Home>Weather and Climate>Historical California Temperature Records


Weather and Climate
Historical California Temperature Records
Modified: March 6, 2024
Explore historical California temperature records and gain insights into the region's weather and climate trends. Discover the impact of weather patterns on California's environment and communities.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Introduction
California, renowned for its diverse landscapes and Mediterranean climate, has long been a focal point for weather and climate enthusiasts. The state's temperature records offer a captivating glimpse into its climatic history, reflecting the interplay of natural variability and human-induced changes. From the sun-kissed beaches of Southern California to the towering redwoods of the north, the Golden State's temperature data provides a rich tapestry of meteorological insights.
As we delve into the historical temperature records of California, we embark on a journey through time, unraveling the intricate patterns of temperature fluctuations that have shaped the state's ecosystems and human activities. These records serve as invaluable windows into the past, offering a nuanced understanding of how California's climate has evolved over the decades and centuries.
In this article, we will explore the early temperature records in California, shedding light on the pioneering efforts that laid the foundation for modern meteorological observations. Furthermore, we will examine the profound impact of climate change on California's temperatures, delving into the trends and anomalies that have emerged in recent years. Additionally, we will highlight notable temperature extremes in California's history, showcasing the remarkable climatic events that have left an indelible mark on the state.
Moreover, we will uncover the pivotal role of historical temperature data in climate research, elucidating how these records contribute to our comprehension of global climate dynamics and inform strategies for mitigating climate-related risks. Through this exploration, we aim to foster a deeper appreciation for the intricate interplay between temperature trends and the broader environmental landscape of California.
Join us as we embark on a compelling odyssey through the annals of California's temperature records, unraveling the captivating story of how temperature observations have shaped our understanding of the state's climate and its enduring significance in the realm of meteorology and climate science.
Early Temperature Records in California
The early temperature records in California serve as a testament to the pioneering spirit of meteorologists and weather enthusiasts who meticulously documented the state's climatic nuances. Dating back to the late 19th century, these records offer a captivating glimpse into California's meteorological history, capturing the ebb and flow of temperatures across its diverse terrain.
In the late 1800s, as California burgeoned with burgeoning urban centers and burgeoning agricultural landscapes, the need for systematic temperature observations became increasingly apparent. This led to the establishment of a network of weather stations, where dedicated individuals diligently recorded daily temperature readings, laying the groundwork for comprehensive climatological archives.
One of the earliest temperature records in California dates back to the 1870s, when the state's nascent meteorological community began assembling a repository of temperature data. These records, often handwritten in logbooks, meticulously chronicled the daily highs, lows, and averages, providing invaluable insights into the state's climatic rhythms.
The advent of the 20th century witnessed a surge in meteorological advancements, with the deployment of more sophisticated instruments and standardized observation protocols. This era marked a pivotal juncture in California's temperature record-keeping, enabling meteorologists to glean a more nuanced understanding of the state's temperature patterns and trends.
The early temperature records not only offer a window into California's climatic past but also serve as a vital resource for contemporary climate researchers. By meticulously analyzing these historical records, scientists can discern long-term temperature trends, identify cyclical patterns, and assess the impact of human activities on the state's climate.
Moreover, these early temperature records provide a foundation for validating and calibrating modern climate models, enhancing the accuracy of projections and forecasts. As California continues to grapple with the complexities of a changing climate, the insights gleaned from these historical temperature records are instrumental in informing adaptive strategies and bolstering resilience against climatic uncertainties.
In essence, the early temperature records in California stand as a testament to the enduring legacy of meteorological pioneers and the invaluable role of historical data in unraveling the intricacies of the state's climate. These records not only chronicle the past but also illuminate the path forward, guiding our efforts to comprehend and mitigate the multifaceted challenges posed by a dynamic and evolving climate.
Impact of Climate Change on California Temperatures
The impact of climate change on California's temperatures has been profound and far-reaching, reshaping the state's climatic landscape in unprecedented ways. Over the past century, California has witnessed a discernible shift in temperature patterns, characterized by rising average temperatures, altered seasonal variations, and an increased frequency of extreme heat events.
One of the most striking manifestations of climate change in California is the upward trend in average temperatures. Long-term temperature records reveal a consistent rise in both daytime and nighttime temperatures across the state, indicative of a warming trend that transcends seasonal fluctuations. This warming phenomenon has significant implications for various sectors, including agriculture, water resource management, and public health, as it influences crop yields, exacerbates water scarcity, and poses health risks associated with heat-related illnesses.
Furthermore, climate change has exerted a discernible influence on the seasonal dynamics of California's temperatures. Shifts in the timing and duration of seasonal transitions, such as prolonged heat waves and delayed onset of cooler temperatures, have become increasingly prevalent, disrupting ecological rhythms and impacting diverse ecosystems. These alterations in seasonal temperature patterns have cascading effects on flora and fauna, influencing migration patterns, reproductive cycles, and overall ecological balance.
The escalation in extreme heat events stands as a stark testament to the impact of climate change on California's temperatures. Heatwaves, characterized by prolonged periods of exceptionally high temperatures, have become more frequent and intense, posing significant challenges to public health, energy infrastructure, and urban resilience. The heightened risk of heat-related illnesses, strain on energy grids, and amplified urban heat island effects underscore the far-reaching consequences of extreme heat events in a warming climate.
Moreover, the interplay between climate change and California's temperatures extends beyond immediate meteorological impacts, permeating into broader socioeconomic and environmental realms. From altering precipitation patterns and exacerbating drought conditions to influencing wildfire dynamics and sea-level rise, the ramifications of changing temperatures reverberate across multiple facets of California's intricate tapestry.
In essence, the impact of climate change on California's temperatures transcends mere statistical trends, permeating into the fabric of the state's ecosystems, communities, and economic activities. As California navigates the complexities of a changing climate, understanding and mitigating the repercussions of altered temperatures stand as imperative endeavors, shaping the trajectory of resilience and adaptation in the face of evolving climatic realities.
Notable Temperature Extremes in California's History
California's diverse topography and climatic variability have set the stage for remarkable temperature extremes that have etched indelible imprints on the state's meteorological annals. From scorching deserts to snow-cloaked peaks, California's varied landscapes have borne witness to a spectrum of temperature records, encapsulating the dynamic interplay of atmospheric forces and geographical influences.
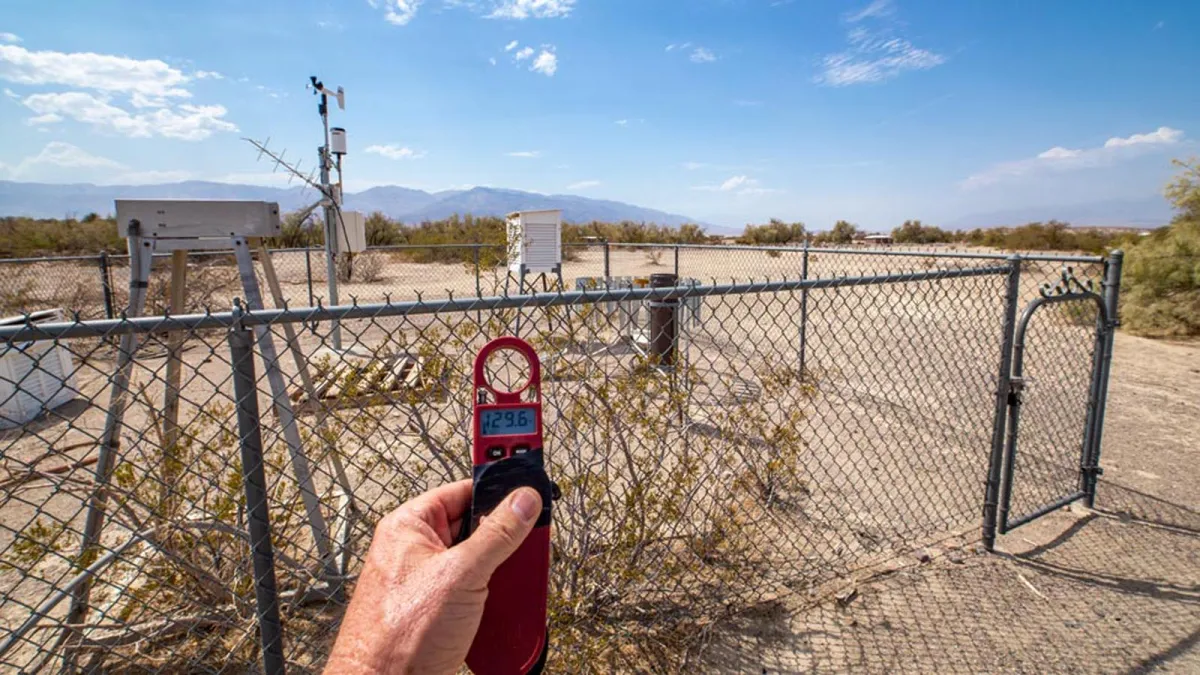
One of the most iconic temperature extremes in California's history unfolded in the scorching expanse of Death Valley. On July 10, 1913, the mercury soared to a staggering 134 degrees Fahrenheit (56.7 degrees Celsius) in Furnace Creek, marking the highest reliably recorded temperature on Earth. This blistering milestone stands as a testament to the extreme heat that can engulf California's arid terrains, underscoring the profound climatic contrasts that define the state.
In contrast to the searing heat of Death Valley, California's mountainous regions have witnessed their own share of temperature extremes. The serene beauty of the Sierra Nevada belies the frigid grip of winter, exemplified by the chilling record set at Boca on January 20, 1937, where the thermometer plummeted to a bone-chilling -45 degrees Fahrenheit (-42.8 degrees Celsius). This stark juxtaposition of temperature extremes underscores the climatic diversity that characterizes California's topography.
The coastal enclaves of California, renowned for their temperate climates, have also experienced notable temperature records. In 1949, the mercury surged to a remarkable 134 degrees Fahrenheit (56.7 degrees Celsius) in the aptly named town of Woodland Hills, epitomizing the rare confluence of intense heat and coastal proximity. This extraordinary temperature extreme serves as a poignant reminder of the climatic surprises that can unfold in California's coastal domains.
Furthermore, California's urban centers have not been immune to temperature extremes, with cities such as Los Angeles and Sacramento bearing witness to their own climatic milestones. The sweltering heat wave of July 2006 propelled Woodland Hills to a scorching 119 degrees Fahrenheit (48.3 degrees Celsius), emblematic of the urban heat island effect that amplifies temperatures in densely populated areas.
These notable temperature extremes in California's history not only serve as compelling meteorological anecdotes but also offer profound insights into the state's climatic tapestry. They underscore the intricate interplay of geographical influences, atmospheric dynamics, and human settlements, shaping our understanding of California's diverse and dynamic climate.
In essence, the temperature extremes woven into California's meteorological narrative stand as testaments to the state's climatic diversity and the captivating interplay of natural forces that have sculpted its meteorological legacy.
The Role of Historical Temperature Data in Climate Research
Historical temperature data plays a pivotal role in climate research, serving as a cornerstone for unraveling the complex dynamics of Earth's climate system. These rich repositories of past temperature observations provide invaluable insights into long-term climatic trends, variability, and the imprint of human activities on the environment. By delving into historical temperature data, climate researchers can discern patterns, identify anomalies, and elucidate the multifaceted interactions shaping our planet's climate.
One of the primary contributions of historical temperature data lies in its capacity to contextualize contemporary climate trends within a broader temporal framework. By juxtaposing modern temperature records with historical data spanning decades or even centuries, researchers can discern discernible shifts in temperature patterns, facilitating a nuanced understanding of climatic changes. This historical context enables scientists to differentiate between natural climatic variability and anthropogenic influences, shedding light on the extent to which human activities have altered the Earth's temperature regime.
Moreover, historical temperature data serves as a vital tool for validating and refining climate models, enhancing their accuracy and predictive capabilities. By comparing model simulations with historical temperature observations, researchers can assess the models' ability to capture past climatic variations and project future temperature trends. This iterative process of model validation and refinement is instrumental in bolstering the reliability of climate projections, informing policy decisions, and fostering resilience against climate-related risks.
Furthermore, historical temperature data facilitates the identification of regional and global temperature trends, enabling researchers to discern spatial variations and hotspots of climatic change. This spatially explicit understanding of temperature dynamics is crucial for assessing the vulnerability of different regions to climate impacts, guiding adaptation strategies, and prioritizing mitigation efforts. Additionally, historical temperature data underpins the assessment of temperature-related hazards, such as heatwaves, and their implications for human health, infrastructure, and ecosystems.
In the realm of climate change attribution, historical temperature data serves as a linchpin for disentangling the contributions of natural variability and human-induced factors to observed temperature trends. Through rigorous statistical analyses and attribution studies, researchers can quantify the extent to which greenhouse gas emissions, land use changes, and other anthropogenic influences have influenced historical temperature patterns. This attribution framework is indispensable for understanding the drivers of past temperature changes and projecting future trajectories under different emission scenarios.
In essence, historical temperature data stands as a bedrock of climate research, offering a treasure trove of insights into the Earth's climatic history and informing our endeavors to comprehend, mitigate, and adapt to the challenges posed by a changing climate. As we navigate the complexities of a warming world, historical temperature data remains an indispensable compass, guiding our quest to unravel the intricacies of Earth's climate system and chart a sustainable course for the future.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the historical temperature records of California encapsulate a rich tapestry of climatic insights, offering a compelling narrative of the state's meteorological evolution. From the pioneering efforts of early meteorologists to the profound impact of climate change on California's temperatures, the annals of temperature observations weave a captivating story of resilience, adaptation, and the enduring interplay between human activities and the environment.
The early temperature records in California stand as testaments to the dedication and ingenuity of meteorological pioneers who meticulously chronicled the state's climatic nuances. These records not only provide a window into California's meteorological past but also serve as invaluable resources for contemporary climate research, guiding our efforts to comprehend and mitigate the multifaceted challenges posed by a dynamic and evolving climate.
The impact of climate change on California's temperatures reverberates across the state's diverse landscapes, reshaping temperature patterns, seasonal dynamics, and the frequency of extreme heat events. As California grapples with the ramifications of a warming climate, understanding the intricate interplay between temperature trends and broader environmental dynamics is imperative for fostering resilience and adaptive strategies.
Notable temperature extremes in California's history, from the scorching deserts to the snow-cloaked peaks, underscore the state's climatic diversity and the captivating interplay of natural forces that have sculpted its meteorological legacy. These extremes serve as poignant reminders of the dynamic climatic contrasts that define California's topography and the resilience of ecosystems and communities in the face of temperature fluctuations.
Moreover, historical temperature data plays a pivotal role in climate research, offering a treasure trove of insights into the Earth's climatic history. By contextualizing contemporary climate trends within a broader temporal framework, historical temperature data enables researchers to discern patterns, validate climate models, and disentangle the contributions of natural variability and human-induced factors to observed temperature trends.
As we navigate the complexities of a changing climate, historical temperature data remains an indispensable compass, guiding our quest to unravel the intricacies of Earth's climate system and chart a sustainable course for the future. The annals of California's temperature records not only chronicle the past but also illuminate the path forward, shaping our endeavors to comprehend, mitigate, and adapt to the challenges posed by a changing climate.