Home>Science & Environment>The Low Temperatures On Gas Giants: Explained

Science & Environment
The Low Temperatures On Gas Giants: Explained
Published: February 19, 2024
Explore the fascinating low temperatures on gas giants and gain a deeper understanding of the science and environment of these massive planets. Discover the explanations behind the extreme cold found on these celestial bodies.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Gas giants, the colossal planets of our solar system, have long captivated the imagination of astronomers and space enthusiasts. These massive celestial bodies, including Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, are known for their awe-inspiring size and unique characteristics. One of the most intriguing aspects of gas giants is their remarkably low temperatures, which stand in stark contrast to the scorching heat experienced on terrestrial planets like Earth. In this article, we will delve into the fascinating realm of gas giants and unravel the mysteries behind their frigid atmospheres. From exploring the composition of their atmospheres to understanding the factors that contribute to their extreme cold, we will embark on a captivating journey to comprehend the enigmatic nature of these distant worlds.
Gas giants, often referred to as "failed stars" due to their composition of primarily hydrogen and helium, possess an otherworldly allure that has piqued the curiosity of scientists and stargazers alike. These immense planets, with their swirling bands of clouds and mesmerizing moons, present a stark departure from the familiar landscapes of rocky planets. As we venture into the depths of space, the enigma of gas giants beckons us to unravel the secrets concealed within their icy shrouds.
In the following sections, we will unravel the complexities of gas giants, shedding light on the atmospheric dynamics that govern their frigid temperatures. By examining the interplay of various factors, including distance from the sun and internal heat sources, we will gain a deeper understanding of the mechanisms that contribute to the bone-chilling cold enveloping these distant worlds. Join us as we embark on an illuminating expedition to demystify the low temperatures that reign supreme on the majestic gas giants of our solar system.
Understanding Gas Giants
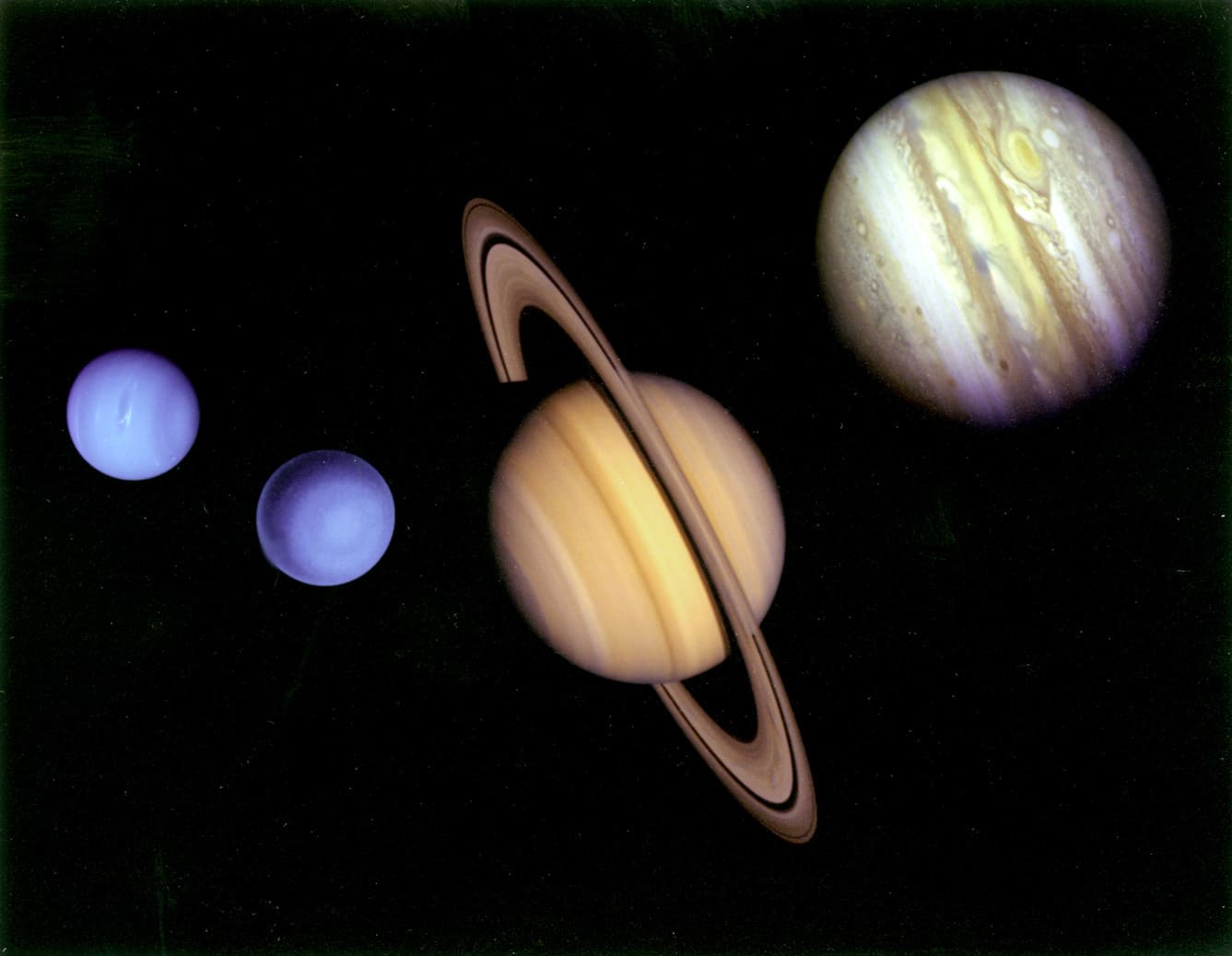
Gas giants, the colossal celestial behemoths that dominate the outer reaches of our solar system, stand as titans among the planets. These massive entities, namely Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune, are characterized by their immense size and gaseous composition, setting them apart from the rocky terrain of terrestrial planets.
At the core of these awe-inspiring giants lies a predominantly hydrogen and helium-rich atmosphere, shrouded in layers of swirling clouds and enigmatic storms. Unlike their terrestrial counterparts, gas giants lack a solid surface, with their gaseous envelopes gradually transitioning into denser regions as depth increases. This unique structure gives rise to their classification as "gas giants," distinguishing them from the rocky planets that populate the inner solar system.
Jupiter, the largest of the gas giants, boasts a mesmerizing array of atmospheric features, including the iconic Great Red Spot—a colossal storm that has raged for centuries. Saturn, renowned for its stunning ring system, presents a spectacle of unparalleled beauty, while Uranus and Neptune, with their icy compositions and distinct bluish hues, exude an ethereal charm that sets them apart from their planetary brethren.
The colossal dimensions of gas giants, coupled with their gravitational influence, have also paved the way for the formation of extensive moon systems. These moons, ranging from the volcanic Io to the ice-encrusted Europa of Jupiter, bear witness to the gravitational prowess of their parent planets, shaping their surfaces and fostering diverse geological landscapes.
Gas giants, with their mesmerizing atmospheric dynamics and captivating moons, stand as celestial marvels that continue to intrigue and inspire astronomers and space enthusiasts. As we delve deeper into the mysteries of these colossal entities, we unravel the intricate tapestry of their atmospheric compositions and the awe-inspiring phenomena that define their enigmatic nature. Join us as we embark on a captivating journey to unravel the mysteries of the gas giants, delving into the depths of their gaseous realms and celestial splendor.
The Atmosphere of Gas Giants
The atmosphere of gas giants is a realm of mesmerizing complexity, characterized by swirling bands of clouds, enigmatic storms, and a rich tapestry of atmospheric dynamics. Composed primarily of hydrogen and helium, these colossal planets boast atmospheres that defy terrestrial conventions, offering a glimpse into the awe-inspiring forces at play in the outer reaches of our solar system.
At the forefront of the gas giants' atmospheric spectacle are the intricate cloud formations that adorn their gaseous envelopes. These planets exhibit a striking array of cloud bands, with Jupiter's mesmerizing bands of alternating light and dark hues standing as a testament to the atmospheric turbulence that shapes these colossal worlds. Saturn, with its ethereal rings and swirling storms, presents a captivating display of atmospheric grandeur, while Uranus and Neptune, with their icy compositions and distinct bluish hues, exude an otherworldly charm that sets them apart from their planetary brethren.
The atmospheric dynamics of gas giants give rise to a diverse array of storms and phenomena that defy terrestrial analogs. Jupiter's Great Red Spot, a colossal storm that has raged for centuries, stands as a testament to the enduring tempests that sweep across these distant worlds. Saturn's hexagonal polar vortex, a mesmerizing geometric feature nestled within its swirling atmosphere, serves as a captivating testament to the enigmatic forces that govern the gas giants' atmospheric dynamics.
Furthermore, the atmospheres of gas giants harbor a rich array of chemical compounds and elements, fostering the formation of complex cloud layers and atmospheric phenomena. The presence of ammonia, methane, and water vapor within these gaseous realms gives rise to the vibrant hues and intricate patterns that adorn the atmospheres of these colossal planets, painting a mesmerizing portrait of celestial beauty that continues to captivate astronomers and space enthusiasts alike.
As we peer into the depths of the gas giants' atmospheres, we are met with a spectacle of unparalleled grandeur and complexity, offering a glimpse into the mesmerizing forces that shape these distant worlds. From the swirling cloud bands to the enigmatic storms that rage across their atmospheres, the gas giants stand as celestial marvels that continue to inspire and intrigue, inviting us to unravel the mysteries concealed within their gaseous realms.
Factors Contributing to Low Temperatures
The bone-chilling temperatures that reign supreme on gas giants are governed by a myriad of factors that collectively shape the frigid nature of these colossal planets. From their immense distance from the sun to the influence of internal heat sources, the interplay of various elements contributes to the perpetually cold environments that define the gas giants.
The Role of Distance from the Sun
One of the primary factors contributing to the low temperatures on gas giants is their substantial distance from the sun. Situated in the outer reaches of the solar system, these colossal planets receive significantly less solar radiation compared to their terrestrial counterparts. The diminished influx of solar energy results in frigid atmospheric conditions, with temperatures plummeting to extremes that defy terrestrial norms. The vast expanse that separates gas giants from the sun shrouds them in perpetual cold, creating an otherworldly environment characterized by icy temperatures and enigmatic atmospheric dynamics.
The Influence of Internal Heat Sources
While the distance from the sun plays a pivotal role in shaping the low temperatures on gas giants, internal heat sources also contribute to the frigid nature of these colossal planets. The gravitational interactions within the gas giants, coupled with the residual heat from their formation, give rise to internal heat sources that permeate their immense atmospheres. This internal heat, generated by the gravitational compression and residual energy from their formation, serves as a counterbalance to the bone-chilling cold enveloping these distant worlds. Despite the presence of internal heat sources, the gas giants remain shrouded in frigidity, with their atmospheres perpetually veiled in icy temperatures that stand as a testament to the awe-inspiring forces at play within these colossal celestial entities.
The interplay of these factors, from the immense distance from the sun to the influence of internal heat sources, collectively shapes the bone-chilling temperatures that reign supreme on the gas giants. As we unravel the complexities of these distant worlds, the enigmatic nature of their frigid atmospheres beckons us to delve deeper into the mesmerizing forces that govern the outer reaches of our solar system.
The Role of Distance from the Sun
The substantial distance of gas giants from the sun stands as a defining factor in shaping the bone-chilling temperatures that prevail on these colossal planets. Situated in the outer realms of the solar system, far beyond the orbits of the terrestrial planets, gas giants such as Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune experience significantly reduced solar radiation compared to their inner solar system counterparts. This diminished influx of solar energy sets the stage for frigid atmospheric conditions that defy terrestrial norms, plunging these distant worlds into an otherworldly realm of perpetual cold.
The vast expanse that separates gas giants from the sun serves as a veil of icy isolation, enveloping these colossal planets in an ethereal shroud of bone-chilling temperatures. The diminished solar radiation, a consequence of their immense distance from the sun, gives rise to atmospheric conditions characterized by extreme cold, fostering an environment that stands as a testament to the enigmatic forces at play in the outer reaches of our solar system.
The impact of this substantial distance from the sun is further underscored by the mesmerizing atmospheric dynamics that unfold within the gaseous realms of these colossal planets. The diminished solar radiation engenders atmospheric processes that diverge from terrestrial conventions, giving rise to a tapestry of swirling cloud bands, enigmatic storms, and atmospheric phenomena that bear witness to the awe-inspiring forces at play within the gas giants' atmospheres.
As we peer into the depths of space, the profound influence of distance from the sun on the gas giants' temperatures beckons us to unravel the mysteries concealed within their icy shrouds. The interplay of celestial forces, from the distant embrace of the sun to the enigmatic atmospheric dynamics, paints a portrait of cosmic grandeur that continues to captivate and inspire, inviting us to delve deeper into the enigmatic nature of these distant worlds.
The Influence of Internal Heat Sources
The bone-chilling temperatures that prevail on gas giants are not solely attributed to their substantial distance from the sun; rather, the interplay of internal heat sources also contributes to the frigid nature of these colossal planets. While the gas giants reside in the outer realms of the solar system, far removed from the radiant embrace of the sun, they harbor internal heat sources that play a pivotal role in shaping their atmospheric dynamics and temperature profiles.
The gravitational interactions within the gas giants, coupled with the residual heat from their formation, give rise to internal heat sources that permeate their immense atmospheres. Despite the absence of a solid surface, the gravitational compression within these colossal planets generates heat, fostering internal temperatures that contribute to the overall thermal equilibrium of these distant worlds. This internal heat, a remnant of the tumultuous processes that accompanied their formation, serves as a counterbalance to the bone-chilling cold enveloping the gas giants, infusing their atmospheres with a delicate interplay of thermal energies.
The influence of internal heat sources manifests in the atmospheric dynamics and thermal gradients that define the gas giants' frigid realms. While the external environment remains shrouded in icy isolation, the presence of internal heat sources engenders atmospheric processes that bear witness to the enigmatic forces at play within these colossal celestial entities. The interplay of thermal energies within the gas giants' atmospheres gives rise to complex convective processes, atmospheric circulation patterns, and thermal gradients that shape the atmospheric dynamics and temperature distributions across these distant worlds.
As we unravel the complexities of the gas giants, the influence of internal heat sources beckons us to delve deeper into the mesmerizing forces that govern the outer reaches of our solar system. The interplay of celestial forces, from the distant embrace of the sun to the enigmatic atmospheric dynamics shaped by internal heat sources, paints a portrait of cosmic grandeur that continues to captivate and inspire, inviting us to peer into the depths of space and unravel the mysteries concealed within the frigid atmospheres of these distant worlds.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the enigmatic gas giants, with their colossal dimensions and frigid atmospheres, stand as celestial marvels that continue to captivate and inspire astronomers and space enthusiasts. The bone-chilling temperatures that reign supreme on these distant worlds are governed by a delicate interplay of celestial forces, from their substantial distance from the sun to the influence of internal heat sources. The mesmerizing atmospheric dynamics, characterized by swirling cloud bands, enigmatic storms, and a rich tapestry of atmospheric phenomena, offer a glimpse into the awe-inspiring forces at play in the outer reaches of our solar system.
The substantial distance of gas giants from the sun sets the stage for frigid atmospheric conditions that defy terrestrial norms, plunging these distant worlds into an otherworldly realm of perpetual cold. The diminished solar radiation, a consequence of their immense distance from the sun, envelops these colossal planets in an ethereal shroud of bone-chilling temperatures, fostering an environment that stands as a testament to the enigmatic forces at play in the outer reaches of our solar system.
Furthermore, the influence of internal heat sources, generated by the gravitational interactions within the gas giants and the residual heat from their formation, contributes to the overall thermal equilibrium of these distant worlds. Despite the presence of internal heat sources, the gas giants remain shrouded in frigidity, with their atmospheres perpetually veiled in icy temperatures that stand as a testament to the awe-inspiring forces at play within these colossal celestial entities.
As we unravel the complexities of the gas giants, the interplay of celestial forces, from the distant embrace of the sun to the enigmatic atmospheric dynamics shaped by internal heat sources, paints a portrait of cosmic grandeur that continues to captivate and inspire. The mysteries concealed within the frigid atmospheres of these distant worlds beckon us to delve deeper into the mesmerizing forces that govern the outer reaches of our solar system, inviting us to peer into the depths of space and unravel the enigmatic nature of these celestial marvels.














