Home>Culinary & Beverages>The Proper Temperature And Time For Reheating Hot Holding Food


Culinary & Beverages
The Proper Temperature And Time For Reheating Hot Holding Food
Published: February 22, 2024
Learn the best practices for reheating hot holding food to ensure food safety and quality. Discover the proper temperature and time guidelines for culinary & beverages.
(Many of the links in this article redirect to a specific reviewed product. Your purchase of these products through affiliate links helps to generate commission for Temperatures.com, at no extra cost. Learn more)
Table of Contents
Importance of Proper Reheating
Proper reheating of hot holding food is crucial for maintaining food safety and quality. Whether in a professional kitchen or at home, ensuring that reheating is done correctly can prevent foodborne illnesses and preserve the flavors and textures of the dishes. When food is not reheated to the appropriate temperature or for the right amount of time, harmful bacteria can thrive, posing health risks to consumers.
By adhering to proper reheating guidelines, the risk of foodborne illnesses, such as salmonella and E. coli, can be significantly reduced. This is especially important for high-risk foods, including meats, dairy products, and cooked grains, which are more susceptible to bacterial contamination when not reheated properly.
Moreover, the quality of the food can be compromised if it is not reheated correctly. Overheating can lead to dry, rubbery textures, while underheating may result in cold spots where bacteria can survive. Following the recommended reheating temperature and time can help maintain the original taste, texture, and appearance of the dish, ensuring a satisfying dining experience for customers or guests.
In professional kitchens, compliance with food safety regulations is essential. Proper reheating practices not only uphold health and safety standards but also contribute to the reputation and success of the establishment. Customers expect their meals to be not only delicious but also safe to consume. By prioritizing proper reheating, chefs and kitchen staff demonstrate their commitment to delivering high-quality, safe food to patrons.
Overall, the importance of proper reheating cannot be overstated. It is a fundamental aspect of food safety and quality assurance, impacting both the health of consumers and the overall dining experience. By understanding and implementing the recommended guidelines for reheating, individuals and foodservice professionals can uphold the highest standards of safety and culinary excellence.
Recommended Temperature for Reheating
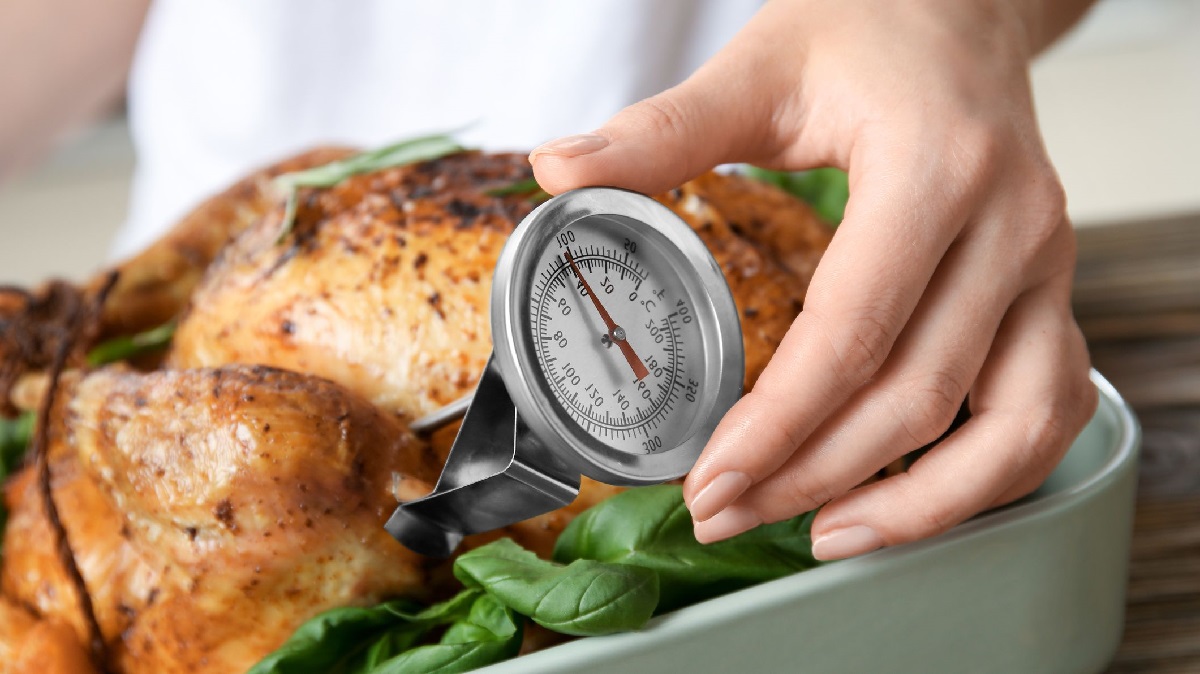
When it comes to reheating hot holding food, the recommended temperature is a critical factor in ensuring food safety and quality. The ideal temperature for reheating cooked foods is 165°F (74°C) or above. This temperature is considered the "kill zone" for bacteria, as it effectively eliminates harmful pathogens that may have developed during the initial cooking and subsequent cooling of the food.
Reaching and maintaining this temperature for a specific duration is essential to destroy any bacteria that may have proliferated during storage. By achieving the recommended reheating temperature, the risk of foodborne illnesses is significantly reduced, safeguarding the health of consumers.
It's important to note that different types of food may require variations in reheating temperatures. For example, when reheating leftovers, such as meats, casseroles, and soups, it's crucial to ensure that the internal temperature reaches 165°F (74°C) throughout. This can be measured using a food thermometer, which provides an accurate assessment of the food's internal temperature.
Additionally, when reheating pre-cooked foods in a microwave, it's essential to rotate and stir the food to ensure even distribution of heat, thereby achieving the recommended temperature uniformly. This practice helps eliminate cold spots where bacteria can survive, further enhancing food safety.
In professional kitchens, adherence to the recommended reheating temperature is not only a best practice for food safety but also a regulatory requirement. Health and safety inspections often focus on proper food handling, including reheating procedures, making it imperative for foodservice establishments to comply with these standards.
By understanding and implementing the recommended reheating temperature, individuals can take proactive measures to protect themselves and others from foodborne illnesses. Whether at home or in a commercial kitchen, prioritizing the use of proper temperatures during reheating is a fundamental step in ensuring the safety and well-being of consumers.
In summary, the recommended temperature for reheating, set at 165°F (74°C) or above, serves as a crucial safeguard against foodborne pathogens, contributing to the overall safety and quality of reheated hot holding food.
Guidelines for Reheating Time
In addition to reaching the recommended temperature, adhering to specific guidelines for reheating time is essential for ensuring the safety and quality of hot holding food. The duration for which food should be reheated varies depending on the type and quantity of the dish. Understanding and implementing these guidelines is crucial for preventing the survival of harmful bacteria and maintaining the integrity of the food.
When reheating hot holding food, the duration of the process is influenced by factors such as the initial cooking method, the thickness of the food, and the quantity being reheated. For instance, dense or thicker foods, such as large cuts of meat or casseroles, require a longer reheating time to ensure that the internal temperature reaches the recommended level consistently.
As a general rule, hot holding food should be reheated to the recommended temperature within a reasonable timeframe. This typically involves heating the food to the specified temperature within 2 hours. This guideline aligns with food safety principles, as it minimizes the time that food spends in the "danger zone," where bacteria can multiply rapidly. By reheating food promptly and efficiently, the risk of bacterial contamination is effectively mitigated.
Furthermore, when reheating large quantities of food, such as in a commercial kitchen or catering setting, it's important to consider the distribution of heat throughout the entire batch. Ensuring that all portions of the food reach the recommended temperature uniformly requires adequate time and attention to detail. This may involve dividing large batches into smaller portions for more effective and consistent reheating.
In the case of leftovers, the reheating time can vary based on the specific dish and the method of reheating. For example, when using a microwave, it's essential to follow the recommended reheating times provided for different types of food. Stirring and rotating the food at intervals during the reheating process can help achieve uniform heating and minimize the overall reheating time.
In professional kitchens, strict adherence to reheating time guidelines is essential for maintaining compliance with food safety regulations. Health authorities and regulatory bodies emphasize the importance of timely and thorough reheating to prevent foodborne illnesses and ensure the safety of consumers.
By understanding and implementing the appropriate guidelines for reheating time, individuals and foodservice professionals can uphold the highest standards of food safety and quality. Whether at home or in a commercial kitchen, prioritizing the correct reheating time is a fundamental aspect of responsible food handling, contributing to the overall well-being of consumers.
In summary, following specific guidelines for reheating time is crucial for achieving uniform and thorough reheating, thereby ensuring the safety and quality of hot holding food.
Best Practices for Hot Holding Food
Maintaining the proper temperature and ensuring the safe handling of hot holding food are essential best practices that contribute to food safety and quality. Whether in a professional kitchen or at home, following these best practices is crucial for preserving the integrity of prepared dishes and safeguarding the health of consumers.
-
Use of Hot Holding Equipment: Utilizing specialized hot holding equipment, such as steam tables, warming trays, and heat lamps, is a fundamental best practice for keeping prepared food at safe temperatures. These tools are designed to maintain consistent heat levels, preventing the growth of harmful bacteria while preserving the quality of the food.
-
Temperature Monitoring: Regularly monitoring the temperature of hot holding equipment and the internal temperature of the food is imperative. Utilizing food thermometers and temperature probes allows for accurate assessments, ensuring that the food remains within the safe temperature range. This proactive approach helps identify and address any deviations promptly.
-
Frequent Stirring and Rotation: When holding food in hot holding equipment, frequent stirring and rotation of the dishes are recommended. This practice promotes even heat distribution, preventing the formation of cold spots where bacteria can survive. Additionally, it helps maintain the consistency and quality of the food throughout the holding period.
-
Covering and Sealing: Covering hot holding containers and trays with lids or wraps helps retain heat and moisture, further enhancing food safety and preventing the dishes from drying out. Proper sealing also minimizes the risk of contamination from external sources, ensuring that the food remains protected until it is served.
-
Regular Cleaning and Maintenance: Keeping hot holding equipment clean and well-maintained is essential for preventing cross-contamination and ensuring optimal functionality. Regular cleaning, sanitization, and maintenance of hot holding units contribute to a hygienic and safe food storage environment.
-
Training and Education: Providing comprehensive training to kitchen staff on the proper procedures for hot holding food is crucial. Educating employees about temperature monitoring, food rotation, and hygiene practices fosters a culture of food safety and ensures that all team members are equipped to uphold best practices consistently.
By incorporating these best practices into food handling protocols, individuals and foodservice professionals can uphold the highest standards of food safety and quality. Prioritizing the safe handling and maintenance of hot holding food not only mitigates health risks but also contributes to the overall satisfaction and well-being of consumers.
In summary, adherence to best practices for hot holding food is a cornerstone of responsible food handling, ensuring that prepared dishes are maintained at safe temperatures and remain of the highest quality until they are served.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Avoiding common mistakes in reheating and hot holding food is crucial for upholding food safety and preserving the quality of prepared dishes. By being mindful of these pitfalls, individuals and foodservice professionals can mitigate risks and ensure that hot holding food remains safe and enjoyable for consumption.
-
Inadequate Temperature Monitoring: Failing to monitor the temperature of hot holding equipment and the internal temperature of reheated food poses a significant risk. Without regular temperature checks, there is a heightened possibility of food entering the "danger zone," where bacteria can multiply rapidly. This oversight can compromise food safety and lead to potential health hazards for consumers.
-
Improper Reheating Techniques: Utilizing incorrect reheating methods, such as uneven heating in microwaves or inadequate heating times, can result in inconsistent temperature distribution. This can create cold spots in the food, providing an environment for bacteria to survive. Additionally, overheating can lead to the degradation of food quality, resulting in undesirable textures and flavors.
-
Extended Holding Periods: Allowing hot holding food to remain at unsafe temperatures for an extended period increases the risk of bacterial contamination. Failure to serve or refrigerate reheated food promptly can compromise its safety and diminish its quality. It is essential to adhere to recommended holding times and promptly cool or serve reheated dishes to minimize risks.
-
Neglecting Food Rotation: In commercial kitchens, neglecting to rotate hot holding food can lead to uneven heating and potential temperature discrepancies. This oversight may result in some portions of the food not reaching the recommended temperature, creating an environment for bacterial growth. Regularly rotating food in hot holding equipment is crucial for ensuring uniform reheating and food safety.
-
Insufficient Cleaning and Maintenance: Inadequate cleaning and maintenance of hot holding equipment can lead to cross-contamination and compromised food safety. Accumulated food debris and improper sanitization can create an environment conducive to bacterial growth, posing risks to both the stored food and subsequent batches.
-
Lack of Staff Training: Failing to provide comprehensive training to kitchen staff on proper reheating and hot holding procedures can result in inconsistent practices and oversight of critical food safety measures. Educating employees on the importance of temperature monitoring, food rotation, and hygiene practices is essential for upholding best practices consistently.
By recognizing and actively avoiding these common mistakes, individuals and foodservice professionals can uphold the highest standards of food safety and quality. Prioritizing proper reheating techniques and hot holding practices is essential for mitigating risks and ensuring the well-being of consumers.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the proper reheating of hot holding food is a critical aspect of food safety and quality assurance. Adhering to recommended reheating temperatures and guidelines for reheating time is essential for preventing the proliferation of harmful bacteria and preserving the integrity of prepared dishes. Whether in a professional kitchen or at home, prioritizing proper reheating practices contributes to the overall safety and satisfaction of consumers.
By understanding the significance of reaching the recommended temperature of 165°F (74°C) or above during reheating, individuals and foodservice professionals can proactively mitigate the risk of foodborne illnesses. This "kill zone" temperature effectively eliminates harmful pathogens, safeguarding the health of consumers and upholding food safety standards. Additionally, following specific guidelines for reheating time ensures that food is thoroughly and uniformly reheated, further reducing the risk of bacterial contamination.
Best practices for hot holding food, including the use of specialized equipment, temperature monitoring, frequent stirring and rotation, proper covering and sealing, regular cleaning and maintenance, and comprehensive staff training, are essential for maintaining safe temperatures and preserving the quality of prepared dishes. These practices contribute to a culture of food safety and ensure that hot holding food remains safe and enjoyable for consumption.
Furthermore, recognizing and actively avoiding common mistakes in reheating and hot holding, such as inadequate temperature monitoring, improper reheating techniques, extended holding periods, neglecting food rotation, insufficient cleaning and maintenance, and lack of staff training, is crucial for upholding the highest standards of food safety and quality.
In both professional and home settings, prioritizing proper reheating practices is not only a fundamental aspect of responsible food handling but also a demonstration of commitment to delivering safe, high-quality food to consumers. By embracing these principles, individuals and foodservice professionals can contribute to a culture of food safety, ensuring that every dish served is not only delicious but also safe to consume.
In essence, the proper temperature and time for reheating hot holding food are integral components of responsible food handling, impacting both the health of consumers and the overall dining experience. By embracing recommended guidelines and best practices, individuals and foodservice professionals can uphold the highest standards of food safety and culinary excellence, fostering a culture of trust and satisfaction among patrons and guests.