Home>Health & Nutrition>Understanding And Managing High Fevers In Children

Health & Nutrition
Understanding And Managing High Fevers In Children
Published: February 19, 2024
Learn how to understand and manage high fevers in children with expert health and nutrition advice. Keep your child healthy and safe.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
- The Importance of Monitoring High Fevers in Children
- Common Causes of High Fevers in Children
- Recognizing the Symptoms of High Fevers in Children
- When to Seek Medical Attention for a High Fever in Children
- Home Remedies for Managing High Fevers in Children
- Medications and Treatments for High Fevers in Children
- Preventing High Fevers in Children
The Importance of Monitoring High Fevers in Children
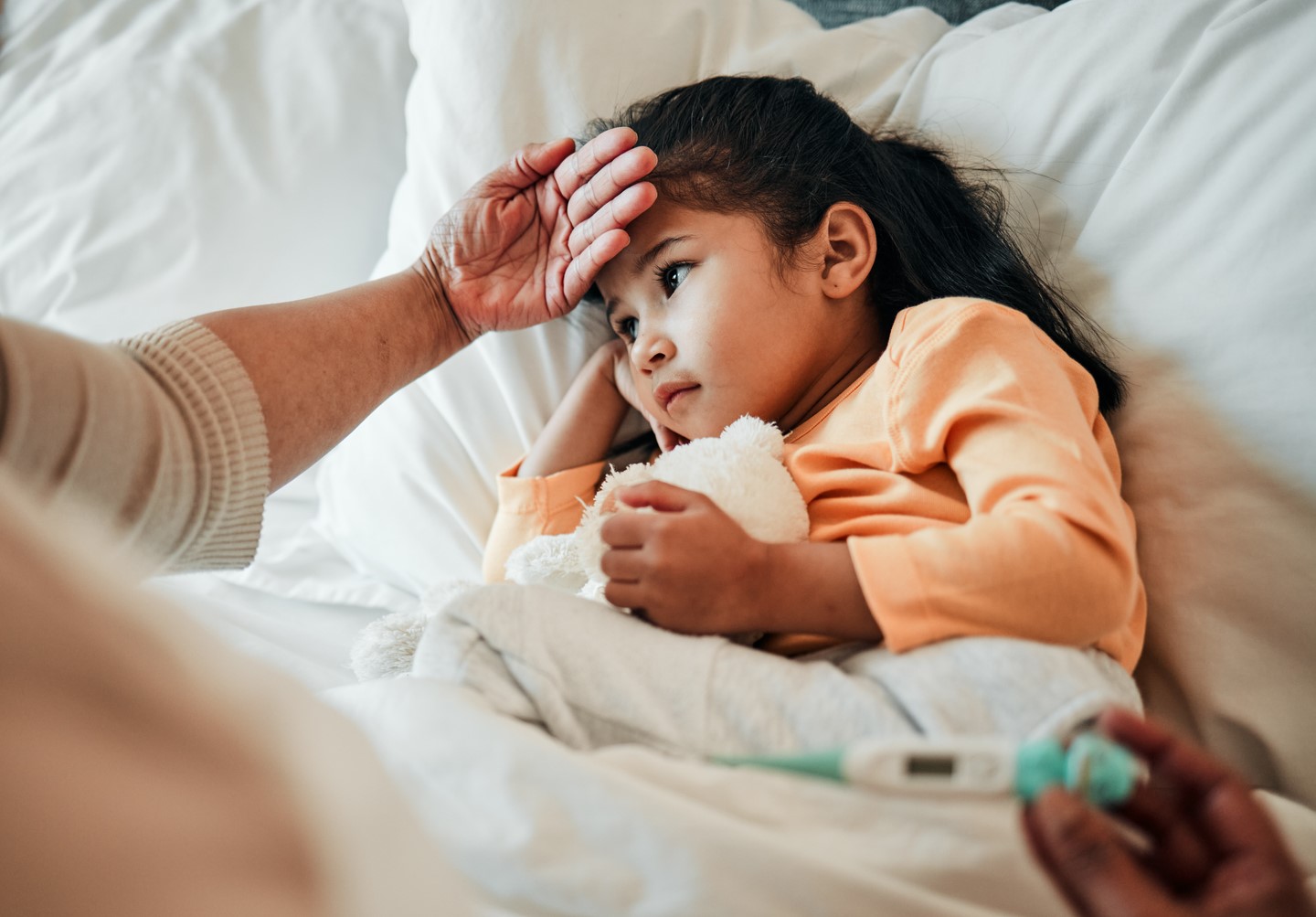
High fevers in children can be a cause of great concern for parents and caregivers. It is essential to understand the significance of monitoring high fevers in children to ensure their well-being. A fever is the body's natural response to an infection or illness, and in most cases, it is not a cause for immediate alarm. However, monitoring a child's fever is crucial for several reasons.
First and foremost, monitoring a high fever in a child allows caregivers to assess the severity of the illness. A persistently high fever may indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires medical attention. By closely monitoring the fever, caregivers can track its duration and intensity, providing valuable information to healthcare professionals.
Furthermore, monitoring a child's fever enables caregivers to observe any accompanying symptoms. High fevers are often accompanied by symptoms such as lethargy, irritability, loss of appetite, and dehydration. These symptoms can provide important clues about the child's overall condition and help determine the appropriate course of action.
In addition, monitoring a high fever in children is essential for evaluating the effectiveness of treatment. Whether using home remedies or prescribed medications, caregivers can gauge the impact of the treatment by tracking the fever's response. This information is valuable for adjusting the treatment plan and seeking medical advice if necessary.
Moreover, monitoring a child's fever is crucial for providing comfort and reassurance. Fever can be distressing for children, causing discomfort and anxiety. By closely monitoring the fever and providing appropriate care, caregivers can offer comfort and support to the child, promoting a sense of security during the illness.
Overall, the importance of monitoring high fevers in children cannot be overstated. It serves as a vital tool for assessing the severity of the illness, observing accompanying symptoms, evaluating treatment effectiveness, and providing comfort to the child. Caregivers play a pivotal role in monitoring and managing high fevers in children, ensuring their well-being and speedy recovery.
Read more: Understanding And Managing Fever In Toddlers
Common Causes of High Fevers in Children
High fevers in children can be attributed to a variety of underlying causes, ranging from common viral infections to more serious medical conditions. Understanding the common causes of high fevers in children is essential for caregivers to identify the root of the fever and take appropriate measures to address it. Here are some prevalent causes of high fevers in children:
-
Viral Infections: Viral infections are one of the most common causes of high fevers in children. Illnesses such as the flu, common cold, and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) can lead to elevated body temperatures as the body's immune system responds to the viral invasion. These infections often present with additional symptoms such as coughing, congestion, and sore throat.
-
Bacterial Infections: Bacterial infections, such as strep throat, urinary tract infections, and pneumonia, can trigger high fevers in children. These infections require prompt medical attention and treatment with antibiotics to address the underlying bacterial cause of the fever.
-
Ear Infections: Ear infections, particularly in younger children, are a frequent cause of high fevers. Inflammation and fluid buildup in the middle ear can result in elevated body temperatures, accompanied by symptoms such as ear pain, irritability, and difficulty sleeping.
-
Gastrointestinal Infections: Gastrointestinal infections, often caused by viruses or bacteria, can lead to high fevers in children. Conditions such as gastroenteritis, commonly known as the stomach flu, can result in fever, vomiting, diarrhea, and dehydration.
-
Teething: The process of teething in infants and toddlers can sometimes cause low-grade fevers. As new teeth emerge, the body's inflammatory response can lead to a slight increase in body temperature. While teething-related fevers are generally low-grade, they can cause discomfort for the child.
-
Immunizations: Following certain vaccinations, children may experience a mild fever as a normal immune response to the vaccine. This is a common and expected reaction and typically resolves within a day or two.
-
Environmental Factors: Exposure to extreme heat, such as during hot summer days or in hot, poorly ventilated environments, can lead to heat-related illnesses and high fevers in children. It is crucial to ensure proper hydration and a cool environment to prevent heat-induced fevers.
Understanding these common causes of high fevers in children empowers caregivers to recognize the underlying factors contributing to the fever. By identifying the cause, caregivers can take appropriate steps to manage the fever and seek medical attention when necessary, ensuring the child's well-being and swift recovery.
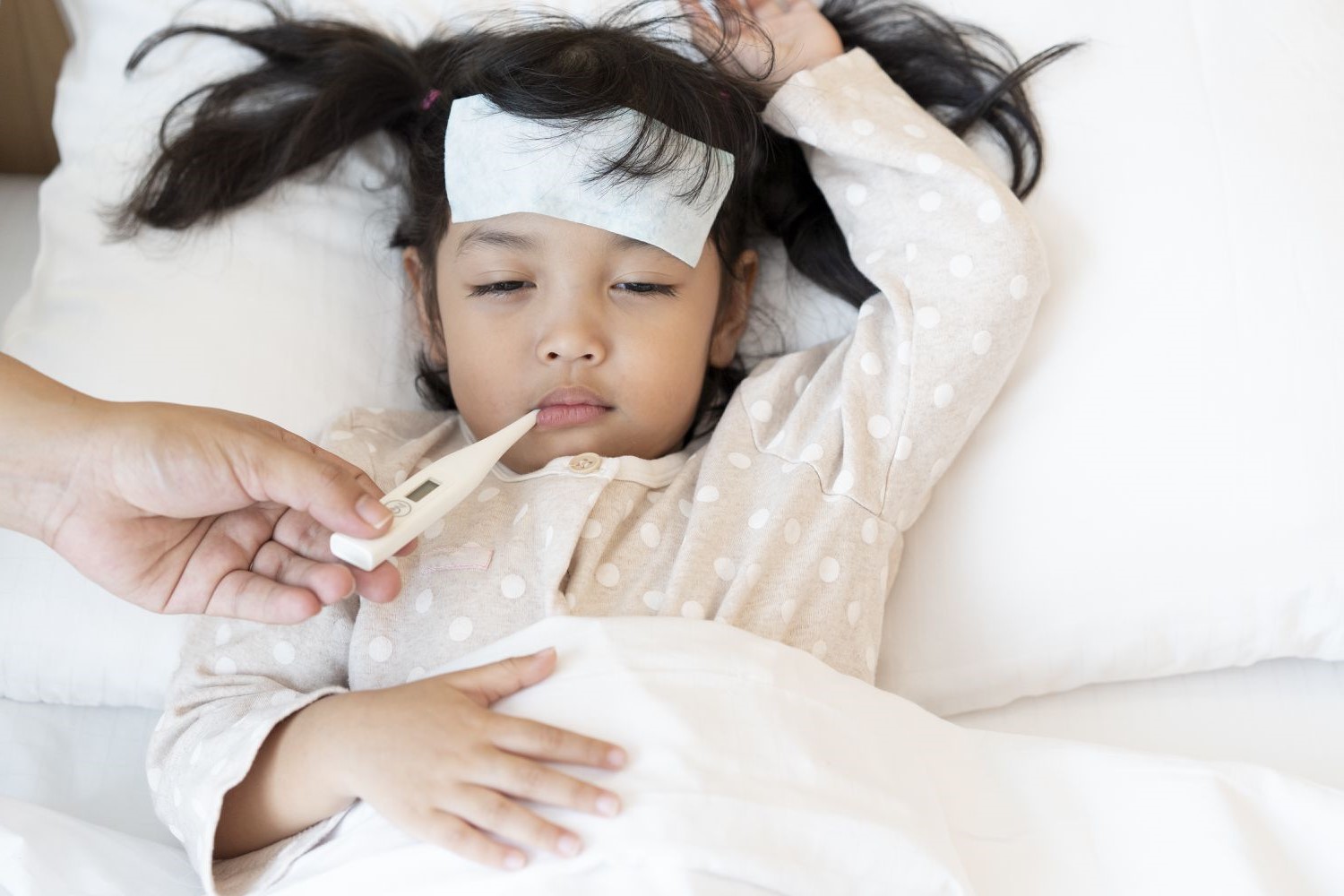
Recognizing the Symptoms of High Fevers in Children
Recognizing the symptoms of high fevers in children is crucial for caregivers to promptly address the child's condition and provide appropriate care. While the presence of a fever itself indicates an elevated body temperature, it is essential to be vigilant for accompanying symptoms that may signal the severity of the illness. Understanding these symptoms enables caregivers to take timely action and seek medical attention when necessary.
Common symptoms accompanying high fevers in children include:
-
Lethargy and Irritability: Children with high fevers often exhibit increased lethargy and irritability. They may appear unusually tired, have difficulty staying awake, or display heightened fussiness and discomfort. Lethargy and irritability can be indicators of the body's response to the fever and underlying illness.
-
Loss of Appetite: A notable decrease in appetite is a common symptom observed in children with high fevers. The fever's impact on the body's metabolism and the child's overall well-being can lead to reduced interest in eating and drinking. It is essential to encourage fluid intake to prevent dehydration, especially when a child is experiencing a fever.
-
Dehydration: High fevers can contribute to increased fluid loss through sweating and evaporation. Dehydration may manifest as dry lips and mouth, decreased urine output, and sunken eyes. Caregivers should monitor the child's hydration status closely and ensure adequate fluid intake to prevent dehydration.
-
Respiratory Symptoms: In some cases, high fevers in children are accompanied by respiratory symptoms such as coughing, congestion, and difficulty breathing. These symptoms may indicate an underlying respiratory infection or illness that requires attention from healthcare professionals.
-
Rash or Skin Changes: Certain infections that cause high fevers in children can also lead to skin manifestations such as rashes or changes in skin color. Caregivers should carefully observe the child's skin for any unusual rashes, spots, or discoloration, as these may provide valuable clues about the underlying condition.
-
Seizures: In rare cases, high fevers in children can trigger febrile seizures. These seizures are typically brief and may involve involuntary movements, loss of consciousness, or unusual eye movements. It is crucial for caregivers to seek immediate medical assistance if a child experiences a febrile seizure.
Recognizing these symptoms of high fevers in children empowers caregivers to respond effectively to the child's condition. By closely monitoring the child for these accompanying symptoms, caregivers can make informed decisions about managing the fever and seeking medical evaluation when necessary. Additionally, understanding these symptoms fosters a proactive approach to providing comfort and support to the child during the illness, promoting their well-being and recovery.
When to Seek Medical Attention for a High Fever in Children
It is essential for caregivers to be vigilant and proactive in recognizing when to seek medical attention for a high fever in children. While fevers are often a natural response to infections and illnesses, certain circumstances warrant prompt evaluation by healthcare professionals to ensure the child's well-being.
Signs that indicate the need for medical attention include:
-
Persistent High Fever: If a child's fever persists and remains consistently high, especially above 102°F (38.9°C), despite the use of fever-reducing medications, it is advisable to seek medical advice. A persistent high fever may indicate a more serious underlying condition that requires evaluation and treatment.
-
Accompanying Symptoms: When a high fever is accompanied by concerning symptoms such as severe headache, stiff neck, persistent vomiting, difficulty breathing, or a rash that does not fade under pressure, it is crucial to seek immediate medical attention. These symptoms may indicate a more severe illness or infection that requires medical assessment.
-
Age and Medical History: For infants under three months of age, any fever should prompt a call to a healthcare provider, as young infants are more susceptible to serious infections. Additionally, children with pre-existing medical conditions or compromised immune systems may require medical evaluation for even low-grade fevers to prevent potential complications.
-
Duration of Fever: If a child's fever persists for more than a few days without showing signs of improvement, medical evaluation is recommended. Prolonged fevers may be indicative of an underlying infection or illness that requires medical intervention.
-
Parental Concern: Caregivers' intuition and concern for the child's well-being should not be overlooked. If caregivers are worried about the child's condition, seeking medical advice and evaluation is warranted to address any potential health issues and provide reassurance.
Seeking timely medical attention when necessary is crucial for ensuring the appropriate management of high fevers in children. Healthcare professionals can conduct a thorough assessment, perform necessary tests, and provide targeted treatment to address the underlying cause of the fever. Prompt medical intervention can help prevent potential complications and promote the child's swift recovery.
By recognizing the signs that indicate the need for medical attention and taking proactive measures to seek appropriate care, caregivers play a pivotal role in safeguarding the health and well-being of children experiencing high fevers.
Home Remedies for Managing High Fevers in Children
When a child develops a high fever, caregivers often seek ways to alleviate the discomfort and promote recovery through home remedies. While it is important to consult a healthcare professional for proper medical guidance, several home remedies can help manage high fevers in children and provide supportive care during the illness.
1. Hydration
Encouraging adequate fluid intake is crucial for managing high fevers in children. Fever can lead to increased fluid loss through sweating, making it essential to prevent dehydration. Offering water, clear broths, electrolyte solutions, and diluted fruit juices can help maintain hydration levels and support the body's immune response.
2. Rest and Comfort
Ensuring that the child gets plenty of rest is vital for recovery. Creating a comfortable and soothing environment can help alleviate the child's discomfort. Using a cool mist humidifier in the room can ease breathing and soothe respiratory symptoms, while providing soft blankets and comfortable bedding can promote restful sleep.
Read more: Ideal Fever Temperature For Children
3. Lukewarm Sponge Bath
A lukewarm sponge bath can help reduce a child's body temperature and provide relief from the discomfort of a high fever. Carefully sponge the child's body with lukewarm water, particularly focusing on the forehead, armpits, and groin area. Avoid using cold water, as it can cause shivering and potentially raise the body's core temperature.
4. Light Clothing
Dressing the child in lightweight and breathable clothing can help regulate body temperature and prevent overheating. Opt for loose-fitting garments made from natural fabrics such as cotton, which allow for better air circulation and comfort.
5. Fever-Reducing Medications
When recommended by a healthcare professional, over-the-counter fever-reducing medications such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen can be used to help lower the child's fever and alleviate discomfort. It is crucial to follow the dosage instructions provided by the healthcare provider and avoid giving aspirin to children, as it can lead to a rare but serious condition called Reye's syndrome.
6. Nutritious and Easily Digestible Foods
Offering nutritious and easily digestible foods can support the child's overall well-being during a fever. Foods such as soups, broths, yogurt, and fruits can provide essential nutrients and hydration while being gentle on the digestive system.
7. Monitoring and Comforting
Continuously monitoring the child's fever and providing comfort and reassurance are essential aspects of home care. Regularly checking the child's temperature, observing for any changes in symptoms, and offering comforting words and gestures can help ease the child's distress and promote a sense of security during the illness.
By incorporating these home remedies into the care routine, caregivers can effectively manage high fevers in children and provide supportive measures to aid in the child's recovery. However, it is important to seek medical advice if the child's condition does not improve or if there are concerns about the severity of the fever or accompanying symptoms.
Medications and Treatments for High Fevers in Children
When it comes to managing high fevers in children, medications and treatments play a crucial role in alleviating symptoms and addressing the underlying causes of the fever. It is important for caregivers to be well-informed about the appropriate use of medications and treatments to ensure the child's well-being and promote a swift recovery.
Fever-Reducing Medications
Fever-reducing medications, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin), are commonly used to lower a child's fever and provide relief from associated discomfort. These medications work by reducing the body's temperature-regulating response, thereby bringing down the fever. It is essential for caregivers to carefully follow the dosage instructions provided by healthcare professionals and adhere to the recommended dosing intervals. Additionally, it is crucial to use the appropriate formulation and strength of the medication suitable for the child's age and weight.
Cooling Techniques
In addition to fever-reducing medications, cooling techniques can be employed to help lower a child's body temperature. Applying a cool, damp cloth to the child's forehead, armpits, and groin area can aid in dissipating heat and providing comfort. Caregivers should avoid using cold water or ice packs, as these can lead to shivering and potentially raise the body's core temperature. A lukewarm sponge bath is another effective method for gently reducing a child's fever and promoting comfort.
Read more: Understanding The Symptoms Of Fever
Medical Evaluation and Treatment
In cases where a child's fever is persistent, accompanied by concerning symptoms, or indicative of a more serious underlying condition, seeking medical evaluation is imperative. Healthcare professionals can conduct a thorough assessment to determine the cause of the fever and recommend targeted treatment. For fevers resulting from bacterial infections, such as strep throat or urinary tract infections, antibiotics may be prescribed to address the underlying cause. It is essential for caregivers to adhere to the prescribed treatment regimen and complete the full course of antibiotics as directed.
Supportive Care
Providing supportive care is essential for managing high fevers in children. This includes ensuring adequate rest, maintaining hydration through fluid intake, and creating a comfortable environment to promote the child's recovery. Monitoring the child's temperature, observing for changes in symptoms, and offering reassurance and comfort are integral components of supportive care.
Prevention of Fever-Induced Complications
Caregivers should be vigilant in monitoring the child for any signs of fever-induced complications, such as dehydration, and take proactive measures to prevent potential health risks. Encouraging fluid intake, offering nutritious foods, and closely observing the child's overall well-being are essential for preventing complications associated with high fevers.
By understanding the appropriate use of medications and treatments, caregivers can effectively manage high fevers in children and contribute to the child's comfort and recovery. It is important to seek medical advice if there are concerns about the severity of the fever, accompanying symptoms, or the child's overall condition. Prompt medical intervention can help address the underlying cause of the fever and prevent potential complications, ensuring the child's well-being.
Preventing High Fevers in Children
Preventing high fevers in children involves implementing proactive measures to minimize the risk of infections and illnesses that can lead to elevated body temperatures. By focusing on preventive strategies, caregivers can play a pivotal role in safeguarding children's health and well-being. Here are essential steps to help prevent high fevers in children:
1. Vaccinations
Ensuring that children receive recommended vaccinations according to the immunization schedule is crucial for preventing various infectious diseases. Vaccines protect children from serious illnesses such as measles, mumps, rubella, influenza, and more, reducing the likelihood of developing high fevers associated with these diseases.
2. Hand Hygiene
Promoting good hand hygiene practices, including regular handwashing with soap and water, helps minimize the spread of germs and infections. Teaching children the importance of hand hygiene and encouraging them to wash their hands before meals, after using the restroom, and after coughing or sneezing can significantly reduce the risk of contracting contagious illnesses.
3. Healthy Lifestyle
Encouraging a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and adequate sleep contributes to a strong immune system. A well-nourished body with sufficient rest is better equipped to fend off infections, reducing the likelihood of developing high fevers.
4. Environmental Hygiene
Maintaining a clean and hygienic environment at home and in communal spaces helps minimize exposure to pathogens. Regular cleaning and disinfection of frequently touched surfaces, toys, and common areas can reduce the spread of germs and lower the risk of infections that may lead to high fevers.
Read more: Understanding Fever: Causes And Symptoms
5. Avoiding Exposure to Sick Individuals
Limiting exposure to individuals who are ill, especially during periods of widespread illness outbreaks, can help reduce the risk of contracting contagious diseases. Practicing social distancing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals can lower the likelihood of infection transmission.
6. Proper Clothing and Weather Precautions
Dressing children appropriately for the weather, especially during extreme temperatures, helps prevent heat-related illnesses and fevers. Ensuring that children are dressed in layers during cold weather and are adequately protected from excessive heat during hot weather reduces the risk of temperature-related health issues.
7. Hydration and Nutrition
Encouraging adequate fluid intake and providing a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports overall health and immune function. Proper hydration and nutrition contribute to the body's ability to fight off infections, reducing the susceptibility to febrile illnesses.
By implementing these preventive measures, caregivers can significantly reduce the likelihood of high fevers in children. Proactive steps to promote vaccination, hygiene, healthy lifestyle habits, and environmental cleanliness contribute to creating a protective shield against febrile illnesses, ensuring the well-being of children.