Home>Health & Nutrition>Heat Exhaustion And Fever: Understanding The Connection


Health & Nutrition
Heat Exhaustion And Fever: Understanding The Connection
Published: February 19, 2024
Learn about the link between heat exhaustion and fever, and how it impacts your health and nutrition. Find tips for prevention and treatment.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
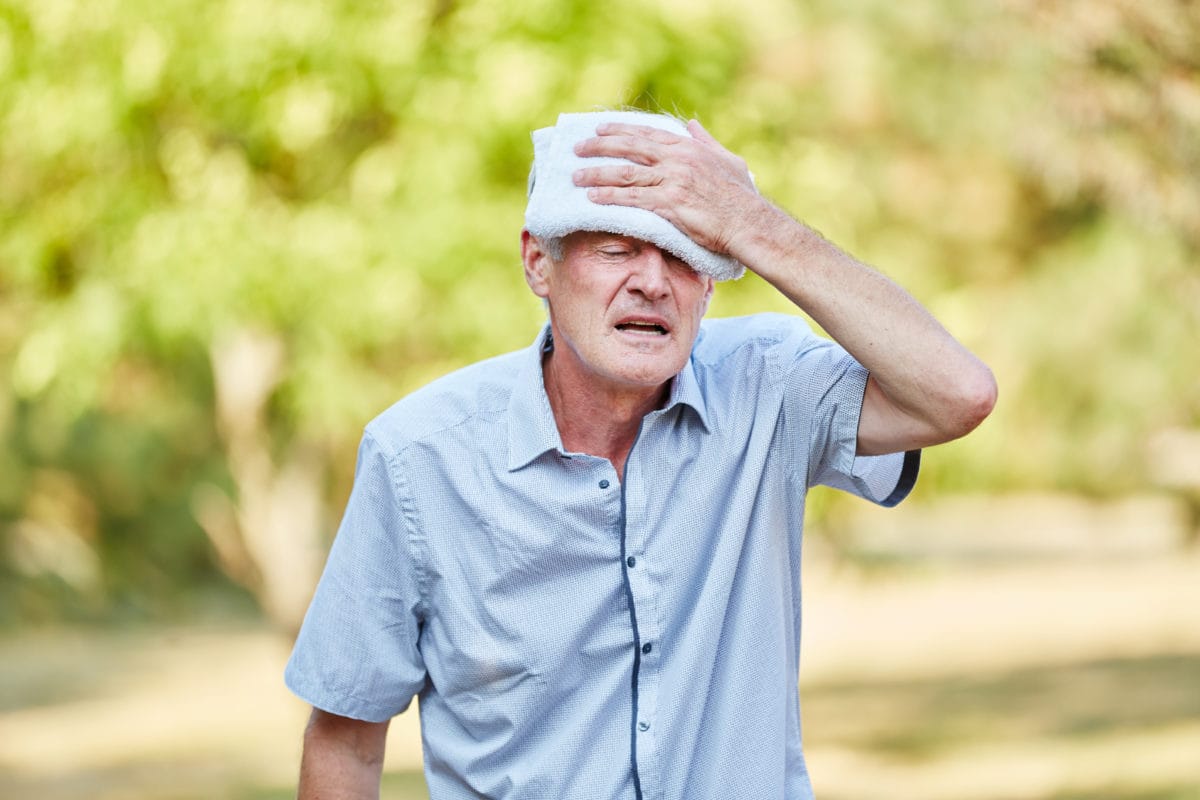
Recognizing the Symptoms of Heat Exhaustion
Heat exhaustion is a serious condition that occurs when the body overheats due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures and inadequate fluid intake. It's crucial to recognize the symptoms of heat exhaustion to prevent it from escalating into a life-threatening situation. Here are the key signs to watch out for:
-
Excessive Sweating: Profuse sweating, especially in hot weather or during physical activity, is a common early sign of heat exhaustion. The body attempts to cool down by releasing sweat, leading to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
-
Weakness and Fatigue: Feeling weak, tired, or lethargic despite minimal physical exertion can indicate heat exhaustion. The body's energy reserves become depleted as it struggles to regulate its temperature.
-
Dizziness and Lightheadedness: Individuals experiencing heat exhaustion may feel dizzy or lightheaded, which can lead to loss of balance and coordination. This symptom is often accompanied by a sensation of the surroundings spinning or tilting.
-
Nausea and Vomiting: Heat exhaustion can cause nausea, stomach discomfort, and vomiting as the body's digestive system becomes compromised. These symptoms can further contribute to dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
-
Headache: A persistent headache, often throbbing or pulsating in nature, can develop as a result of heat exhaustion. The combination of dehydration and increased blood flow to the skin's surface can trigger vascular changes that lead to headaches.
-
Pale, Clammy Skin: The skin may appear pale, cool, and clammy to the touch as the body redirects blood flow to the skin's surface in an attempt to release heat. This can result in a decrease in blood flow to vital organs, exacerbating the symptoms of heat exhaustion.
-
Rapid Heart Rate and Breathing: An elevated heart rate and rapid breathing are common physiological responses to heat exhaustion. The body attempts to circulate blood more efficiently and increase oxygen intake to support the cooling process.
-
Muscle Cramps: Painful muscle cramps, particularly in the legs or abdomen, can occur due to electrolyte imbalances and dehydration. These cramps may hinder mobility and exacerbate the overall discomfort associated with heat exhaustion.
Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for prompt intervention. If you or someone else exhibits signs of heat exhaustion, it's essential to move to a cooler environment, hydrate with water or electrolyte-rich beverages, and rest. Ignoring these symptoms can lead to heatstroke, a severe and potentially life-threatening condition. Therefore, being vigilant and responsive to the signs of heat exhaustion is paramount for maintaining overall well-being, especially during hot weather or strenuous physical activities.
Read more: Understanding The Symptoms Of Fever
Understanding the Causes of Fever
Fever, a temporary increase in body temperature, is a common physiological response to various internal and external factors. Understanding the underlying causes of fever is essential for recognizing when it signals a more serious health issue. Here are the primary factors that can lead to fever:
-
Infections: One of the most prevalent causes of fever is infections, which can be bacterial, viral, or fungal in nature. When the body's immune system detects the presence of pathogens, such as bacteria or viruses, it initiates a cascade of responses to combat the invaders. This includes releasing pyrogens, substances that act on the hypothalamus in the brain to raise the body's temperature. Common infectious diseases that induce fever include the flu, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, and COVID-19.
-
Inflammatory Conditions: Fever can also arise as a result of inflammatory conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, or systemic lupus erythematosus. In these cases, the body's immune system triggers inflammation as a response to perceived threats, leading to elevated body temperature as part of the immune response.
-
Heat-Related Illnesses: Exposure to high environmental temperatures can cause heat-related illnesses, including heat exhaustion and heatstroke. When the body's internal cooling mechanisms are overwhelmed, core body temperature rises, resulting in fever. This is a critical distinction from infectious fever, as it necessitates different management strategies.
-
Medications and Vaccines: Certain medications, particularly antibiotics and vaccines, can induce fever as a side effect. This is often a transient response as the body adjusts to the medication or mounts an immune response to the vaccine components.
-
Cancers: Some cancers, particularly hematologic malignancies like leukemia and lymphoma, can lead to fever as a result of the body's immune response to the abnormal growth of cancerous cells. Additionally, tumors can produce substances that cause fever as a paraneoplastic syndrome.
-
Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions characterized by an overactive immune system, such as lupus and certain types of vasculitis, can trigger fever as a manifestation of the body's immune response attacking its own tissues.
Understanding the diverse causes of fever underscores the importance of thorough evaluation to determine the underlying trigger. By identifying the specific cause, healthcare providers can tailor treatment to address the root issue, whether it involves managing an infection, adjusting medications, or addressing an underlying inflammatory or neoplastic condition. Moreover, recognizing the potential causes of fever empowers individuals to seek timely medical attention when necessary, ensuring appropriate management and resolution of the underlying condition.
The Impact of Heat Exhaustion on Body Temperature
Heat exhaustion exerts a profound impact on the body's temperature regulation mechanisms, leading to a cascade of physiological responses that can significantly compromise overall well-being. When the body is exposed to high temperatures and engages in strenuous physical activity, its ability to dissipate heat becomes challenged, resulting in a rise in core body temperature. This elevation in temperature triggers a series of reactions that underscore the severity of heat exhaustion.
The body's natural response to heat exposure involves vasodilation, the widening of blood vessels near the skin's surface, to facilitate heat dissipation through radiation and convection. However, in the context of heat exhaustion, this process becomes inadequate, leading to a state of thermal imbalance. As a result, the body struggles to maintain its core temperature within the normal range, leading to a rise in internal heat levels.
The impact of heat exhaustion on body temperature extends beyond the immediate discomfort experienced by affected individuals. Elevated core body temperature can disrupt essential physiological processes, including enzymatic activity, cellular metabolism, and the function of vital organs. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and impaired cardiovascular function, further exacerbating the rise in body temperature.
Moreover, the body's thermoregulatory system becomes overwhelmed, leading to an increased risk of heat-related complications. Heat exhaustion can progress to heatstroke, a life-threatening condition characterized by a core body temperature exceeding 104°F (40°C). At this critical juncture, the body's ability to regulate temperature is severely compromised, resulting in multi-organ dysfunction and neurological disturbances.
The impact of heat exhaustion on body temperature also extends to cognitive function, as elevated temperatures can impair neurological processes, leading to confusion, disorientation, and in severe cases, loss of consciousness. This underscores the urgent need for intervention to mitigate the effects of heat exhaustion and prevent further escalation of body temperature.
In summary, the impact of heat exhaustion on body temperature is multifaceted, encompassing disruptions to thermoregulation, cellular function, and neurological processes. Recognizing the significance of these effects is paramount for implementing timely interventions to restore thermal balance, prevent complications, and safeguard overall well-being. Vigilance in monitoring body temperature and promptly addressing heat-related symptoms is crucial for mitigating the impact of heat exhaustion and promoting a swift recovery.
Managing Heat Exhaustion and Fever
Managing heat exhaustion and fever requires a comprehensive approach aimed at alleviating symptoms, restoring thermal balance, and addressing the underlying causes. Prompt and effective management is crucial to prevent complications and promote a swift recovery for individuals affected by these conditions.
Heat Exhaustion Management
-
Immediate Cooling: The primary goal in managing heat exhaustion is to lower the body's core temperature. This involves moving the affected individual to a cooler environment, preferably indoors with air conditioning or in the shade. Removing excessive clothing and applying cool, wet cloths to the skin can aid in dissipating heat.
-
Hydration: Rehydration is essential to counteract fluid loss due to excessive sweating. Encouraging the individual to drink water or electrolyte-rich beverages helps restore fluid and electrolyte balance. Avoiding beverages containing alcohol or caffeine is crucial, as they can exacerbate dehydration.
-
Rest: Adequate rest is paramount for individuals with heat exhaustion. Physical exertion should be minimized, and the affected individual should be encouraged to lie down and elevate their legs to improve circulation.
-
Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of the individual's condition is necessary to ensure that symptoms do not worsen. This includes observing vital signs, such as heart rate and blood pressure, and assessing the individual's responsiveness and overall well-being.
Read more: Understanding And Managing Fever In Toddlers
Fever Management
-
Identifying the Underlying Cause: Determining the root cause of the fever is essential for targeted management. This may involve diagnostic tests, such as blood work, imaging studies, or cultures to identify infectious agents.
-
Medication: In cases where fever is causing significant discomfort or is associated with an underlying infection, antipyretic medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, may be recommended to lower the body temperature and alleviate symptoms.
-
Hydration: Adequate fluid intake is crucial to prevent dehydration, especially when fever is accompanied by sweating or increased respiratory rate. Water, oral rehydration solutions, and clear broths can help maintain hydration levels.
-
Rest and Comfort: Individuals with fever should be encouraged to rest and avoid strenuous activities. Dressing in lightweight clothing and maintaining a comfortable room temperature can help alleviate discomfort.
-
Medical Evaluation: Persistent or high fevers, particularly in the presence of other concerning symptoms, warrant medical evaluation. Seeking professional medical attention is crucial to address underlying infections, inflammatory conditions, or other potential causes of fever.
By implementing these comprehensive management strategies, individuals can effectively address heat exhaustion and fever, promoting recovery and minimizing the risk of complications. It is essential to tailor management approaches to the specific needs and circumstances of each individual, ensuring personalized care and support throughout the recovery process.
Seeking Medical Attention for Heat-Related Illnesses
Seeking prompt medical attention for heat-related illnesses is crucial to ensure proper evaluation, management, and prevention of potential complications. While initial interventions for heat exhaustion may be implemented on-site, certain circumstances warrant immediate medical assessment and care. Here's a detailed overview of when seeking medical attention is essential for heat-related illnesses:
Persistent or Worsening Symptoms
If an individual's symptoms of heat exhaustion, such as excessive sweating, weakness, dizziness, nausea, and rapid heart rate, persist or worsen despite initial interventions, medical attention is warranted. Persistent symptoms may indicate a more severe case of heat exhaustion or the progression toward heatstroke, necessitating professional evaluation and treatment.
Altered Mental Status
Any alteration in mental status, including confusion, disorientation, agitation, or loss of consciousness, requires urgent medical assessment. These neurological symptoms can signify a critical escalation of heat-related illness and may indicate the onset of heatstroke, a life-threatening condition that demands immediate medical intervention.
Read more: Understanding Fever: Causes And Symptoms
High Fever
In cases where heat exhaustion is accompanied by a high fever, typically exceeding 104°F (40°C), seeking medical attention is imperative. High fever in the context of heat-related illness may indicate the progression to heatstroke or the presence of an underlying infection, necessitating thorough evaluation and targeted management by healthcare professionals.
Prolonged Exposure to Heat
Individuals who have been exposed to prolonged periods of high heat, especially in the absence of adequate cooling measures, should seek medical attention if they experience symptoms of heat exhaustion. Prolonged exposure can exacerbate the severity of heat-related illness and increase the risk of complications, underscoring the need for professional assessment.
Underlying Health Conditions
Individuals with pre-existing medical conditions, such as cardiovascular disease, respiratory disorders, or certain medications that affect thermoregulation, should seek medical attention if they develop symptoms of heat exhaustion. These individuals may be at higher risk of complications and require specialized care to address the interplay between their underlying health conditions and heat-related illness.
Suspected Heatstroke
Suspected cases of heatstroke, characterized by a core body temperature exceeding 104°F (40°C) and neurological disturbances, demand immediate medical attention. Heatstroke is a medical emergency that requires rapid cooling, fluid resuscitation, and intensive care to prevent organ damage and systemic complications.
In summary, recognizing the circumstances that warrant medical attention for heat-related illnesses is essential for ensuring timely and appropriate care. By seeking professional evaluation and intervention when necessary, individuals can mitigate the impact of heat-related illness, prevent complications, and facilitate a swift and comprehensive recovery.