Home>Health & Nutrition>Understanding Fever: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment


Health & Nutrition
Understanding Fever: Causes, Symptoms, And Treatment
Modified: April 28, 2024
Gain a comprehensive understanding of fever, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. Explore valuable insights on health and nutrition.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
Fever is a natural response of the body to various internal and external factors. It is a temporary increase in body temperature, often indicating that the immune system is actively fighting off an infection or illness. Understanding fever, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment, is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Fever is not an illness in itself, but rather a sign that the body is working to combat an underlying issue. It is a common occurrence in both children and adults and can be caused by a wide range of factors, from minor infections to more serious medical conditions.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the science behind fever, explore the common causes of elevated body temperature, discuss how to recognize the symptoms of fever, and provide insights into seeking appropriate treatment. Additionally, we will explore home remedies that can help alleviate fever symptoms and discuss when it is necessary to seek medical attention.
By gaining a deeper understanding of fever and its implications, individuals can make informed decisions about managing their health and well-being. Whether it's knowing when to rest and allow the body to heal naturally or seeking medical intervention when necessary, being well-informed about fever is essential for maintaining optimal health.
Throughout this article, we will provide valuable insights and practical tips to empower readers to navigate the experience of fever with confidence and knowledge. Let's embark on this journey to unravel the mysteries of fever and equip ourselves with the tools to address it effectively.
The Science Behind Fever
Fever, also known as pyrexia, is a complex physiological response orchestrated by the body's internal mechanisms. It is a fundamental component of the immune system's defense against infections and other pathological conditions. The regulation of body temperature is primarily governed by the hypothalamus, a vital region of the brain responsible for maintaining homeostasis.
When the body detects the presence of pathogens or other foreign invaders, such as bacteria or viruses, it triggers a series of events to combat these threats. One of the key responses is the release of pyrogens, which are substances that stimulate the hypothalamus to elevate the body's temperature set point. This results in a cascade of physiological changes aimed at creating an environment unfavorable for the survival and replication of the invading pathogens.
The elevation in body temperature serves several crucial purposes in the body's defense against infections. Firstly, it enhances the activity of immune cells, such as white blood cells, and promotes the production of certain proteins that aid in combating the underlying cause of the fever. Additionally, the higher temperature can directly inhibit the growth and spread of certain microorganisms, contributing to the body's efforts to overcome the infection.
Furthermore, fever can also modulate the body's metabolic processes, increasing the rate of chemical reactions involved in immune responses. This heightened metabolic activity can enhance the efficiency of various immune functions, including the recognition and elimination of pathogens.
It's important to note that fever is a carefully orchestrated response and is generally well-tolerated by the body. However, in some cases, particularly in individuals with certain pre-existing medical conditions or compromised immune systems, fever can pose risks and may require closer monitoring and medical intervention.
Understanding the intricate science behind fever underscores its significance as a protective mechanism rather than a mere symptom of illness. By recognizing the sophisticated biological processes at play, individuals can appreciate the body's remarkable ability to mobilize its defenses in the face of health challenges. This knowledge also underscores the importance of supporting the body's natural response to fever while remaining vigilant for any signs that may warrant medical attention.
Common Causes of Fever
Fever can arise from a multitude of underlying causes, ranging from common infections to more serious medical conditions. Understanding the diverse triggers of fever is essential for identifying the underlying issue and determining the appropriate course of action. Here are some common causes of fever:
-
Infections: One of the most prevalent causes of fever is infections, which can be bacterial, viral, fungal, or parasitic in nature. Respiratory infections, such as the common cold, influenza, and pneumonia, often manifest with fever as the body combats the invading pathogens. Similarly, urinary tract infections, skin infections, and gastrointestinal infections can also provoke fever as part of the body's immune response.
-
Inflammatory Conditions: Various inflammatory disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and systemic lupus erythematosus, can trigger fever as a result of the body's heightened immune activity. In these conditions, the immune system may mistakenly target healthy tissues, leading to chronic inflammation and associated fever.
-
Heat-Related Illnesses: Exposure to extreme environmental temperatures or prolonged physical exertion in hot conditions can lead to heat-related illnesses, including heat exhaustion and heat stroke. These conditions can cause the body's temperature to rise significantly, resulting in fever as a protective response to the heat stress.
-
Medication Reactions: Certain medications, particularly antibiotics, can induce fever as an adverse reaction. This is commonly observed in drug-induced hypersensitivity reactions, where the body's immune system reacts to specific medications, leading to fever and other symptoms.
-
Vaccinations: Following immunizations, some individuals may experience low-grade fever as a normal response to the vaccine components. This transient fever is typically mild and self-limiting, serving as an indication that the body is mounting an immune response to the vaccine.
-
Cancer: In some cases, fever can be a sign of an underlying malignancy, such as leukemia or lymphoma. The fever associated with cancer, known as paraneoplastic fever, is often attributed to the body's response to the presence of cancer cells or the release of certain inflammatory substances by the tumor.
-
Autoimmune Disorders: Autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, and vasculitis, can lead to recurrent or persistent fever due to the immune system's aberrant activation against the body's own tissues.
-
Other Causes: Additionally, fever can be provoked by a range of other factors, such as trauma, blood clots, and certain endocrine disorders.
By recognizing the diverse array of potential triggers for fever, individuals can better comprehend the underlying mechanisms at play when fever arises. This understanding is pivotal in guiding appropriate measures for addressing the root cause of fever and promoting effective recovery.
Recognizing Symptoms of Fever
Recognizing the symptoms of fever is crucial for prompt intervention and effective management of the underlying cause. While the most obvious sign of fever is an elevated body temperature, there are several other accompanying symptoms that can provide valuable insights into the nature and severity of the fever. Here are the key symptoms to watch for when identifying fever:
-
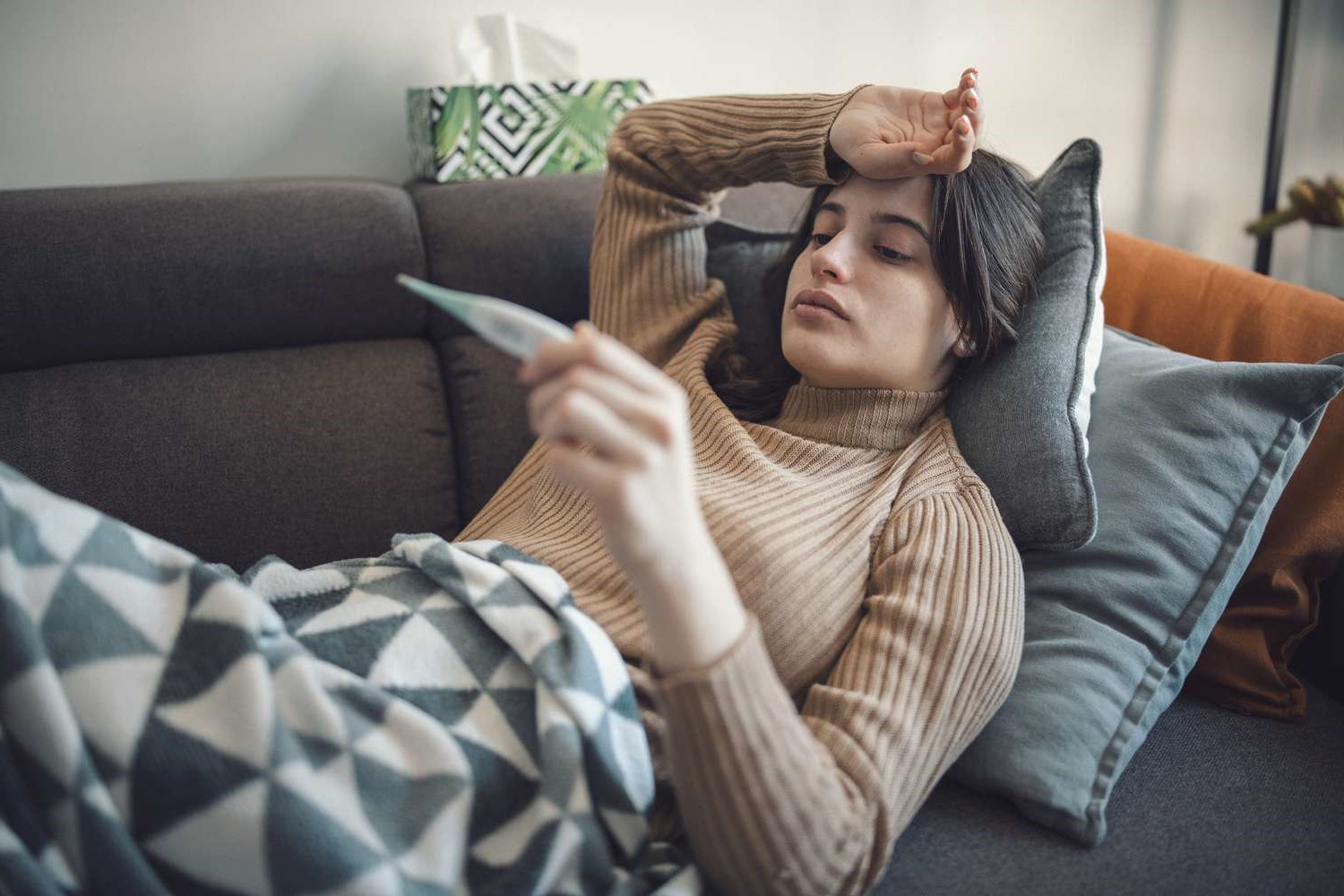
Elevated Body Temperature: The hallmark symptom of fever is an increase in body temperature above the normal range, which is typically around 98.6°F (37°C) when measured orally. In adults, a fever is generally considered present when the body temperature exceeds 100.4°F (38°C). However, it's important to note that the definition of fever can vary based on individual baseline temperatures and the method of measurement.
-
Chills and Shivering: Many individuals experience chills and shivering as the body attempts to generate and conserve heat in response to the elevated temperature. These involuntary muscle contractions are the body's way of raising its internal temperature to match the new set point established by the hypothalamus.
-
Sweating: As the fever breaks or fluctuates, profuse sweating may occur as the body works to cool down. This can lead to clammy skin and a feeling of dampness, signaling a shift in the body's temperature regulation.
-
Generalized Weakness and Fatigue: Fever often accompanies a sense of overall weakness and fatigue, which can significantly impact daily activities and productivity. The body's heightened metabolic activity during fever can contribute to feelings of exhaustion and lethargy.
-
Headache and Body Aches: Many individuals experience headaches and muscle aches during fever episodes. These symptoms can be attributed to the body's inflammatory response and the release of certain chemicals that sensitize pain receptors.
-
Loss of Appetite: Fever can lead to a diminished appetite and a general lack of interest in food and fluids. This can contribute to dehydration and a decrease in essential nutrient intake, necessitating careful attention to hydration and nutrition during fever episodes.
-
Irritability and Restlessness: Fever can affect mood and behavior, leading to irritability, restlessness, and difficulty in sleeping. These psychological manifestations are often a result of the body's physiological response to the underlying cause of the fever.
-
Specific Symptoms Based on Underlying Cause: In addition to these general symptoms, the specific underlying cause of the fever may present with additional symptoms. For instance, respiratory infections may manifest with cough, sore throat, and nasal congestion, while urinary tract infections can lead to urinary symptoms and abdominal discomfort.
By being attentive to these symptoms, individuals can promptly recognize the presence of fever and take appropriate measures to address the underlying cause. Additionally, monitoring these symptoms can provide valuable information to healthcare providers when seeking medical attention for fever-related concerns.
Seeking Treatment for Fever
When it comes to seeking treatment for fever, the approach largely depends on the underlying cause, the severity of symptoms, and the individual's overall health status. While fever itself is not a disease, it often signifies an underlying health issue that requires attention. Here are the key considerations for seeking treatment for fever:
Read more: Understanding Fever: Causes And Symptoms
Hydration and Rest
In many cases, especially when fever is mild and attributed to common viral infections, adequate rest and hydration are fundamental components of the treatment. Ensuring sufficient fluid intake, such as water, herbal teas, and electrolyte solutions, helps prevent dehydration, which can exacerbate fever-related symptoms. Additionally, ample rest allows the body to allocate energy towards combating the underlying cause of the fever.
Over-the-Counter Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) medications, such as acetaminophen (paracetamol) and ibuprofen, can be used to alleviate fever and associated discomfort. These medications work by reducing the body's temperature set point and mitigating symptoms like headaches and muscle aches. However, it's essential to use these medications as directed and adhere to recommended dosages, especially when considering their use in children or individuals with pre-existing medical conditions.
Addressing Underlying Infections
When fever is attributed to bacterial infections, such as strep throat or urinary tract infections, healthcare providers may prescribe antibiotics to target the specific causative pathogens. It's crucial to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed to ensure the eradication of the infection and prevent potential complications.
Medical Evaluation
If fever persists for an extended period, is accompanied by severe symptoms, or is recurrent without a clear cause, seeking medical evaluation is imperative. Healthcare providers can conduct a thorough assessment to identify the underlying issue, which may involve physical examinations, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. This comprehensive evaluation is essential for diagnosing and addressing potential underlying conditions contributing to the fever.
Monitoring High-Risk Individuals
Certain individuals, such as young children, older adults, and those with compromised immune systems or chronic medical conditions, may require closer monitoring and prompt medical attention when experiencing fever. These populations are more susceptible to complications from fever and its underlying causes, necessitating vigilant observation and timely intervention.
Addressing Underlying Conditions
In cases where fever is a symptom of chronic medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders or malignancies, treatment focuses on managing the underlying condition in addition to addressing fever-related symptoms. This may involve disease-specific medications, immune-modulating therapies, or other targeted interventions to address the root cause of the fever.
By understanding the diverse approaches to treating fever, individuals can make informed decisions about managing their symptoms and seeking appropriate medical care when necessary. It's important to recognize that while fever is a common occurrence, it can serve as a valuable indicator of underlying health issues that warrant attention and intervention.
Home Remedies for Fever
When dealing with fever, incorporating simple yet effective home remedies can complement medical interventions and promote comfort during the recovery process. These remedies aim to alleviate symptoms, support the body's natural healing mechanisms, and enhance overall well-being. Here are several home remedies that can be beneficial for managing fever:
Adequate Hydration
Maintaining optimal hydration is crucial during fever episodes. Consuming ample fluids, including water, herbal teas, clear broths, and electrolyte-rich beverages, helps prevent dehydration and supports the body's efforts to regulate temperature. Additionally, staying hydrated can ease symptoms such as dry mouth and fatigue commonly associated with fever.
Read more: Understanding The Symptoms Of Fever
Cool Compresses
Applying cool compresses to the forehead, neck, and armpits can help lower body temperature and provide relief from discomfort. Dampening a washcloth with cool water and gently placing it on the forehead or other pulse points can promote a soothing sensation and aid in reducing fever-associated heat.
Rest and Comfort
Allowing the body ample rest is essential for expediting the recovery process. Creating a comfortable and conducive environment for rest, such as maintaining a cool room temperature and using lightweight bedding, can help ease discomfort and promote relaxation. Adequate rest supports the body's immune response and aids in combating the underlying cause of the fever.
Herbal Remedies
Certain herbal remedies, such as chamomile, peppermint, and ginger teas, are known for their soothing properties and can contribute to overall comfort during fever. These herbal infusions can help alleviate symptoms like nausea, headaches, and muscle aches, while also providing hydration and essential nutrients.
Lukewarm Baths
Taking lukewarm baths or showers can assist in reducing body temperature and promoting a sense of well-being. Avoid using cold water, as it can lead to shivering and potentially elevate body temperature. Instead, opting for lukewarm water can help cool the body gradually and provide relief from fever-related discomfort.
Nutritious, Easily Digestible Foods
Consuming light, nutrient-dense meals that are easy to digest can support the body's energy levels and overall well-being during fever. Incorporating foods such as soups, broths, fruits, and vegetables provides essential nutrients and hydration while minimizing digestive strain.
Comforting Environment
Creating a calm and soothing environment can contribute to overall comfort and well-being during fever. Dimming lights, playing gentle music, and engaging in relaxation techniques can help alleviate stress and promote a sense of tranquility, which is beneficial for supporting the body's natural healing processes.
By integrating these home remedies into the management of fever, individuals can enhance their comfort, support the body's natural healing mechanisms, and complement medical interventions when necessary. It's important to note that while these remedies can provide relief from symptoms, seeking medical attention is essential for persistent or severe fever, especially in high-risk individuals.
When to Seek Medical Attention for Fever
While many fever episodes can be managed effectively at home, there are certain circumstances that warrant prompt medical attention. Recognizing when to seek medical care for fever is crucial for addressing underlying health concerns and mitigating potential complications. Here are key indicators that necessitate seeking medical attention for fever:
Persistent High Fever
If a fever persists for an extended period, especially if it remains consistently high or shows no signs of improvement despite home remedies and over-the-counter medications, it is essential to consult a healthcare provider. Persistent high fever can indicate a more serious underlying infection or medical condition that requires thorough evaluation and targeted treatment.
Severe Symptoms
The presence of severe symptoms alongside fever, such as difficulty breathing, chest pain, severe headache, confusion, persistent vomiting, or uncontrolled diarrhea, warrants immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate complications that require urgent assessment and intervention to prevent further health risks.
High-Risk Populations
Certain individuals, including young children, older adults, pregnant women, and those with pre-existing medical conditions or compromised immune systems, are at higher risk of experiencing complications from fever. For these populations, even mild fever may necessitate closer monitoring and prompt medical evaluation to ensure timely intervention and prevent potential health risks.
Recurrent Fever without Clear Cause
When fever recurs intermittently without a clear underlying cause, it may indicate an unresolved infection, inflammatory condition, or other health issue that requires medical assessment. Recurrent fever can be a sign of an underlying chronic condition that necessitates thorough evaluation to determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Suspected Infections or Exposures
If there is a known exposure to infectious diseases or a suspicion of specific infections, seeking medical attention for fever is crucial. This is particularly important when there is a potential exposure to contagious illnesses or when fever is accompanied by symptoms specific to certain infections, such as rash, sore throat, or urinary symptoms.
Read more: Causes And Remedies For Nighttime Fever
Worsening Symptoms
If fever is accompanied by worsening symptoms, such as increasing pain, persistent weakness, or the development of new concerning signs, it is advisable to seek medical evaluation. Worsening symptoms may indicate a progression of the underlying condition, necessitating timely medical intervention to prevent complications.
By recognizing these indicators and promptly seeking medical attention when necessary, individuals can ensure comprehensive evaluation and appropriate management of fever-related concerns. Timely medical intervention is essential for addressing underlying health issues, preventing potential complications, and promoting optimal recovery.
Conclusion
In conclusion, fever is a remarkable manifestation of the body's intricate defense mechanisms, serving as a vital indicator of underlying health challenges. Understanding the science behind fever, including its physiological basis and diverse causes, empowers individuals to navigate fever episodes with knowledge and confidence. From common infections to inflammatory conditions and heat-related illnesses, fever can arise from a myriad of triggers, necessitating a comprehensive approach to its management.
Recognizing the symptoms of fever, such as elevated body temperature, chills, and fatigue, enables individuals to promptly address the underlying cause and seek appropriate treatment. Whether it involves rest, hydration, over-the-counter medications, or medical evaluation, the management of fever is tailored to the specific context of the individual's health status and the nature of the underlying condition.
Moreover, the integration of home remedies, such as adequate hydration, cool compresses, and nutritious foods, complements medical interventions and promotes comfort during the recovery process. These simple yet effective measures contribute to overall well-being and support the body's natural healing mechanisms.
It is crucial to recognize the circumstances that warrant medical attention for fever, especially in high-risk populations and when accompanied by severe or persistent symptoms. Timely medical evaluation is essential for addressing underlying health concerns, mitigating potential complications, and ensuring optimal recovery.
By embracing a holistic understanding of fever and its implications, individuals can make informed decisions about managing their health and seeking appropriate care when necessary. Fever, far from being a mere symptom, serves as a sentinel of the body's resilience and its ongoing battle against internal and external threats. With this knowledge, individuals are better equipped to navigate fever episodes with vigilance, resilience, and a proactive approach to well-being.