Home>Home, Lifestyle & DIY>Optimal Temperature Range For Succulents


Home, Lifestyle & DIY
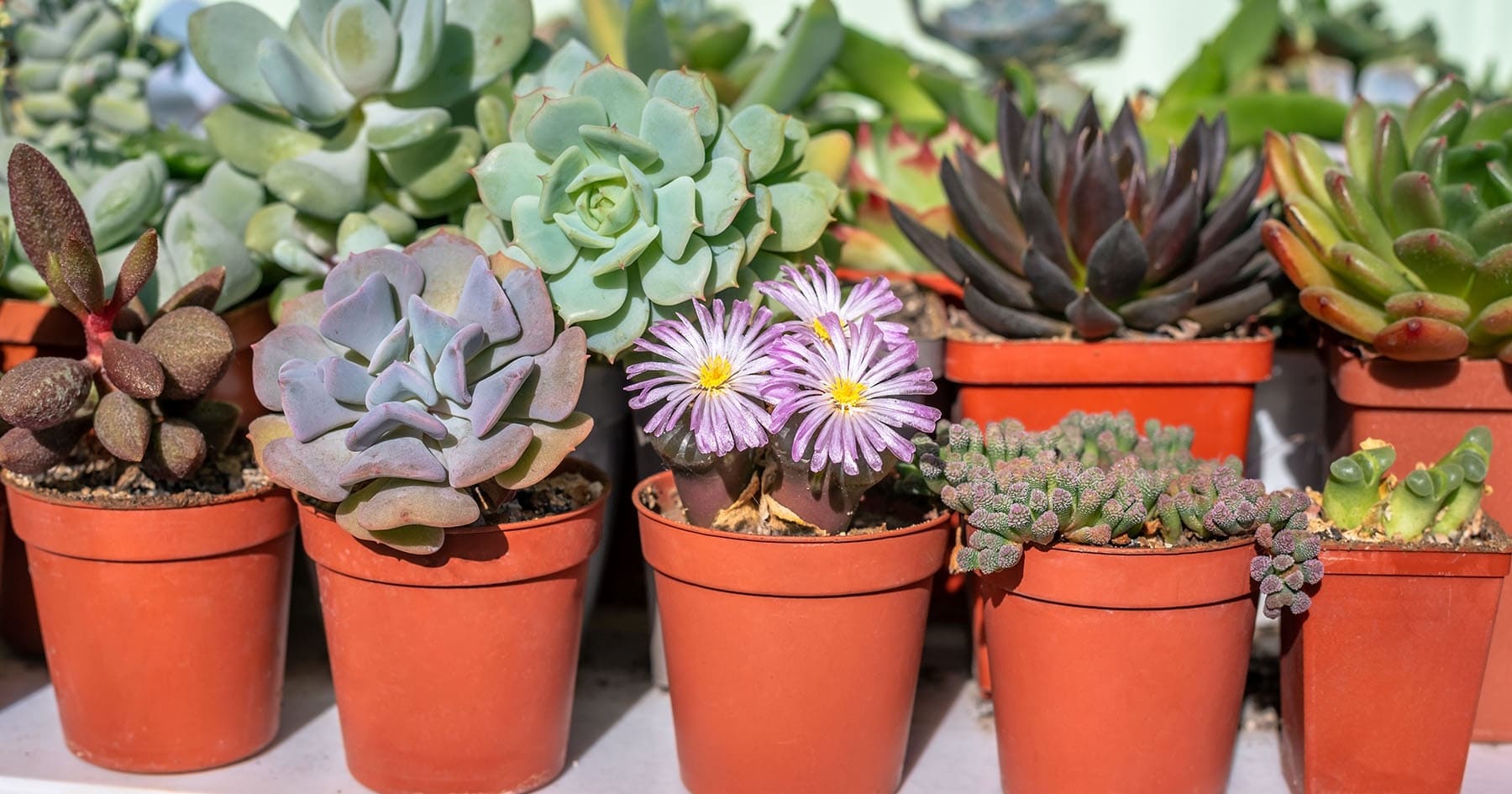
Optimal Temperature Range For Succulents
Published: February 22, 2024
Discover the ideal temperature range for succulents in your home and DIY lifestyle. Learn how to create the perfect environment for these low-maintenance plants.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Understanding Succulents
Succulents are a diverse group of plants known for their ability to store water in their leaves, stems, and roots. This unique adaptation allows them to thrive in arid environments where water is scarce. The term "succulent" is derived from the Latin word "sucus," which means sap or juice, highlighting the plant's capacity to retain moisture.
These plants come in a wide array of shapes, sizes, and colors, ranging from the iconic rosettes of Echeveria to the striking architectural forms of Agave. Their remarkable diversity has made succulents a popular choice for both indoor and outdoor gardens, as well as in landscaping and xeriscaping projects.
Succulents are well-suited to various climates, from deserts to tropical regions, and can be found on every continent except Antarctica. Their resilience and adaptability have contributed to their widespread appeal among gardeners, botanists, and nature enthusiasts.
One of the most fascinating aspects of succulents is their unique anatomy, which sets them apart from other plant species. Their fleshy leaves, often covered in a waxy or powdery coating, serve as reservoirs for storing water, enabling the plants to survive extended periods of drought. Additionally, their shallow root systems efficiently absorb moisture from the soil, further enhancing their ability to endure harsh environmental conditions.
Succulents have also evolved specialized mechanisms to minimize water loss. Unlike traditional leaf structures, which facilitate gas exchange through small openings called stomata, succulents have adapted to open their stomata at night when temperatures are cooler, reducing the risk of excessive water evaporation during the heat of the day.
Furthermore, succulents exhibit remarkable diversity in their reproductive strategies. While many species reproduce through seeds, others can propagate through offsets, cuttings, or even individual leaves, making them relatively easy to propagate and share among enthusiasts.
Understanding the unique characteristics and adaptations of succulents is essential for cultivating these plants successfully. By appreciating their natural resilience and water-storing capabilities, gardeners can provide the optimal growing conditions to ensure the health and vitality of these captivating botanical wonders.
Factors Affecting Succulent Growth
Succulent growth is influenced by a myriad of factors, each playing a crucial role in shaping the overall health and development of these remarkable plants. Understanding these factors is essential for creating an environment that fosters optimal growth and vitality. Let's delve into the key elements that impact the growth of succulents:
1. Light Intensity and Duration
Succulents thrive in bright, indirect sunlight, making light a critical factor in their growth. Insufficient light can lead to etiolation, causing the plants to become elongated and weak. Conversely, excessive exposure to intense sunlight may result in sunburn and leaf damage. Striking a balance by providing adequate light intensity and duration is essential for promoting robust growth and vibrant foliage.
2. Watering Practices
The frequency and method of watering significantly impact succulent growth. Overwatering can lead to root rot and other moisture-related issues, while underwatering may cause the plants to become dehydrated and stunted. Finding the right watering schedule and ensuring proper drainage are essential for maintaining healthy succulents.
3. Soil Composition
The type of soil used for succulents is a critical factor in their growth. Well-draining soil with good aeration is essential to prevent waterlogged conditions that can be detrimental to succulent roots. A balanced soil mix that provides adequate support while allowing excess water to drain away is crucial for promoting healthy root development and overall plant growth.
Read more: The Optimal Temperature Range For Cats
4. Temperature and Humidity
Succulents exhibit varying temperature and humidity preferences based on their natural habitats. While they are renowned for their ability to withstand arid conditions, extreme temperatures and humidity levels can impact their growth. Finding the optimal temperature range and humidity levels for specific succulent species is vital for ensuring their well-being and promoting robust growth.
5. Nutrient Availability
Proper nutrition is essential for succulent growth. While these plants are adapted to thrive in nutrient-poor environments, providing a balanced and appropriate fertilizer regimen can support their overall health and vitality. Understanding the specific nutritional requirements of different succulent species is crucial for promoting optimal growth and flowering.
By considering these factors and tailoring the growing conditions to meet the unique needs of succulents, enthusiasts can cultivate thriving and resilient plants that showcase their inherent beauty and resilience. Each factor plays a pivotal role in shaping the growth and development of succulents, highlighting the intricate balance required to create an environment conducive to their flourishing.
Importance of Temperature for Succulents
The temperature plays a pivotal role in the growth and overall well-being of succulents, exerting a profound influence on their physiological processes and adaptive mechanisms. As resilient plants adapted to arid and semi-arid environments, succulents have evolved to thrive within specific temperature ranges, making it essential for enthusiasts and gardeners to understand the significance of temperature in cultivating these botanical wonders.
Temperature directly impacts various aspects of succulent physiology, including photosynthesis, respiration, and water uptake. Optimal temperatures facilitate efficient photosynthetic activity, enabling succulents to convert light energy into chemical energy and synthesize organic compounds essential for growth and maintenance. Additionally, moderate temperatures support balanced respiration rates, ensuring that the plants can utilize stored energy reserves while maintaining metabolic equilibrium.
Furthermore, temperature profoundly influences water uptake and transpiration in succulents. Within the optimal temperature range, these plants can efficiently absorb and utilize water, contributing to their ability to thrive in arid conditions. Moderate temperatures also play a crucial role in regulating transpiration rates, minimizing water loss and enhancing the plants' capacity to retain moisture, a vital adaptation for surviving in dry environments.
The importance of temperature extends beyond physiological processes, impacting the overall growth, development, and flowering patterns of succulents. Optimal temperatures promote robust root development, ensuring efficient water and nutrient uptake, while also supporting the formation of healthy foliage and stems. Moreover, temperature fluctuations can influence the timing and duration of flowering in many succulent species, underscoring the profound impact of temperature on their reproductive cycles.
Understanding the importance of temperature for succulents involves recognizing the diverse temperature preferences exhibited by different species. While some succulents thrive in hot, desert-like conditions, others prefer milder temperatures found in semi-arid regions or high-altitude environments. By aligning the growing conditions with the specific temperature requirements of each species, enthusiasts can create an environment that fosters optimal growth and vitality.
In essence, temperature serves as a fundamental determinant of succulent health and resilience, shaping their adaptive strategies and growth patterns. By acknowledging the significance of temperature and tailoring the growing environment to meet the unique thermal needs of succulents, enthusiasts can cultivate thriving plants that exemplify the beauty and tenacity of these remarkable botanical treasures.
Ideal Temperature Range for Succulents
The ideal temperature range for succulents is a critical factor in ensuring their optimal growth and well-being. While succulents are renowned for their ability to thrive in arid and semi-arid environments, they exhibit diverse temperature preferences based on their natural habitats and evolutionary adaptations. Understanding the ideal temperature range for succulents is essential for creating a conducive environment that promotes their resilience and vitality.
In general, most succulents thrive within a temperature range of 60°F to 80°F (15°C to 27°C) during the growing season. These moderate temperatures provide an optimal balance that supports photosynthetic activity, efficient water uptake, and overall metabolic equilibrium. However, it's important to note that specific succulent species may have varying temperature requirements based on their native regions and ecological niches.
For succulents originating from desert environments, such as various species of cacti and Agave, higher temperatures ranging from 70°F to 90°F (21°C to 32°C) are often preferred during the active growing season. These plants have evolved to thrive in hot, arid conditions, and the elevated temperatures support their physiological processes, including water storage and utilization, while also influencing their flowering patterns.
On the other hand, succulents native to high-altitude regions or cooler climates, such as certain Sedum and Sempervivum species, may thrive in lower temperature ranges, typically between 50°F to 70°F (10°C to 21°C). These plants have adapted to milder temperatures and benefit from cooler growing conditions that mimic their natural habitats, promoting robust growth and vibrant foliage.
Understanding the specific temperature preferences of different succulent species is crucial for providing an environment that aligns with their evolutionary adaptations and ecological requirements. By tailoring the growing conditions to meet the ideal temperature range for each species, enthusiasts can create a nurturing environment that fosters the health, resilience, and natural beauty of these captivating plants.
In essence, the ideal temperature range for succulents encompasses a spectrum of preferences dictated by their diverse ecological origins. By recognizing and accommodating these temperature requirements, enthusiasts can cultivate thriving succulents that exemplify the remarkable adaptability and enduring allure of these extraordinary botanical wonders.
Read more: Optimal Temperature Ranges For PETG Filament
Effects of Extreme Temperatures on Succulents
Extreme temperatures, whether excessively high or low, can exert profound effects on the physiology and overall well-being of succulents. These remarkable plants, renowned for their resilience in arid environments, are not immune to the challenges posed by extreme temperature fluctuations. Understanding the impact of extreme temperatures on succulents is essential for cultivating thriving and resilient plants that exemplify their inherent beauty and adaptability.
High Temperatures
Excessive heat can pose significant challenges to succulents, particularly those adapted to moderate or cooler climates. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to a range of physiological stress responses, including accelerated water loss through transpiration, cellular damage due to heat-induced oxidative stress, and impaired photosynthetic efficiency. Additionally, extreme heat can disrupt metabolic processes, leading to reduced growth rates and diminished overall vitality in succulents.
Furthermore, high temperatures can impact the reproductive cycles of succulents, influencing the timing and duration of flowering. In some cases, prolonged exposure to extreme heat may result in the premature cessation of flowering or the production of smaller, less vibrant blooms. This can affect the plants' ability to propagate and perpetuate their genetic diversity, underscoring the far-reaching consequences of extreme heat on succulent reproductive success.
Low Temperatures
Conversely, extreme cold poses its own set of challenges for succulents, particularly those originating from warmer or subtropical regions. Frost and freezing temperatures can cause cellular damage, leading to tissue necrosis and discoloration in succulent foliage. The formation of ice crystals within plant cells can rupture cell walls, disrupting vital physiological processes and compromising the structural integrity of the plants.
Moreover, prolonged exposure to low temperatures can impede metabolic activity and growth, resulting in stunted development and reduced resilience in succulents. Cold stress can also impact the water balance within plant tissues, leading to dehydration and desiccation, particularly in species adapted to milder climates.
Adaptive Strategies
Despite the potential detrimental effects of extreme temperatures, succulents have evolved remarkable adaptive strategies to mitigate the impact of temperature fluctuations. These include specialized mechanisms for water storage, heat tolerance, and frost resistance, allowing succulents to endure challenging environmental conditions.
By understanding the effects of extreme temperatures on succulents, enthusiasts can implement proactive measures to protect their plants during temperature extremes. This may involve providing shade and adequate ventilation during periods of high heat, as well as employing frost protection measures, such as covering plants or relocating them to sheltered areas during cold spells.
In essence, the effects of extreme temperatures on succulents underscore the intricate balance between their adaptive resilience and vulnerability to environmental stressors. By acknowledging these effects and implementing targeted strategies to mitigate temperature-related challenges, enthusiasts can cultivate thriving succulents that embody the enduring allure and tenacity of these extraordinary botanical wonders.
Read more: The Ideal Temperature Range For Dogs
Tips for Maintaining Optimal Temperature for Succulents
-
Understanding Species-Specific Requirements: Research the specific temperature preferences of the succulent species in your collection. Different succulents have varying temperature requirements based on their natural habitats. By understanding these preferences, you can create microclimates or tailored environments to accommodate the diverse needs of your plants.
-
Utilizing Thermal Mass: Incorporate thermal mass, such as large rocks or ceramic containers, in your succulent garden. These materials can absorb heat during the day and release it slowly at night, helping to moderate temperature fluctuations and create a more stable microclimate for your plants.
-
Employing Shade Structures: Install shade structures, such as pergolas or shade cloth, to provide protection from intense sunlight and excessive heat. By creating shaded areas in your garden, you can shield your succulents from the potential stress of high temperatures, especially during the peak of summer.
-
Implementing Ventilation: Ensure adequate ventilation in your growing area to prevent the buildup of excessive heat. Good air circulation can help dissipate heat and maintain a more temperate environment for your succulents, especially in enclosed spaces or greenhouses.
-
Monitoring Temperature Extremes: Regularly monitor weather forecasts and be prepared to take protective measures during temperature extremes. This may involve relocating potted succulents to shaded areas during heatwaves or providing insulation and frost protection during cold spells.
-
Utilizing Mulch: Apply a layer of organic mulch, such as wood chips or straw, around the base of your succulents. Mulch helps insulate the soil, moderating temperature fluctuations and reducing the risk of extreme heat or cold impacting the roots of your plants.
-
Selecting Appropriate Planting Locations: When planting succulents in the ground, choose locations that offer natural protection from temperature extremes. South-facing slopes or areas with natural windbreaks can provide a more sheltered environment for your plants.
-
Adjusting Container Placement: If growing succulents in containers, adjust their placement based on the seasonal temperature variations. During hot periods, consider moving containers to shadier spots, while in cooler seasons, position them in sunnier locations to optimize temperature conditions.
By implementing these tips, you can create an environment that promotes the optimal temperature range for your succulents, supporting their growth, resilience, and overall well-being. Understanding the nuanced interplay of temperature and employing proactive measures will enable you to cultivate thriving succulents that showcase their inherent beauty and adaptability.