of hot or cold substances, breathing through the mouth, or skin perspiration can influence the reliability of oral and axillary temperature readings. In contrast, rectal temperature measurements remain relatively unaffected by these external variables, providing a more consistent and dependable assessment of the individual's core body temperature.
In clinical settings, healthcare professionals rely on rectal temperatures to gauge the severity of hyperthermia and monitor the effectiveness of cooling interventions. By obtaining precise and reliable core body temperature measurements, medical teams can make informed decisions regarding the appropriate cooling methods, such as cold water immersion or evaporative cooling techniques, tailored to the individual's specific condition.
In summary, the importance of rectal temperatures in hyperthermia diagnosis cannot be overstated. These measurements offer a more accurate reflection of core body temperature, enabling healthcare professionals to swiftly and effectively address hyperthermia and minimize the associated risks. By prioritizing the use of rectal temperatures in hyperthermia diagnosis, medical practitioners can enhance the precision of their assessments and optimize the delivery of targeted interventions, ultimately improving patient outcomes in cases of hyperthermia.
Causes of Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia can arise from various factors, each contributing to the body's inability to regulate its temperature effectively. Understanding the diverse causes of hyperthermia is essential for identifying potential risk factors and implementing preventive measures. The following factors can lead to the onset of hyperthermia:
-
Environmental Conditions: Exposure to high temperatures and humidity, especially in hot climates or confined spaces without adequate ventilation, can overwhelm the body's cooling mechanisms, leading to hyperthermia. Prolonged exposure to extreme heat, such as during heatwaves or in environments with high humidity levels, poses a significant risk of heat-related illnesses, including hyperthermia.
-
Physical Exertion: Engaging in strenuous physical activities, particularly in hot weather, can elevate the body's core temperature, potentially resulting in hyperthermia. Intense exercise or labor-intensive work in high-temperature environments can lead to excessive heat production within the body, surpassing its cooling capacity and triggering hyperthermia.
-
Dehydration: Insufficient fluid intake or excessive fluid loss through sweating, vomiting, or diarrhea can disrupt the body's thermoregulatory mechanisms, impeding its ability to dissipate heat. Dehydration diminishes the body's capacity to maintain a stable internal temperature, increasing the risk of hyperthermia, especially in conjunction with exposure to high temperatures.
-
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as heat stroke, heat exhaustion, and malignant hyperthermia, can precipitate hyperthermia. Individuals with pre-existing health issues, including cardiovascular diseases, respiratory disorders, or neurological conditions, may be more susceptible to developing hyperthermia, particularly when exposed to heat stress or engaging in vigorous physical activities.
-
Medication and Substance Use: Certain medications, such as anticholinergics, stimulants, and some psychiatric drugs, can interfere with the body's thermoregulatory processes, potentially leading to elevated body temperatures. Additionally, substance abuse, including the use of illicit drugs or alcohol, can disrupt the body's heat regulation, increasing the likelihood of hyperthermia.
-
Age and Vulnerable Populations: Infants, young children, older adults, and individuals with compromised immune systems are at a higher risk of developing hyperthermia due to their reduced ability to regulate body temperature effectively. Factors such as age-related physiological changes, chronic medical conditions, or limited mobility can exacerbate the susceptibility of these populations to hyperthermia.
By recognizing the multifaceted causes of hyperthermia, individuals can take proactive measures to mitigate the associated risks. Implementing preventive strategies, such as staying hydrated, avoiding prolonged exposure to extreme heat, and being mindful of medication effects, is crucial for minimizing the incidence of hyperthermia and safeguarding overall well-being.
Symptoms and Complications of Hyperthermia
Hyperthermia manifests through a spectrum of symptoms, ranging from mild discomfort to severe, life-threatening complications. Recognizing these symptoms is paramount for prompt intervention and mitigating the risk of adverse outcomes associated with elevated body temperature.
Symptoms
-
Heat Cramps: These involuntary muscle contractions often occur during physical exertion in hot environments. They are characterized by intense pain and spasms, typically affecting the legs, arms, or abdomen.
-
Heat Exhaustion: Individuals experiencing heat exhaustion may display symptoms such as profuse sweating, weakness, dizziness, nausea, and headache. Skin may feel cool and moist, and the individual may appear pale.
-
Heat Stroke: This represents a critical stage of hyperthermia, marked by a body temperature exceeding 104°F (40°C). Symptoms include hot, dry skin, rapid pulse, confusion, disorientation, and even loss of consciousness. Heat stroke demands immediate medical attention as it can lead to organ damage and death if left untreated.
Complications
-
Dehydration: Prolonged hyperthermia can lead to excessive fluid loss through sweating, potentially resulting in dehydration. This can further exacerbate the body's inability to regulate temperature, leading to a vicious cycle of worsening hyperthermia.
-
Organ Dysfunction: Severe hyperthermia, particularly in the form of heat stroke, can precipitate organ dysfunction, including kidney failure, liver damage, and neurological impairment. The elevated body temperature places immense stress on vital organs, compromising their function and potentially causing long-term health complications.
-
Neurological Impairment: High body temperatures can adversely affect the central nervous system, leading to confusion, seizures, and in severe cases, coma. These neurological manifestations underscore the urgency of addressing hyperthermia to prevent irreversible neurological damage.
-
Cardiovascular Strain: The cardiovascular system is significantly impacted by hyperthermia, with elevated temperatures placing strain on the heart and blood vessels. This can lead to irregular heart rhythms, decreased blood flow to vital organs, and in extreme cases, cardiac arrest.
By understanding the diverse symptoms and potential complications of hyperthermia, individuals can remain vigilant and take proactive measures to prevent its onset. Swift recognition of symptoms and timely intervention are crucial in mitigating the risk of complications and ensuring favorable outcomes for those affected by hyperthermia.
Treatment Options for Hyperthermia
Addressing hyperthermia promptly is essential to prevent its progression and mitigate the associated risks. The following treatment options are employed to effectively manage hyperthermia and restore the body's normal temperature regulation:
1. Active Cooling Measures
Rapid cooling techniques, such as cold water immersion or the application of ice packs to the groin, neck, and armpits, are utilized to lower the body's core temperature swiftly. These methods facilitate heat dissipation and aid in restoring the body's thermoregulatory balance.
2. Hydration and Electrolyte Replacement
Replenishing fluids and electrolytes is crucial in managing hyperthermia, particularly in cases involving dehydration. Intravenous fluids may be administered to restore the body's fluid balance and support vital physiological functions.
3. Monitoring and Supportive Care
Continuous monitoring of vital signs, including body temperature, heart rate, and blood pressure, is essential in assessing the individual's response to treatment. Supportive care, such as oxygen therapy and close observation for any signs of organ dysfunction, is integral in managing severe cases of hyperthermia.
4. Pharmacological Interventions
In certain instances, medications may be employed to facilitate the body's cooling process. Antipyretic drugs, such as acetaminophen, may be administered to help reduce fever and alleviate discomfort associated with hyperthermia.
5. Environmental Modifications
Creating a cooler environment by utilizing fans, air conditioning, or cool compresses can aid in lowering the individual's body temperature. Relocating the individual to a shaded or air-conditioned area is crucial in preventing further heat-related stress.
6. Professional Medical Care
Seeking immediate medical attention is imperative in cases of severe hyperthermia, particularly heat stroke. Healthcare professionals are equipped to provide advanced interventions, including advanced cooling techniques and critical care support, to address life-threatening hyperthermia effectively.
By employing a combination of these treatment options, healthcare providers can effectively manage hyperthermia and minimize the risk of complications. Timely intervention, tailored to the severity of the condition, is pivotal in ensuring favorable outcomes for individuals affected by hyperthermia.
The comprehensive approach to hyperthermia management encompasses not only the reduction of body temperature but also the restoration of fluid and electrolyte balance, as well as the prevention of further heat-related stress. Through the implementation of these treatment strategies, healthcare professionals can safeguard the well-being of individuals experiencing hyperthermia, promoting recovery and preventing adverse outcomes associated with elevated body temperature.